Delays, Deferment, and Continuous At-Sea Deterrence: The United Kingdom’s Increasing Nuclear Stockpile and the Infrastructure That Makes it Happen
Between 2006 and 2015, the United Kingdom repeatedly and publicly announced its intentions to decrease the size of its nuclear weapons stockpile, most recently committing to at most 180 weapons by the mid-2020s. As the years went by, non-government policy experts and nuke watchers assumed that the UK Government was making good on its word and that the UK nuclear arsenal would continue to gradually reduce. In reality, the United Kingdom is thought to have maintained a nuclear stockpile of approximately 225 weapons, and, in a surprise move in 2021, the United Kingdom declared that it would extend the ceiling of its “overall nuclear weapon stockpile” to no more than 260 weapons. This constituted an abrupt about-face from its previous commitments and trajectory.
However, the infrastructure underpinning the sustainability of the United Kingdom’s nuclear weapons and their modernization has experienced significant budgetary and scheduling challenges. Furthermore, the UK has dramatically reduced the public transparency of its nuclear forces, making it increasingly difficult to understand and debate the true scope of these challenges.
The UK’s Nuclear Warhead Modernization
Announced in 2005, the Atomic Weapons Establishment’s (AWE) Nuclear Warhead Capability Sustainment Programme (NWCSP) was an initiative to deliver infrastructure and technology to sustain the United Kingdom’s current stockpile and underpin its warhead replacement program. Each of these main infrastructure and technology projects is named after a constellation: Project Orion for a high-power research laser that began operations in 2013, Project Leo for a small parts manufacturing facility, Project Pegasus for the manufacturing of uranium components effort, and so on. Several of these projects under the NWCSP related to techniques used for nuclear weapons development in place of explosive testing. Part of the NWCSP mission also involved refurbishing the United Kingdom’s current warheads for integration with the U.S.-supplied, upgraded Mk4A aeroshell, which was completed in 2023. The NWCSP was scheduled to run from April 2008 until April 2025 and was removed from the MOD Government Major Projects Portfolio data starting in 2022, indicating it could have been downsized from a large-scale development initiative.
In February 2020, the UK defence secretary announced a new warhead program—the A21/Mk7/ Astraea. This new warhead is currently in the concept stage but is planned to eventually replace the Mk4A/Holbrook beginning in the late 2030s. As was the case with the previous version, the A21/Mk7 Astraea design and production will have a “very close connection” to the future US W93/Mk7.
In 2023, the MOD confirmed that £127 million had been spent on the A21 Astraea warhead replacement program as of March 2022. The total cost of the replacement program has not been released, given it is still in the early stages. However, even if cumulative costs are released, individual costs associated with the warhead modernization program will be challenging to identify due to changes in UK budgetary reporting practices. In 2023, nuclear-related programs and expenditures—including the AWE and the NWCSP—were compiled into one heading under Defence Nuclear Enterprise (DNE), which appears as a single line item in the departmental estimates. This makes it impossible to see the direct in-service costs associated with the individual programs. DNE funding was also “ringfenced” within the MOD budget to protect it against spending cuts.
The UK’s declaration that its stockpile ceiling will be raised to 260 raises several questions. In the early- to mid-2000s, the United Kingdom possessed a stockpile of roughly 280 warheads, but in 2010 announced it would reduce this level to “no more than 225 warheads.” To be able to increase this level to up to 260 warheads, as announced by the UK government in 2021, it seems some of the retired warheads—or components from them—must have been retained in some form. The United Kingdom appears to use the term “stockpile” to describe operational, deployed, and retired weapons. The timeline for potentially increasing the stockpile to up to 260 is not known, but if it is a relatively short timeline, it would seem to require reconstituting some retired warheads. If it is a longer timeline, it could potentially involve increasing the number of A21 Astraea warheads in the future. Of the “no more than 225” warhead stockpile level, the United Kingdom has previously explained that 120 warheads would be operationally available, of which 40 would be deployed on the single ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) on patrol at all times. The reason for increasing the stockpile to up to 260 warheads appears to be derived from an interest in increasing the number of “operationally available” warheads to be able to deploy a full warhead load on the SSBN fleet—something the recent warhead level did not allow.
Critical Infrastructure
Any warhead design, manufacturing, and testing occurs at the AWE site at Aldermaston while the warheads are assembled, maintained, and decommissioned at AWE Burghfield. These two sites are critical to maintaining the United Kingdom’s existing stockpile and will play a significant role in the new warhead replacement program.
Upgrades at AWE Burghfield
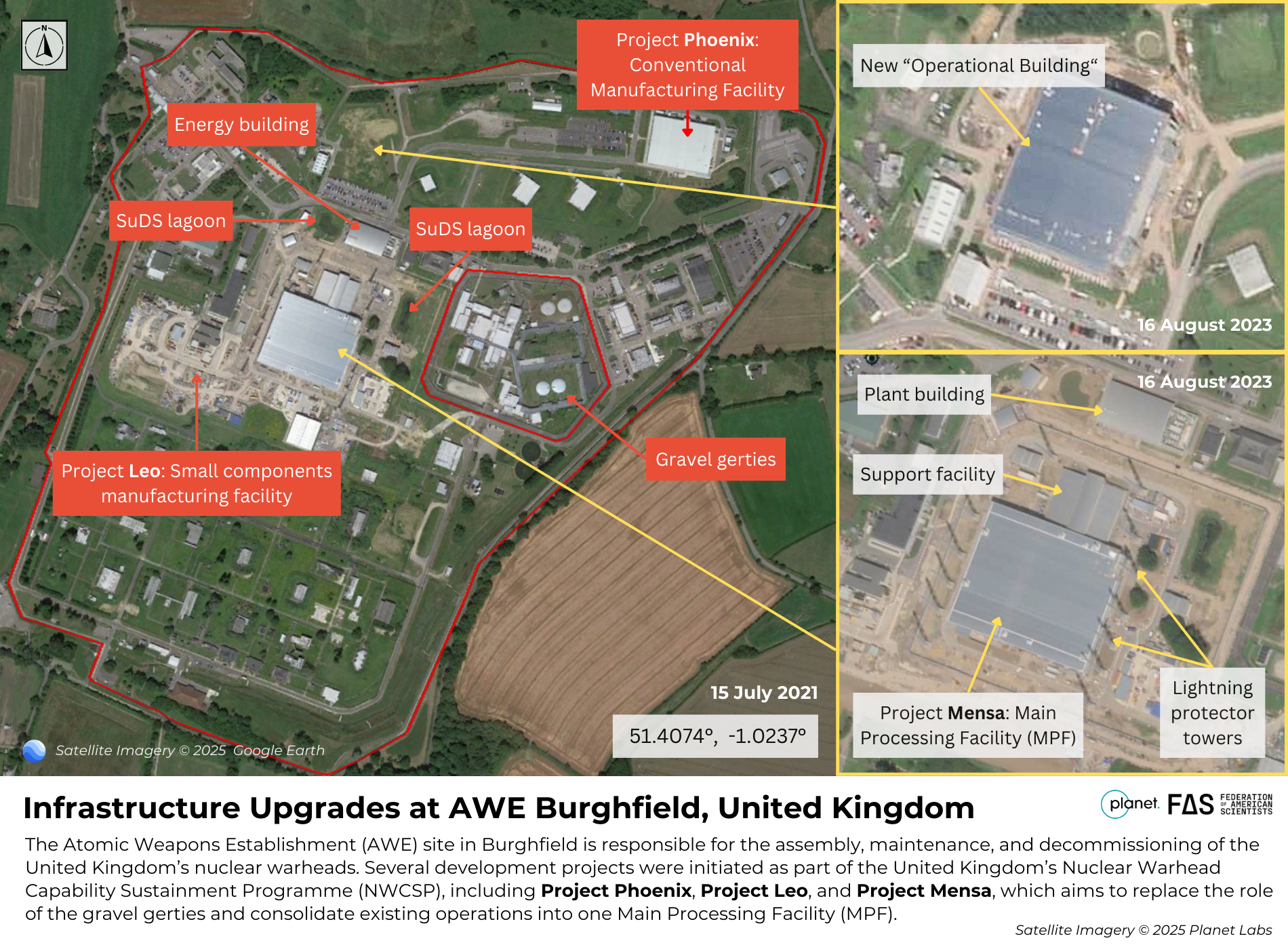
Project MENSA—one of the infrastructure programs under the NWCSP—aims to consolidate existing nuclear warhead assembly and disassembly operations into a single building located in the center of the AWE Burghfield complex called the Main Processing Facility (MPF). MENSA will replace the existing Gravel Gertie bunkers used for warhead assembly and disassembly on the eastern part of the campus, which are designed to collapse inward in the event of an explosion. Other new infrastructure for this project includes a support building and 16 lightning protector towers to accompany the MPF, as well as an associated plant building, gatehouses, vehicle inspection bays, substation buildings, security fences, access roads, and Sustainable Drainage System (SuDS) infrastructure.
Project MENSA’s completion has been delayed by more than seven years, and its expected cost is £1.36 billion over its original total budget of £0.8 billion. Construction progress at the site can be observed through satellite imagery and should be nearing completion of construction according to the MoD’s 2024 Major Project Portfolio data.
Upgrades at AWE Aldermaston
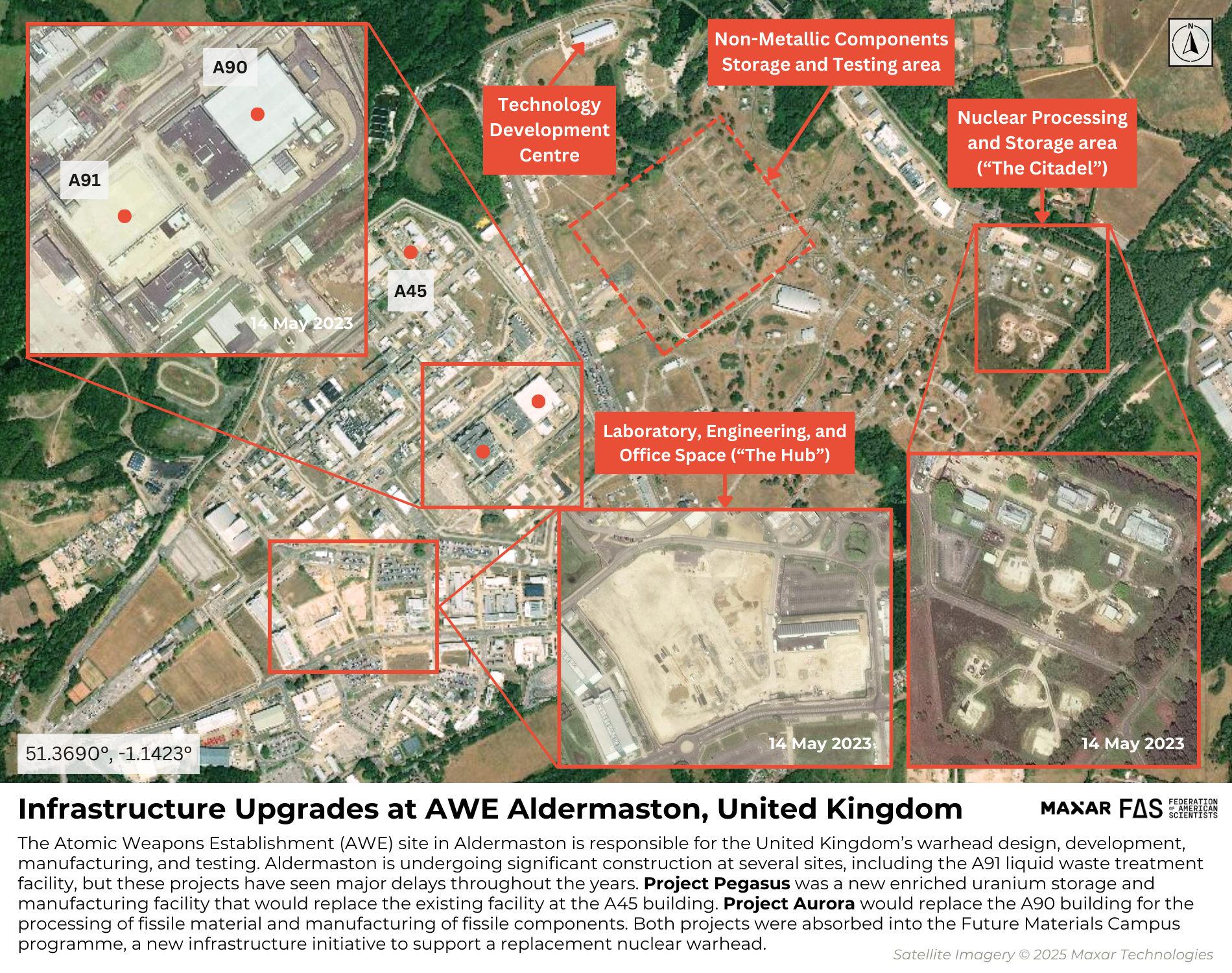
AWE Aldermaston, where warhead design, development, manufacturing, assembly, and testing occur, is also undergoing significant upgrades and revitalization. In 2024, AWE announced two new infrastructure programs—the Future Infrastructure Programme (FIP) for general infrastructure and the Future Materials Campus (FMC) for nuclear material manufacturing and storage—to consolidate existing programs and invest in new ones to increase capacity for maintaining, manufacturing, and storing nuclear weapons. The procurement process for these multi-year, multi-billion pound projects began on April 22 and December 12, 2024, respectively. The FMC, in particular, will be a collection of facilities, including nuclear science and technology centers and laboratories, to be built at AWE Aldermaston. This program will replace two major projects that initially fell under the NWCSP—Project Pegasus and Project Aurora.
Project Pegasus was described as a new enriched uranium storage and manufacturing facility at AWE Aldermaston that would replace the existing enriched uranium handling facility located at the A45 building. Work began in 2003, and the original projected service date was 2016. The approved cost was originally £634 million before it skyrocketed to £1.7 billion. After a six-year delay and a three-year pause, construction of the new storage facility began, and the manufacturing facility was scheduled to be finished by 2030. The severe delays were mainly due to challenges with the supply chain environment and an “overly complex technical solution” that resulted in additional construction and safety costs and a “reassessment” of the project design and requirements.
The UK government was also in the early design phase of Project Aurora, an infrastructure project for a new plutonium manufacturing facility that would replace the current A90 building at AWE Aldermaston. This program was experiencing delays due to resourcing problems, supply chain shortages, and high-skilled workforce challenges. Project Aurora was removed from the NWCSP and added as an independent program to the MOD’s Major Projects Portfolio in 2022. Projects Aurora and Pegasus were both removed from the 2024 version of the MOD’s Major Projects Portfolio database, likely due to their absorption into the new FMC program.
The other central element of NWCSP is the delivery of a new hydrodynamics facility. In 2010, the United Kingdom and France signed the Teutates Treaty, which allowed for cooperation on warhead physics research between the two nations. From this agreement, the EPURE radiographic facility was built at Valduc in France, and a joint UK-France Technology Development Centre was established at Aldermaston. These facilities will support hydrodynamic research that will allow the study of the effects of aging and manufacturing processes on nuclear warheads without nuclear explosive testing. Because of the Teutates program, the UK’s original plans for a ‘Project Hydrus’ hydrodynamics facility were canceled.
Outstanding Challenges
The facilities described above are deemed crucial to the United Kingdom’s effort to modernize and refurbish its nuclear deterrent. However, the significant delays and cost overruns have elicited criticism from the public and concern from government authorities over the years. In August 2024, the House of Commons reported a spending deficit on nuclear programs across the Defence Equipment Plan. Over the next ten years (2023 to 2033), costs are forecasted at £117.8 billion, of which only £109.8 billion had been budgeted for when the report was released.
Alongside these warhead development and infrastructure programs, the United Kingdom is also replacing its four SSBNs with the new Dreadnaught class, the first of which is expected to enter service in the early 2030s. This modernization has also been plagued by cost increases and threatens to be delayed, given maintenance issues with the existing fleet.
Moreover, the recent decrease in UK government transparency regarding the status of its nuclear arsenal and modernization program reflects a worrisome global trend. The United Kingdom has not publicly declared the approximate size of its stockpile since 2010, following the Obama Administration’s decision to release its stockpile number. In 2021, the MOD referred to the 2010 announcement again but did not explicitly say what the stockpile number was. Moreover, it said it would “no longer give public figures for our operational stockpile, deployed warhead or deployed missile numbers.”
Additionally, the MOD said in 2023 that it was withholding information on planned in-service dates for many of the above-referenced projects for “reasons of national security” and did not release this information in its 2022, 2023, and 2024 Major Projects Portfolio data. Finally, the MOD has published an annual update to Parliament since 2011 on the progress of nuclear weapons upgrades, but there has been no report published for 2023 or 2024.
While some of this backsliding is likely rooted in concerns about public perception of persistent programmatic delays, the overall picture raises concerns about a pattern of declining transparency and reduced public ability to monitor and hold the UK government accountable for its nuclear weapons program.
Reawakening a Nuclear Legacy: The Potential Return of the US Nuclear Mission to RAF Lakenheath
In the spring of 2022, researchers at the Federation of American Scientists began reading newly released U.S. Defense Department budget documents to look for updates concerning the Pentagon’s priorities for the next fiscal year. As the researchers poured over hundreds of pages, two words suddenly captured their attention: the Biden administration’s Fiscal Year (FY) 2023 budget request had added “the UK” to a list of countries receiving upgrades to their “special weapons” storage sites under a 13-year NATO investment program. The term “special weapons” is often used by the U.S. government when referring to nuclear weapons. However, the United States has not deployed nuclear weapons in the United Kingdom for nearly two decades. Those two words sparked dozens of questions, years of continued research, and a new local movement of protests against the return of a potential nuclear mission to RAF Lakenheath.
This new report provides an account of the nuclear history of RAF Lakenheath and the role it played in the US nuclear mission until nuclear weapons were withdrawn in 2008. The report then explains the mounting evidence from three years of collection of documentation and observations that show the United States Air Force is re-establishing its nuclear mission on UK soil for the first time in nearly two decades.
As of February 2025, there are no known public indications that nuclear weapons have been deployed to RAF Lakenheath – we assess that the return of the nuclear mission is intended primarily as a backup rather than to deploy weapons now. However, if this were to happen, it would break with decades of policy and planning and reverse the southern focus of the European nuclear deployment that emerged after the end of the Cold War. Even without weapons present, the addition of a large nuclear air base in northern Europe is a significant new development that would have been inconceivable just a decade-and-a-half ago.
The authors would like to thank Matt Korda and Kate Kohn for their invaluable contributions to this report, as well as the Joseph Rowntree Charitable Trust for their support.
Don’t Let American Allies Go Nuclear
President Trump is moving quickly to push U.S. allies to invest even more in their own defense. NATO allies have already committed to spend 3% of their GDP on defense, yet the U.S. is now calling for them to spend at least 5%. It is likely that U.S. allies in East Asia will soon face similar calls to do more. Greater investments in conventional capabilities make a lot of sense. However, there are some U.S. policy experts, officials and academics calling for more U.S. allies to go nuclear to reduce U.S. defense requirements. These calls are dangerously misguided and ignore the threat any proliferation – including by U.S. allies – poses to American security interests. They must be rejected wholesale by the Trump Administration.
One of the most enduring successes of U.S. national security policy has been its effort to limit the number of states with nuclear weapons. Predictions that dozens of countries might possess nuclear weapons did not materialize because of concerted U.S. actions. The risks include the reality that U.S. allies can and often do experience internal instability or even regime collapse, that any state with nuclear weapons creates a risk that those materials or knowhow can be stolen or diverted, that any state with nuclear weapon in a crisis might actually use those weapons, and lastly the reality that states with their nuclear weapons are less susceptible open to U.S. influence. There may be reasons why a state may want to go nuclear from their own perspective but there are few if any lasting benefits to American security that comes from proliferation to friends and allies.
Nine countries currently have nuclear weapons, but perhaps 40 additional states are technically advanced enough to build nuclear weapons if they chose to do so. Many of these states are U.S. allies or partners, including in Europe as well as Japan, South Korea, and even the island of Taiwan. That these states never went nuclear (although some tried) is due to a combination of factors, including the credibility of U.S. defense commitments to their security, the pressure America brought to bear when these states indicated a potential interest in building independent nuclear arsenals, and the recognition that if the world was serious about getting rid of all nuclear weapons then their spread was a step in the wrong direction.
The re-election of Donald Trump has understandably spooked many U.S. allies, renewing doubts that America will come to their aid. The growth of China’s military and economic power relative to the United States is adding to these concerns. More allies are asking now, just as they did during the Cold War if America would really risk Boston to protect Berlin, or Seattle to protect Seoul. As this question festers and as America’s relative power over China and other states ebbs, the lure to encourage U.S. friends to develop nuclear weapons of their own to deter or defeat an attack will grow. After all, the theory goes, why should the United States worry if its friends go nuclear?
In the real world, however, the spread of nuclear weapons anywhere complicates and undermines U.S. security. One reason is states are not always stable. In the 1970s, the U.S. supported its Treaty partner Iran acquiring nuclear reactors and advanced technology but in 1979, that regime was overthrown by the Islamic Revolution. Pakistan went nuclear when the U.S. needed its help fighting the Soviets in Afghanistan, and has faced wave after wave of instability and crisis. And South Korea is a more recent challenge. For the last few decades, South Korea was considered a stable and vibrant democracy – even hosting a Summit for Democracy last year. Under President Yoon, South Korea has voiced increasing interest in an independent nuclear arsenal. And just last year, a former Trump official, Elbridge Colby, expected to serve in a senior policy role at the Pentagon publicly encouraged South Korea to build their own nuclear weapons to deter North Korea and enable the U.S. to focus more on China. The situation in South Korea, with an impeached President and no clear sense of who controls the country’s military, would be a lot more dangerous if Seoul had nuclear weapons.
This is not just an issue for newer nuclear weapons states. Prior to the Soviet Union’s collapse in 1991, a coup created confusion for days over exactly who had the ability to control Soviet nuclear weapons. Following the USSR’s demise, nuclear weapons and materials remained at risk of theft and diversion for years and required massive U.S. efforts and investments to prevent their loss. And even the United States is not immune from these risks. The 2021 insurrection raised nuclear risk to the point that the Speaker of the House had to publicly ask the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs about the risk that President Trump might use nuclear weapons in a gambit to remain in power, and Chairman Milley took extraordinary steps to insert himself into the nuclear chain of command to preempt that risk. Any nuclear arsenal anywhere is a potential danger if political circumstances change.
And states with nuclear weapons create a nuclear risk if nuclear technology, materials and knowhow are stolen or diverted. Five of today’s nuclear weapon states – America, Russia, China, France, and Pakistan – have either knowingly or unwittingly helped other states go nuclear. Even if theft or transfer were not an issue, when new states have gone nuclear in the past, others have followed. America’s nuclear success led the Soviet Union to build them as well. This in turn led the UK and France to follow suit. These four nuclear weapon programs fueled China’s desire to join the club. Beijing having the bomb drove India to do the same, which then led Pakistan to follow suit.
And any nuclear state might decide one day to use those weapons. Every nuclear leader must get every nuclear decision right, every time or boom. The history of U.S. and Soviet nuclear deterrence is marked as much by nuclear misunderstandings and potential accidents as by stable deterrence. India and Pakistan have the same problem. It is reasonable to assume new nuclear states with nuclear weapons would encounter many of the same risks.
And finally, from a very direct Americentric point of view, each state that acquires their own nuclear weapons lessens the ability of the United States to influence, control or dictate security outcomes in that state and region. While not the message U.S. diplomats use openly when trying to work diplomatically to stop proliferation, the issue of influence is as relevant to U.S. allies as adversaries. To the extent that the U.S. security is enhanced by being able to heavily influence how states around the world act, then enabling the spread of nuclear weapons undermines that ability.
It is and will continue to be tempting for the next Administration to find rapid and easy solutions to long-standing security challenges. Empowering U.S. allies to do more so Washington can do and spend less, or focus more effectively on fewer challenges is an understandable policy outcome. But enabling, or looking the other way at the spread of nuclear weapons is not in America’s interests anymore today than it was in the 20th century.
Doomsday Clock at 89 Seconds to Midnight Signals Growing Nuclear Risk
Today, the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists announced that the Doomsday Clock is 89 seconds to midnight.
Created in 1974, the Clock is a symbolic representation of how close humanity is to global catastrophe—or midnight—due to man-made technologies. The Clock is set by the Bulletin’s Science and Security Board, a group of experts on nuclear risk, biological threats, disruptive technologies, and climate change. Each time the Doomsday Clock is set, it is a visual reminder of the work to be done.
While the Clock has remained at 90 seconds for the past three years, today, the Bulletin announced that the Clock has moved 1 second to midnight, symbolizing a time of “unprecedented danger.” This is the closest the Doomsday Clock has ever been to midnight, even through events like the Cuban Missile Crisis, the creation of the hydrogen bomb, 9/11, and North Korea’s first test of a nuclear weapon. The Science and Security Board explained that this change was due mainly to a rise in nuclear stockpiles, warming global temperatures, and advances in disruptive technologies. A “countdown to zero” metaphor, the Clock is used as a plea from scientists and experts for policy changes that would reduce the risk of nuclear war and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Daniel Holz, the Chair of the Science and Security Board, stated that “the countries that possess nuclear weapons are increasing the size of all of their arsenals, investing hundreds of billions of dollars in weapons that can destroy civilization many times over.”
The Federation of American Scientists was founded over 75 years ago after the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki with a commitment to the use of science and technology for the betterment of humanity. To this day, the staff continues to work towards the reduction of nuclear risks and to support evidence-based policy decisions.
In 2024, the Nuclear Information Project of the Federation of American Scientists reported on several of the risks that contributed to the clock’s hand moving forward.
All nuclear weapons states are undergoing nuclear weapons modernization programs. While not all states are necessarily increasing the number of warheads in their stockpiles, a combination of nuclear signaling, the degradation of arms control, and massive spending indicate that we are entering an age of arms racing. All of these indicators demonstrate that states are further prioritizing nuclear weapons in their national security strategies, potentially at the expense of more proximate security priorities.
As long as nuclear weapons exist, nuclear war remains possible. The Nuclear Information Project provides transparency of global nuclear arsenals through open source analysis. It is through this data that policy makers can call for informed policy change. Pursuing policy options that lower the risks of nuclear war and global catastrophe should be of the utmost importance. In 2024, The Global Risk team at Federation of American Scientists proposed several options as part of FAS’s Day One Project.
Pursuing a Missile Pre-launch Notification with China as a Risk Reduction Measure
With tensions and aggressive rhetoric on the rise, the next administration needs to prioritize and reaffirm the necessity of regular communication with China on military and nuclear weapons issues to reduce the risk of misunderstandings. Details regarding a proposed agreement between China and the United States can be found in this policy memo.
Removing Arbitrary Deployment Quotas for Nuclear Force Posture
Congress should ensure that no amendments dictating the size of the intercontinental ballistic missile force are included in future National Defense Authorization Acts. For more on reducing costs in the ICBM force and adjusting to current strategic objectives, read this policy memo.
Introducing Certification of Technical Necessity for Resumption of Nuclear Explosive Testing
The United States should continue its voluntary moratorium on explosive nuclear weapons tests and implement further checks on the president’s ability to call for a resumption of nuclear testing. On preventing environmental contamination, unnecessary spending, public health crises, and security threats due to resuming nuclear testing, read more here.
Saving Billions on the US Nuclear Deterrent
Life-extending the existing Minuteman III missiles is the best way to field an ICBM force without sacrificing funding for other priorities. Read more in this policy memo.
Federation of American Scientists Releases Latest United States Edition of Nuclear Notebook
Washington, D.C. – January 13, 2025 – Today, the Federation of American Scientists released “United States Nuclear Weapons, 2025”—its estimate and analysis of the U.S. nuclear weapons arsenal. The annual report, published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, estimates that the United States maintains a stockpile of approximately 3,700 warheads, about 1,700 of which are deployed.
Under several successive presidential administrations, the United States has pursued an ambitious nuclear modernization program, including upgrades to each leg of its nuclear arsenal. Under the Biden administration, however, the debate has shifted to begin assessing ways that the United States could potentially increase the number of nuclear weapons that could be deployed on its current launchers by uploading more warheads.
Despite mounting cost overruns and program delays in its nuclear modernization efforts, the incoming Trump administration has signaled it may pursue additional nuclear weapons programs and further expand the role that these weapons play in U.S. military strategy, based in part on the recommendations of the 2023 Strategic Posture Commission.
Nuclear Signaling
In recent years, the United States sought to use its nuclear arsenal to signal both its resolve and capability to adversary nations—an effort likely to continue and grow in the coming years. Past efforts at nuclear signaling include increased nuclear-armed bomber exercises, updating nuclear strike plans, nuclear submarine visits to foreign ports, and participation in NATO’s annual Steadfast Noon nuclear exercise. In addition, the Biden administration announced that its new nuclear employment guidance determined “it may be necessary to adapt current U.S. force capability, posture, composition, or size,” and directed the Pentagon “to continuously evaluate whether adjustments should be made.” This language effectively leaves it to the incoming Trump administration to decide whether to expand the U.S. arsenal in response to China’s buildup (read a detailed FAS analysis by Adam Mount and Hans Kristensen here).
Modernization and Nuclear Infrastructure
Nuclear modernization continues for all three legs of the nuclear triad. For the ground-based leg, the new ICBM reentry vehicle––the Mk21A––is expected to enter the Engineering and Manufacturing development phase in FY25. It will be integrated into the Sentinel ICBM and carry the new W87-1 warheads currently under development. The Sentinel ICBM program continues to run over-budget as all 450 launch centers must be renovated to accommodate the new missile, and new command and control facilities, launch centers, training sites, and curriculum for USAF personnel must be created. For the sea leg, the first Columbia-class ballistic missile submarine (SSBN)––the USS District of Columbia––passed its 50 percent construction completion metric in August 2024, and the USS Wisconsin passed 14 percent in September. The new SSBNs will include a reactor that, unlike the Ohio class SSBNs, will not require refueling for the entirety of its lifecycle. The program faces delays and is projected to cost five times more than the Navy’s estimates For the air leg, the Air Force is developing a new nuclear air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) known as the AGM-181 LRSO, as well as the B-21 Raider and new gravity bombs, including the B61-12 and B61-13.
Throughout 2024, infrastructure upgrades at various U.S. ICBM bases were visible. This includes a new Weapons Generation Facility at Malmstrom Air Force Base and a Missile-Handling and Storage Facility and Transporter Storage Facility at F.E. Warren Air Force Base, as well as test silos at Vandenberg Space Force Base.
Finally, in addition to these ongoing upgrades, the United States is also considering developing a new non-strategic nuclear sea-launched cruise missile (SLCM-N), which was proposed during the first Trump administration. Despite the Biden administration’s attempt to cancel the program, Congress has forced the administration to establish the SLCM-N as a program of record. The SLCM-N was originally expected to use the W80–4 warhead that is being developed for the LRSO; however, this is currently being renegotiated. The warhead and delivery platform are expected to be finalized in early 2025.
The Nuclear Notebook is published in the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists and freely available here.
This latest issue follows the release of the 2024 UK Nuclear Notebook. The next issue will focus on China. Additional analysis of global nuclear forces can be found at FAS’s Nuclear Information Project.
ABOUT THE NUCLEAR NOTEBOOK
The FAS Nuclear Notebook, co-authored by Hans M. Kristensen, Matt Korda, Eliana Johns, and Mackenzie Knight, is an effort by the Nuclear Information Project team published bi-monthly in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. The joint publication began in 1987. FAS, formed in 1945 by the scientists who developed the nuclear weapon, has worked since to increase nuclear transparency, reduce nuclear risks, and advocate for responsible reductions of nuclear arsenals and the role of nuclear weapons in national security.
The Federation of American Scientists’ work on nuclear transparency would not be possible without generous support from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, Longview Philanthropy, the Jubitz Foundation, the New-Land Foundation, Ploughshares, the Prospect Hill Foundation, and individual donors.
ABOUT FAS
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) works to advance progress on a broad suite of contemporary issues where science, technology, and innovation policy can deliver dramatic progress, and seeks to ensure that scientific and technical expertise have a seat at the policymaking table. Established in 1945 by scientists in response to the atomic bomb, FAS continues to work on behalf of a safer, more equitable, and more peaceful world. More at fas.org
The 2024 DOD China Military Power Report

The Department of Defense has finally released the 2024 version of the China Military Power Report. We will provide additional analysis of the Chinese arsenal in early 2025 but offer these observations for now:
The report estimates that China, as of mid-2024, had more than 600 nuclear warheads in its stockpile, an increase of roughly 100 warheads compared with the estimate for 2023 and about 400 warheads since 2019. As we have stated for several years, this increase is unprecedented for China and contradicts China’s obligations under the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty. DOD assesses that the Chinese nuclear buildup “almost certainly is due to the PRC’s broader and longer-term perceptions of progressively increased U.S.-PRC strategic competition.”
The breakdown of the DOD estimate comes with considerable uncertainty. It appears to assume that sufficient warheads have been produced to arm many – perhaps up to one third – of the silos in the three new ICBM silo fields in northern China. Different assumptions about how those silos will be armed greatly influence warhead projections:
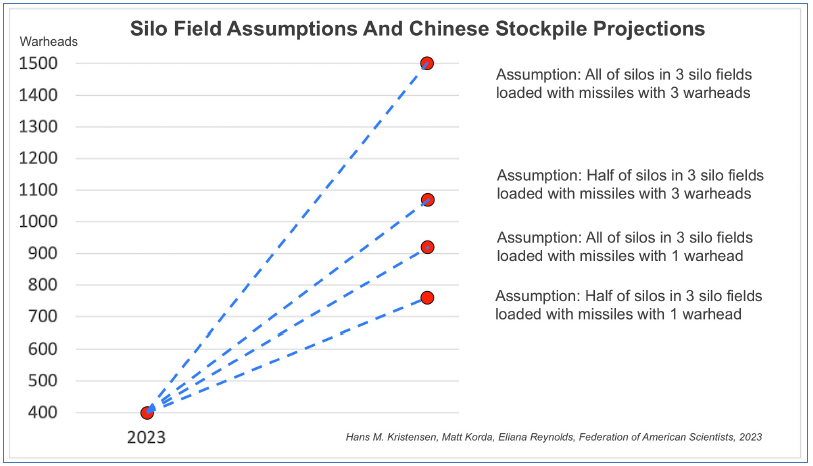
Different assumptions about how China will arm it’s missile silos can significantly influence warhead number projections.
Matching the warhead estimate with the known force structure also depends on how many of the new liquid-fuel silos under construction in the mountains of central/southeastern China are operational, and how many of missiles carry multiple warheads. Other variables are how many warheads are assigned to the DF-26 IRBM launchers (probably not all of them), how many of the six SSBNs have been upgraded to the JL-3 SLBM and whether it is assigned multiple warheads, and how many DF-41 ICBM launchers are operational and how many warheads each missile is assigned.
As in previously years, the DOD report misleadingly describes the Chinese warheads as “operational.” This gives the false impression that they’re all deployed like Russia and U.S. nuclear warheads on their operational forces and has already created confusion in the public debate by causing some to compare all Chinese warheads with the portion of US warheads that are deployed. What DOD calls China’s “operational” warheads is equivalent to DOD’s entire nuclear warhead stockpile, whether deployed, operational, or reserve.
Except for perhaps a small number, the vast majority of Chinese warheads are thought to be in storage and not deployed on the launchers. This situation may be changing with a higher readiness level and emerging launch-on-warning capability.
The report repeats earlier projections that China might have over 1,000 warheads by 2030 but does not mention previous projections of 1,500 warheads by 2035. But this expansion requires additional plutonium production. The report confirms that China “has not produced large quantities of plutonium for its weapons program since the early 1990s” and anticipates that it “probably will need to begin producing new plutonium this decade to meet the needs of its expanding nuclear stockpile.”
ICBMs
The report lists 550 ICBM (Intercontinental-Range Ballistic Missile) launchers with 400 ICBMs, an increase of 50 launcher and 50 missiles compared with last year’s report. That is more ICBM launchers than the United States has, although far from all the Chinese silos are armed.
It is unclear what operational status a missile must have to be included in the count or whether 400 is simply the total number of missile available for the launchers. If it means operational (which I don’t think is the case), then 400 ICBMs would imply a significant number of the new silos loaded.
The report includes a map that appears to match previous FAS analysis of the three silo fields:
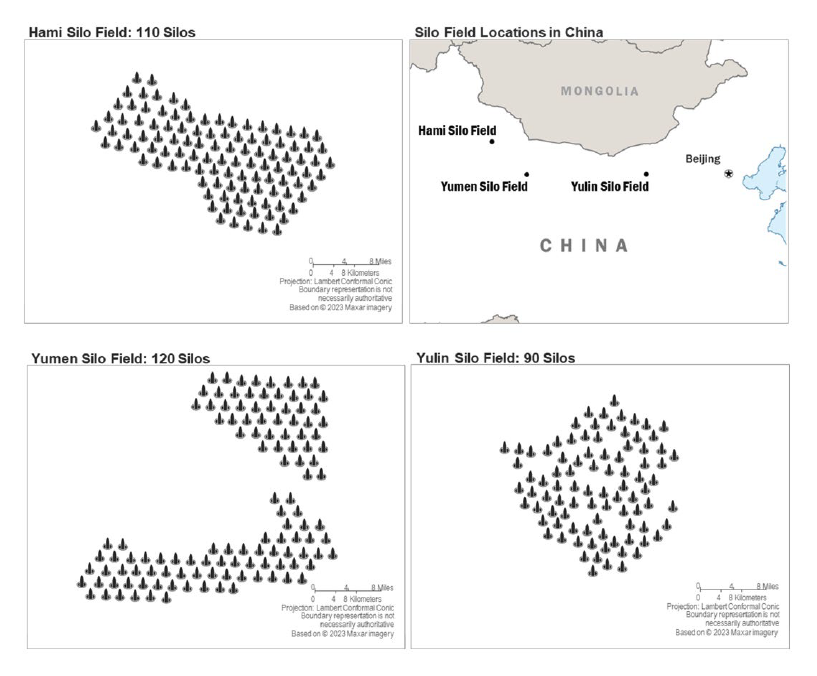
The DOD map of the three northern silo fields appears to match earlier FAS analysis.
The report states that the three ICBM fields were probably completed in 2022 and that PLARF has loaded “at least some” ICBMs into the silos. The report says China “probably continues to arm” the silo fields.
For now, the new silo fields appear intended for the solid-fuel DF-31A. The DOD report identifies a new version of the DF-31 (CSS-10 Mod 3), which is probably the version intended for the silos.
The ICBM estimate appears to come with several caveats. One is that the number of ICBM launchers is not the same as the number of operational ICBMs. A silo launcher appears to be counted when construction is completed, whether it is operational with missile or not. To get to 550 launchers, it is necessary to count everything, including all the 320 silos in the three new northern silo fields as well as all the silos under construction in the southeastern mountains.
The report says the silo construction in the central/southeastern part of China will probably result in about 50 silos there, matching estimates made by FAS and others. The report confirms that those new silos are intended for DF-5 liquid-fuel missiles and appears to suggest that at least two brigades with the new silos are intended for the new multi-megaton DF-5C that it says China is now fielding.
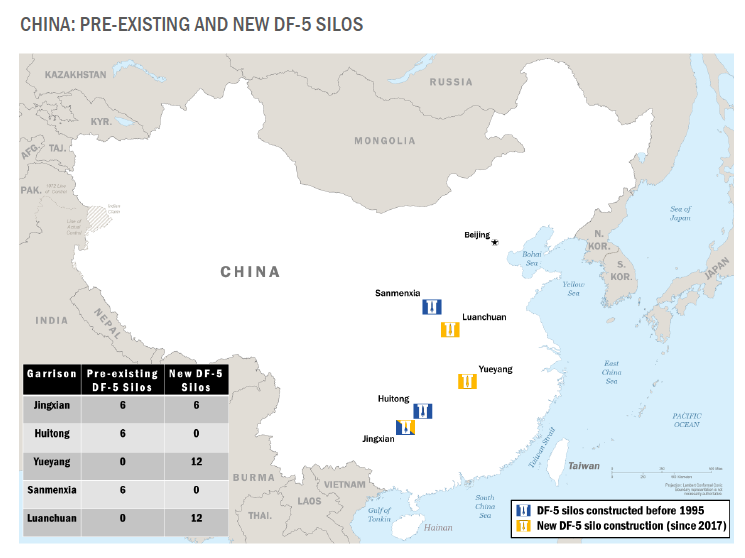
The 2024 China Military Power Report confirms reports by FAS, Ben Reuter, and Decker Eveleth about the modernization of the DF-5 silos in central/southeastern China.
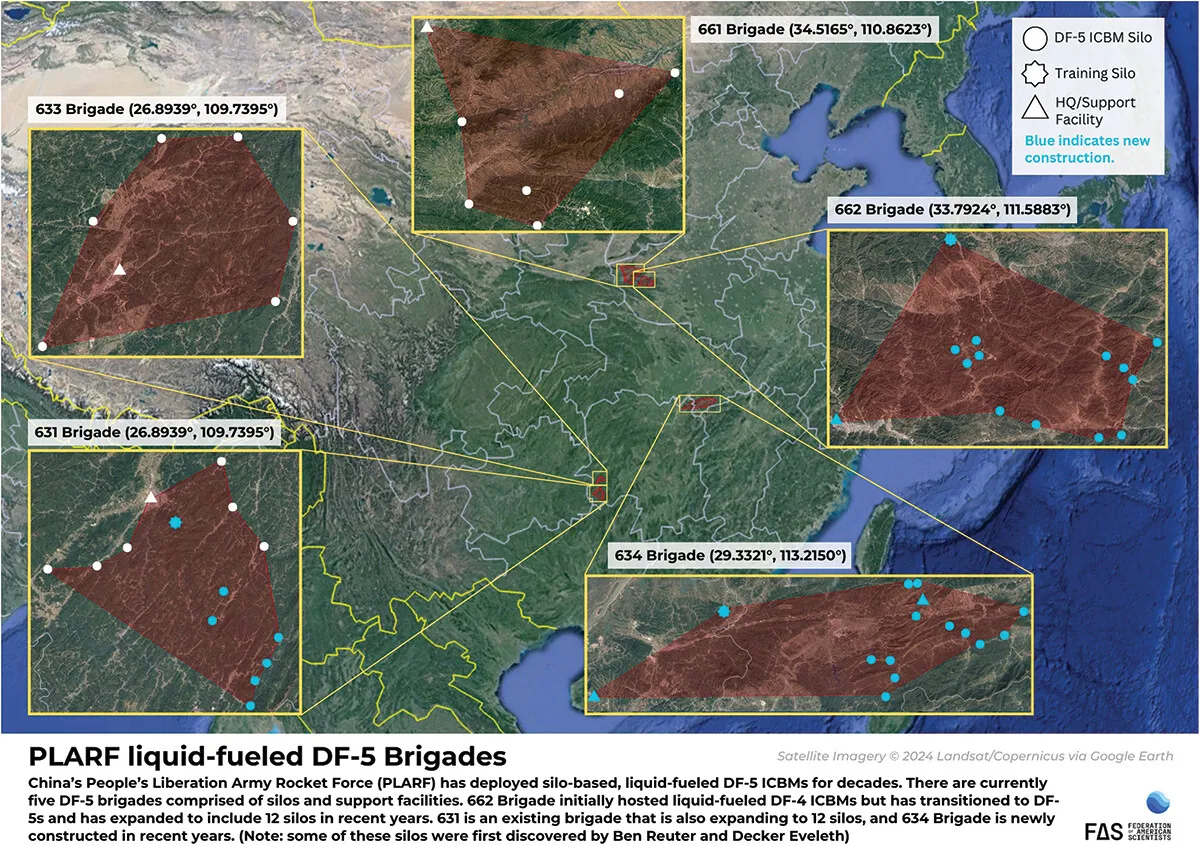
The report does not say how many of the new DF-5 silos – if any – have been loaded with missiles.
The new DF-41 ICBM is not said to be deployed in silos but so far only as a road-mobile system in a few brigades. But the DOD report says China might pursue silo and rail deployments for the missile in the future.
The new DF-27 is described as dual-capable and while capable of shorter ICBM ranges mainly be intended for conventional IRBM missions.
IRBMs and MRBMs
The report lists 250 IRBM (Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile) launchers with 500 missiles, the same as in 2023. This force apparently consists entirely of the DF-26, of which the report identifies three versions. Previously an anti-ship version was identified in addition to the basic version, so it is unclear if the first two versions are used to differentiate between the conventional and nuclear versions. Regardless, the DF-26 is replacing the DF-21 MRBM (Medium-Range Ballistic Missile) and the report says there are no longer any brigades with “dual nuclear-conventional capable DF-21Cs” (which is odd because the C was the conventional and the A was the nuclear).
The DF-17 MRBM maneuverable glide vehicle is described as conventional.
SSBNs
The report says that China continues to operate six Jin-class Type 094 SSBNs (nuclear powered ballistic missiles submarines) equipped with either the JL-2 or the 10,000-km range JL-3 SLBM (Sea-Launched Ballistic Missile). Despite the longer range of the JL-3 SLBM, it is not capable of targeting the Continental United States from the South China Sea. A submarine would have to deploy up into the shallow Bohai Sea to be able to target part of CONUS.
The DOD report says the six SSBNs “are conducting at sea deterrent patrols.” In the U.S. Navy, that means the missiles are armed with nuclear warheads, but the DOD report does not explicitly say this is the case for China.
The report says the SSBNs are “representing the PRC’s first viable sea-based nuclear deterrent,” and says China “has the capacity to maintain a constant at sea deterrent presence.” More Jin-class SSBNs apparently are under construction.
The next-generation Type 096 apparently is not yet under construction. It is said it will get a new longer-range missile, although it is unclear if that is older language that used to refer to the JL-3. The report says the Type 096 SSBN “probably is intended to field MIRVed SLBMs,” indicating that the SLBMs on the current Jin-class are not.
Bombers
The report repeats previous statements that China is fielding a nuclear version of the H-6 medium-range bomber. The nuclear version H-6N is capable of carrying a large air-launched ballistic missile that “may be” nuclear capable. Although China is often said to have a Triad, the air-leg is nascent and still only includes one brigade that is developing tactics and procedures for the PLAAF nuclear mission.
As mentioned above, we will provide additional analysis of the DOD report and Chinese nuclear forces early in the new year. More information: The Nuclear Information Project
The Federation of American Scientists’ work on nuclear transparency would not be possible without generous support from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, Longview Philanthropy, the Jubitz Foundation, the New-Land Foundation, Ploughshares, the Prospect Hill Foundation, and individual donors.
Pursuing A Missile Pre-Launch Notification Agreement with China as a Risk Reduction Measure
While attempts at dialogue and military-to-military communication with China regarding its growing nuclear arsenal have increased, the United States has so far been unable to establish permanent lines of communication on nuclear weapons issues, let alone reach a substantive bilateral arms control agreement with China. Given the simmering tensions between the United States and China, lack of communication can be dangerous. Miscommunication or miscalculation between the two nuclear powers – especially during a crisis – could lead to escalation and increased risk of nuclear weapons use.
In an effort to prevent this, the next U.S. presidential administration should pursue a Missile Pre-Launch Notification Agreement with China. The agreement should include a commitment by each party to notify the other ahead of all strategic ballistic missile launches. Similar agreements currently exist between the United States and Russia and between China and Russia. One between the United States and China would be a significant confidence-building measure for reducing the risk of nuclear weapons use and establishing a foundation for future arms control negotiations.
Challenge and Opportunity
Between states with fragile relations, missile launches may be seen as provocative. In the absence of proper communication, a surprise missile test launch in the heat of a tense crisis could trigger overreaction and escalate tensions. Early warning systems are made to detect incoming missiles, but experts estimate that the US early-warning system would have just two minutes to determine if the attack is real or serious enough to advise the president on a possible nuclear counterattack. For example, when the Soviet Union test-launched four submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) in 1980, the US early warning system projected that one of the missiles appeared to be headed toward the United States, resulting in an emergency threat assessment conference of US officials.
Establishing regular communications is increasingly important as China grows its nuclear arsenal of quick-launching ballistic missiles, with the Pentagon estimating that China’s arsenal may reach 1,000 warheads by 2030. This is creating increasing concern about China’s intentions for how it might use nuclear weapons. In reaction, some US officials are signaling that it may be necessary for the United States to field new nuclear weapons systems or increase the number of deployed warheads. Defense hawks even advocate curtailing diplomatic communication with China, arguing that talks would allow China leverage and insight into US nuclear thinking.
With tensions and aggressive rhetoric on the rise, the next administration needs to prioritize and reaffirm the necessity of regular communication with China on military and nuclear weapons issues to reduce the risk of misunderstandings and conflict and mitigate the chance of accidental escalation and miscalculation.
The opportunity for negotiating an agreement with China exists despite heightened tensions. Although still inadequate, military-to-military communications between China and the United States have improved since a breakdown in 2022 following Speaker Nancy Pelosi’s visit to Taiwan, to which China responded with military exercises, missile tests, and sanctions on the island.
On November 6, 2023, Chinese Director-General of the Department of Arms Control Sun Xiaobo and US Assistant Secretary of State for Arms Control, Deterrence, and Stability Mallory Stewart discussed nonproliferation and nuclear transparency during the first US-China arms control talk in five years. Days later, Presidents Biden and Xi decided to resume military-to-military conversations and encouraged a follow-up arms control talk. A high-level China-US defense policy talk at the Pentagon in early January 2024 followed this summit. Most recently, Presidents Biden and Xi agreed in Lima, Peru that humans, not artificial intelligence, should have control over the decision to launch nuclear weapons. These meetings show promising signs of improved dialogue, but the United States’ continual emphasis on China as a competitor and China’s recent cancelation of arms control talks with the United States over Taiwan continue to undermine progress.
Policy Models
A Missile Pre-Launch Notification Agreement between China and the United States should include a commitment to provide at least 24 hours of advanced notice of all strategic ballistic missile tests including the planned launch and impact locations. The agreement would build on historical models of risk reduction measures between other states. For example, at the 1988 Moscow Summit, the United States and the Soviet Union signed the Agreement on Notifications of Launches of Ballistic Missiles to notify each other of the planned date, launch area, and area of impact no less than 24 hours in advance of any intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) or submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) launches. These notifications were communicated through established Nuclear Risk Reduction Centers. The Strategic Arms Reduction Talks (START), signed in 1991, followed up on the notification agreement by including an agreement to provide more information, such as telemetry broadcast frequencies, in addition to the planned launch date and the launch and reentry area.
The two countries expanded on this agreement through the Memorandum of Agreement on the Establishment of a Joint Center for the Exchange of Data from Early Warning Systems and Notifications of Missile Launches (also known as JDEC MOA) and the Memorandum of Understanding on Notifications of Missile Launches (PLNS MOU). The purpose of these agreements, signed in 2000, was to prevent a nuclear attack based on a false early warning system notification, and the agreements were carried forward into the New START treaty that entered into force in 2011.
While Russia has suspended its participation in the New START treaty and increased its threatening rhetoric around the potential use of nuclear weapons in its war in Ukraine, the Russian Foreign Ministry said that Russia would continue to provide notification of ballistic missile launches to the United States. This demonstrates the value of communication amid tensions and conventional conflict to prevent misunderstanding.
In 2009, Russia and China signed a pre-launch notification agreement, marking China’s first bilateral arms control agreement. This agreement was extended in 2020 for another 10 years and covers launches of ballistic missiles with ranges over 2,000 km that are in the direction of the other country. The United States and China have no such arrangement. However, China did notify the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and the Japanese Coast Guard 24 hours before an ICBM launch into the Pacific Ocean on September 25, 2024. This launch appeared to be the first test into the Pacific China has conducted in over thirty years, and the gesture of notifying the United States beforehand was, according to a Pentagon spokesperson, “a step in the right direction to reducing the risks of misperception and miscalculation.” With this notification, the groundwork and precedent for dialogue on a missile pre-launch notification agreement has been laid.
Plan of Action
Create and present a draft agreement
The next administration should direct the State Department Bureau of Arms Control, Deterrence, and Stability to draft a proposal for a missile pre-launch notification agreement requiring mutual pre-launch notifications for missile launches with ranges of 2,000 km or more, as well as the sharing of launch and impact locations.
The US Assistant Secretary of State for Arms Control, Deterrence, and Stability should present the draft proposal to China’s Director-General of the Department of Arms Control of the Foreign Ministry.
Invite President Xi Jinping to participate in talks
The administration should propose a neutral site in the Asian-Pacific region, possibly in Hanoi, Vietnam, for a meeting between the US president and President Xi Jinping to emphasize the shared goal of trade security and discuss a missile test launch agreement. The meeting should include other high-level military commanders, including the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and Secretary of Defense, as well as their relevant Chinese counterparts.
Continue notifying China of all US missile test launches
The next administration should continue the precedent set by China in September 2024 to voluntarily provide advance notification of all ballistic missile test launches even in the absence of a negotiated agreement, like was done in the November 2024 Minuteman launch, and even if done unilaterally going forward. Such action would improve the prospect for reaching a negotiated agreement by demonstrating good faith and commitment to conflict mitigation.
Raise the topic of missile launch notifications in P5 meetings
China has since assumed the rotating position of Chair of the P5, which could be a useful forum for considering new proposals for risk reduction measures among all nuclear states. After direct engagement with China on an agreement, China may have an interest in working with the United States to lead a multilateral agreement, as China would have more control over the language, international recognition for nuclear risk reduction, and improved security amid global nuclear modernization.
The next administration should direct The Special Representative of the President for Nuclear Nonproliferation under the Bureau of International Security and Nonproliferation to raise the topic of missile launch notifications and a potential launch notification agreement during the P5 process meeting ahead of the 2025 Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT) preparatory conference.
In order to work constructively with China on reducing the risk of nuclear use, a pre-launch notification agreement should, for now, be decoupled from any other arms control measures that would propose limiting China’s nuclear weapons stockpile or any launch capabilities. While comprehensive arms control may be an ultimate goal, linking the two at the outset would complicate talks significantly and likely prevent an agreement from coming to fruition; the United States should start with small steps to foster trust between the two nations and deepen regular military-to-military communication.
Pursuing and negotiating a Missile Pre-Launch Notification Agreement with China will emphasize common objectives and help prevent escalation by miscommunication.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
Removing Arbitrary Deployment Quotas for Nuclear Force Posture
Every year since Fiscal Year 2017, Congress has passed an amendment to the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) that prohibits reducing the quantity of deployed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) below 400. This amendment inhibits progress on adapting the U.S. ICBM force to meet the demands of the new geostrategic environment and restricts military planners to a force structure based on status quo rather than strategic requirements. Congress should ensure that no amendments dictating the size of the ICBM force are included in future NDAAs; this will allow the size of the ICBM force to be determined by strategic military requirements, rather than arbitrary quotas set by Congress.
Challenge and Opportunity
Congressional offices that represent the districts where ICBMs are located work together on a bipartisan basis to advocate for the indefinite sustainment of their ICBM bases. This group of lawmakers, known as the “Senate ICBM Coalition,” consists of senators from the three ICBM host states – Wyoming, Montana, and North Dakota – plus Utah, where ICBM sustainment and replacement activities are headquartered at Hill Air Force Base. Occasionally, senators from Louisiana – the home state of Air Force Global Strike Command – have also participated in the Coalition’s activities.
Over the past two decades, the members of the coalition have played an outsized role in dictating U.S. nuclear force posture for primarily parochial reasons – occasionally even overriding the guidelines set by U.S. military leaders – in order to prevent any significant ICBM force reductions from taking place.
In 2006, for example, this congressional coalition successfully reduced the mandated life expectancy for the Minuteman III ICBM from 2040 to 2030, thus accelerating the deployment of a costly new ICBM by effectively shortening the ICBM’s modernization timeline by a decade. As U.S. Air Force historian David N. Spires describes in On Alert: An Operational History of the United States Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Program, 1945-2011, “Although Air Force leaders had asserted that incremental upgrades, as prescribed in the analysis of land-based strategic deterrent alternatives, could extend the Minuteman’s life span to 2040, the congressionally mandated target year of 2030 became the new standard.”
In another notable example, during the Fiscal Year 2014 NDAA negotiations, senators from the ICBM coalition inserted amendments into the bill that explicitly blocked the Obama administration from conducting the environmental assessment that would be legally necessary in order to reduce the number of ICBM silos. In a subsequent statement, coalition members specifically boasted about how they had overruled the Pentagon on the ICBM issue: “the Defense Department tried to find a way around the Hoeven-Tester language, but pressure from the coalition forced the department to back off.”
By inserting these types of amendments into successive NDAAs, the ICBM coalition has been highly successful in preventing the Department of Defense from fully determining its own nuclear force posture.
The force posture of the United States’ ICBMs, however, is not – and has never been – sacred or immutable. The current force level of 400 deployed ICBMs is not a magic number; the number of deployed U.S. ICBMs has shifted dramatically since the end of the Cold War, and it could be reduced even further for a variety of reasons, including those related to national security, financial obligations, the United States’ modernization capacity, or a good faith effort to reduce deployed U.S. nuclear forces.
When the Bush administration deactivated the “Odd Squad” at Malmstrom Air Force Base in the mid-2000s, for example – bringing the ICBM force down from 500 to 450 – the main driver was economics, not security: the 564th Missile Squadron used completely different and more expensive communications and launch control systems from the rest of the Minuteman III force. (See: David N. Spires, On Alert: An Operational History of the United States Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Program, 1945-2011, 88 2nd ed., pp. 185.)
By legislating an arbitrary quota for the number of ICBMs that the United States must deploy at all times, Congress is leaving successive presidential administrations and Departments of Defense hamstrung with regards to shaping future force posture.
Plan of Action
In order to ensure that the Department of Defense is no longer held to arbitrary force posture requirements that have little basis in military strategy, Congress should ensure that no amendments dictating the size of the ICBM force are included in future NDAAs. If such amendments are included, however, they should be based on strategic needs established by presidential and Defense Department guidance documents.
Conclusion
The stakes of inaction on this front are significant, particularly from a cost perspective, as the maintenance of this arbitrary 400-ICBM quota has served to heavily bias procurement outcomes towards significantly more expensive options. For example, in part due to this arbitrary 400-ICBM quota, the Pentagon’s procurement process for the next-generation ICBM yielded a preference for producing a brand-new missile – the Sentinel – rather than life-extending the current Minuteman III, deploying a smaller number, and cannibalizing the retired missiles for parts that would facilitate the life-extension process.
While this adapted life-extension could have likely been accomplished at a fraction of the cost of building a completely new missile, the Sentinel acquisition program, in contrast, is now approximately 81 percent over-budget and more than two years behind schedule relative to Pentagon estimates from 2020. This constituted an overrun in “critical” breach of the Nunn-McCurdy Act.
To that end, it is imperative that Congress take action to ensure that ICBM force posture is shaped by security requirements, rather than parochial and arbitrary metrics that limit the financial and military flexibility of both the Pentagon and the President.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
Biden Nuclear Weapons Employment Guidance Leaves Nuclear Decisions to Trump
In early November 2024, the United States released a report describing the fourth revision to its nuclear employment strategy since the end of the Cold War and the third since 2013. The public report summarizes a classified employment guidance reportedly issued by President Joseph Biden in April and was submitted to Congress as required by law (and is sometimes known as the section 491 report after the relevant section of the U.S. Code).
The Nuclear Weapons Employment Planning Guidance of the United States “directly informs DoD’s development of nuclear employment options for consideration by the President in extreme circumstances and establishes requirements that shape U.S. nuclear weapons capabilities and posture.”
The report is notable as the first known effort by a U.S. president to provide guidance on the nuclear employment strategy amid growing concern about China’s dramatic buildup of nuclear forces. The report does not reflect the recommendation of the Congressional Strategic Posture Commission and several other expert groups to expand the size or capability of the nation’s nuclear forces. However, because of an ambiguity in the text about what is required to “deter” multiple adversaries simultaneously, the report is likely to support the narrative that the Biden administration accepts the need for an eventual buildup. Biden’s guidance appears to leave major questions in nuclear strategy to the incoming Trump administration.
Timing and tone
Like its predecessor, the Biden administration released its nuclear employment guidance report following the election of a new president. The timing of these releases decreases the time that administration officials can work with planners and acquisition managers on implementation and therefore reduces their ability to affect plans. The timing of the release also decreases the presidents’ ability to inform and assure allies, given outstanding questions about whether, when, and how the incoming president will modify nuclear strategy.
The 2024 report marks a distinct shift in tone from the unclassified 2020 report, which summarized the classified employment guidance issued in April 2019. The unclassified summary was a broad defense of US nuclear strategy and devoted considerable time to arguing against proposed shifts that had been debated in Congress, in public, and on the campaign trail (including a sizable section arguing against a “sole purpose” declaration that the incoming president had endorsed while a candidate). In this sense, the 2024 report is less a political and persuasive document than a simple summary of the president’s guidance. Where the 2020 report sought to constrain the incoming president, the authors of the 2024 guidance appear to have taken pains to leave options open.
Ambiguity on the “two peer problem”
Contrary to public reports, the new guidance does not “reorient America’s deterrent strategy to focus on China’s rapid expansion in its nuclear arsenal.” Although the importance of China is increasing, Russia is still the focus due to its much larger nuclear arsenal.
The report also does not directly articulate or address the so-called “two peer problem”—the concern that US nuclear forces are insufficient to simultaneously deter both Russia and China. The document does note that “growing collaboration and collusion between Russia, the PRC, the DPRK, and Iran” raises the “possibility of coordinated or opportunistic aggression.” But it does not state that Russia and China are peer threats, apparently reflecting the description in the 2022 Nuclear Posture Review that China is “a growing factor in evaluating our nuclear deterrent.”
The new guidance document refers to “multiple nuclear competitors,” but does not explicitly use the “two peer” description frequently used in the public debate by defense officials and others. While the guidance report does not repeat quantitative estimates for China’s buildup that appear in Department of Defense reports, it does state that China has attained a “nascent nuclear triad.” That description credits China with sophisticated air and sea legs, both of which lag significantly behind the capability of US forces, especially the bomber leg. In practice, China is unlikely to become a peer of Russia and the United States in total stockpiled warheads, ballistic missile submarines, or in long-range bombers in the foreseeable future.

The 2024 nuclear weapons employment guidance is the fourth revision since the end of the Cold War and the third since 2013.
The guidance report simply states that “it may be necessary to adapt current U.S. force capability, posture, composition, or size,” and directs the Pentagon “to continuously evaluate whether adjustments should be made.” This language effectively leaves it to the incoming Trump administration to decide whether to expand the U.S. arsenal in response to China’s buildup. Though some Biden administration officials have hinted that they expect to need more capacity, the employment guidance report does not establish a presumption one way or the other.
The closest that President Biden’s guidance comes to an answer to the “two peer problem” is to direct that “the United States be able to deter Russia, the PRC, and the DPRK simultaneously in peacetime, crisis, and conflict.” Yet the document does not require U.S. forces to maintain the capability to perform other or all objectives against multiple adversaries simultaneously. It does not, for example, require the U.S. forces to limit damage against multiple peer adversaries simultaneously or to restore deterrence in the event that it fails—both objectives that are likely to carry higher quantitative or qualitative requirements than deterrence. Including either requirement would effectively endorse the recommendation of the Strategic Posture Commission that China’s buildup demands that the United States follow suit.
The language of the employment strategy report does not clearly indicate whether U.S. forces are required to perform these more demanding objectives. The president could have stated, for example, that U.S. forces are not required to maintain the capability to limit damage against multiple adversaries simultaneously. Without this statement, many will continue to assume that this requirement does exist because counterforce deterrence requires damage limitation.
The 2024 employment strategy does not add any requirement to increase the size of U.S. strategic forces, but it does help to lay the groundwork for future increases. It is a far cry from the 2013 employment strategy’s conclusion that the United States could “ensure the security of the United States and our Allies and partners and maintain a strong and credible strategic deterrent while safely pursuing up to a one-third reduction in deployed nuclear weapons from the level established in the New START Treaty.”
Guidance on other issues
On conventional forces, the 2024 employment guidance requires “the integration of non-nuclear capabilities into U.S. nuclear planning.” This language reflects similar passages in each US nuclear policy document since the end of the cold war. The 2013 version referred to planning “to assess what objectives and effects could be achieved through integrated non-nuclear strike options, and to propose possible means to make these objectives and effects achievable.” The 2020 version noted that the Pentagon “is pursuing the integration of conventional and nuclear planning when appropriate.”
Like its predecessor, the 2024 guidance does not adopt the Obama administration’s aspiration to increase reliance on conventional forces for kinetic strike. Even more than the 2020 document, the 2024 language portrays conventional forces as supportive of the “nuclear deterrence mission.” The language could pertain to, for example, interoperability of nuclear and conventional forces for signaling or strike missions, which is fully consistent with the Trump administration’s concept of “conventional-nuclear integration.” However, the 2024 document is more direct in requiring changes to nuclear plans and characterizes the classified guidance as placing a “greater emphasis” on non-nuclear capabilities. For the guidance to have the intended effect on plans, U.S. officials would have to participate in revisions to operational plans in the coming years, a process that is no longer possible for Biden appointees.
The integration of non-nuclear planning is facilitated by adaptive nuclear planning, according to the guidance document. Unlike deliberate plans, which are flexible employment plans tailored to deter and, if necessary, achieve objectives against specific nuclear-armed adversaries, adaptive plans “would be implemented as needed in a crisis or conflict to tailor deterrence operations and employment options in accordance with the emerging circumstances of a contingency.” The guidance stresses the increasing “importance of managing escalation in U.S. planning for responding to limited strategic attack…including reducing the likelihood of a large-scale nuclear attack…” Adaptive nuclear planning is not new but the guidance document explains it is linked to non-nuclear options as well.
On the law of armed conflict, the 2024 guidance reiterates previous statements that “all nuclear plans must be consistent with the Law of Armed Conflict,” though it does not clarify what this requires or how compliance is assessed. The 2024 document does not repeat its predecessors’ statements on civilian targeting. It does not repeat the 2013 language that the United States “will not intentionally target civilian populations or civilian objects,” nor the lower bar in the 2022 document removes the clause on “civilian objects.” The elision does not signal an intention to target civilian populations or objects and is probably the result of an attempt to reduce the length of the report. However, the oversight may make it difficult to assess whether the Trump administration is reinterpreting its law of armed conflict obligations.
On arms control, the document promises that the United States “will abide by the central limits of the New START Treaty for the duration of the Treaty as long as it assesses that Russia continues to do so,” but offers no assurances beyond February, 2026, either reciprocal or unilateral. The guidance states that “future bilateral agreements or arrangements with Russia… will need to account for U.S. deterrence requirements and other strategic threats globally.” U.S. arms control agreements with Russia have always done that so the explicit condition in the new guidance appears intended to constrain bilateral arms control. However, the passage lends more ammunition to opponents of arms control.
On sole authority, the document goes out of its way to affirm that the president has taken no steps to adjust the requirements or procedure for nuclear launch authorization. Especially in the final months of the first Trump administration, several current and former U.S. officials expressed concern about the existing system of sole authority. When Donald Trump again takes custody of the nuclear codes in January, he will find no new guardrails on his ability to order use of U.S. nuclear weapons.
Conclusion
As the 2024 nuclear employment guidance report states, it offers “more continuity than change with the approach of previous administrations.” The Biden administration could have chosen to try to influence ongoing debates on strategy and force structure, but instead prefers to leave these questions to the incoming Trump administration.
President’s Biden’s employment strategy does break with previous administration’s in one important respect. As written, it does little to advance President Obama’s objective to decrease the nation’s reliance on its nuclear arsenal. It is possible that certain components of the document—on the requirement to “deter” multiple adversaries simultaneously and on integration of nonnuclear capabilities—are intended to advance this goal but the current text will likely do more to increase reliance on nuclear forces.
And with the declaration in June that “we may reach a point in the coming years where an increase from current deployed numbers is required” if the trajectory of adversary arsenals doesn’t change, the Biden administration has essentially set the stage for the Trump administration to increase the deployed arsenal.
If the president’s intention was to reduce reliance on nuclear forces and reduce upward pressure for new nuclear forces, senior administrations should clarify the language before leaving office.
The Federation of American Scientists’ work on nuclear transparency would not be possible without generous support from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, Longview Philanthropy, the Jubitz Foundation, the New-Land Foundation, the Ploughshares Fund, the Prospect Hill Foundation, and individual donors.
Saving Billions on the US Nuclear Deterrent
The United States Air Force is replacing its current arsenal of Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) with an entirely new type of ICBM, known as Sentinel (previously known as the Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent or GBSD). Sentinel’s price tag continues to grow beyond initial expectations, with the program on track to become one of the country’s most expensive nuclear modernization projects ever.
As it stands, the Sentinel program is risky, draws funding away from more urgent priorities, and will exacerbate the Pentagon’s budget crisis. A better approach would be to life-extend a portion of the current ICBM force (the Minuteman III) in the near term in order to spread the costs of nuclear modernization out over the longer term. This approach will ensure that the United States can field a capable ICBM force on a continuous basis without compromising other critical security priorities.
Challenge and Opportunity
The Sentinel ICBM program involves (1) a like-for-like replacement of the 400 Minuteman III ICBMs currently deployed across Colorado, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, and Wyoming, (2) the creation of a full set of test-launch missiles, and (3) upgrades to launch facilities, launch control centers, and other supporting infrastructure. Sentinel would keep ICBMs in the United States’ nuclear arsenal until at least 2075.
Unfortunately, the Sentinel program is riddled with challenges and flawed assumptions that have significantly increased both its cost and risk, and that will continue to do so over the coming years, as described below.
Sentinel’s price tag continues to grow beyond initial expectations
The Sentinel program’s ever-increasing price tag indicates that the program is not nearly as cost-effective as initially projected. In 2015, the Air Force issued a preliminary estimate that Sentinel (then “GBSD”) would cost $62.3 billion to acquire. One year later, the Pentagon’s Cost Analysis & Program Evaluation (CAPE) office projected that Sentinel could more realistically cost $85 billion, a 37% increase from the Air Force’s estimate. In August 2020, CAPE’s projected Sentinel acquisition cost jumped again to $95.8 billion, with total life-cycle costs reaching as high as $263.9 billion1. In October 2020, the Pentagon reported that CAPE’s latest life-cycle estimate was $1.9 billion greater than its 2016 estimate, but did not explain why the estimate had grown. In January 2024, the Air Force notified Congress that the Sentinel program would cost 37 percent more than projected and take at least two years longer than estimated–an overrun in “critical” breach of Congress’ Nunn-McCurdy Act. The overrun put Sentinel’s anticipated cost at approximately $130 billion. In July 2024, upon certifying the Sentinel program to continue after its Nunn-McCurdy breach, the Pentagon announced a new CAPE estimate of $140.9 billion, constituting an 81% increase compared to the 2020 estimate.
As Sentinel matures over the coming years and schedule delays compound these cost issues, it will likely incur further cost increases. Sentinel is on track to become one of the country’s most expensive nuclear-related line items over the next decade.
Sentinel draws funding away from more urgent priorities
By its own admission, the Pentagon cannot afford all the weapons it wants to buy. In July 2020, the then-Air Force Chief of Staff, General Dave Goldfein, remarked that the Sentinel program represents “the first time that the nation has tried to simultaneously modernize the nuclear enterprise while it’s trying to modernize an aging conventional enterprise,” and added that “[t]he current budget does not allow you to do both.”
Funding tradeoffs at the Pentagon have already become apparent. In early 2020, for example, a decision to dramatically increase the budget of the National Nuclear Security Administration directly led to a Virginia-class submarine being cut from the Navy’s budget plan. Compounding the problem is the fact that the Pentagon is currently facing a “bow wave” of major expenditures. The bills for several big-ticket procurement projects—including Sentinel, the Long-Range Standoff Weapon, the F-35 fighter, the B-21 bomber, the Columbia-class ballistic missile submarine, and the KC-46A tanker—will all come due over the next decade. With growing recognition that the Pentagon simply cannot afford to foot so many major bills simultaneously, these large procurement projects have been characterized as “fiscal time bombs”,
The Sentinel program is already impacting funding of other defense programs with its latest batch of cost overruns. The Pentagon admitted in a July 2024 press release that they certified the Sentinel program to continue despite its critical cost and schedule overruns, partly because Sentinel “is a higher priority than programs whose funding must be reduced to accommodate the growth in cost of the program.” In reality, however, the Air Force does not yet know which programs will face funding reductions to offset Sentinel’s increase. General James Slife, Vice Chief of Staff of the Air Force, stated in July 2024 that because Sentinel’s cost growth will be realized several years from now, “it is a decision for down the road to decide what trade-offs we’re going to need to make in order to be able to continue to pursue the Sentinel program.”
With these funding issues in mind, it is imperative to think carefully about whether spending $141 billion to acquire the Sentinel right now makes sense. It may well be a better use of funds to focus on pressing security objectives––such as hardening U.S. command-and-control systems against cyber threats.
Life-extending part or all of the Minuteman III ICBM force—instead of moving to acquire Sentinel as quickly as possible—would constitute a cheaper and less risky option for the United States to field a viable ICBM force at New START levels for at least the next two decades. The Pentagon’s primary justification for pursuing the Sentinel program was the assumption that building an entirely new missile force from scratch would be cheaper than life-extending the Minuteman III force. This assumption stands in stark contrast to an Air Force-sponsored analysis that “[a]ny new ICBM alternative will very likely cost almost two times—and perhaps even three times—more than incremental modernization of the current Minuteman III system.”
The Pentagon’s assumption also does not match historical precedent. In 2012, after the completion of a comprehensive round of Minuteman III life-extension programs, the Air Force admitted that it cost only $7 billion to turn the Minuteman III ICBMs into “basically new missiles except for the shell.” There is little public evidence to suggest that a similar round of life-extension programs would cost significantly more. Even if the programs were more expensive, the added expense is unlikely to come anywhere close to Sentinel’s projected $141 billion acquisition fee; tripling the previous $7 billion price tag for Minuteman III upgrades would still amount to less than one-sixth of the acquisition price of Sentinel.
If a life-extension option were pursued in lieu of Sentinel, it is likely that the Minuteman III’s critical subsystems would eventually need to be replaced. Replacement appears to be technologically feasible. Lieutenant General Richard Clark, the Air Force’s deputy chief of staff for strategic deterrence and nuclear integration, testified to the House Armed Services Committee in March 2019 that it would be possible to extend the lives of the Minuteman III’s propulsion and guidance systems one more time, despite his stated preference for proceeding with the GBSD. Furthermore, a 2014 RAND report commissioned by Air Force Global Strike Command found “no evidence that would necessarily preclude the possibility of long-term sustainment.” In fact, the report noted, “we found many who believed the default approach for the future is incremental modernization, that is, updating the sustainability and capability of the Minuteman III system as needed and in perpetuity.”
Plan of Action
The next administration should revise its nuclear employment guidance to accept a slightly higher threshold for risk with regard to its ICBM force. This action is critical for enabling a life-extended Minuteman III force because the Pentagon’s interest in pursuing Sentinel is largely driven by its own interpretation of presidential nuclear-employment guidance. If the Air Force believes that the Minuteman III might dip below a preset reliability threshold, then the service will push for Sentinel in order to meet the current nuclear-employment guidance.
Revising the guidance to accept a slightly higher threshold for risk would reduce the need to pursue Sentinel immediately. This revision would first be publicly reflected in the next administration’s Nuclear Posture Review, and would then be translated into policy by the Pentagon.
It is important to emphasize that (1) presidential revisions to the nuclear-employment guidance are not unusual, and (2) revising the nuclear-employment guidance would have little bearing on strategic stability. In a nuclear first strike, an adversary would still be forced to target every silo. This means that a life-extended Minuteman III force would theoretically produce the same deterrence effect as a brand-new Sentinel force.
To provide additional support for the guidance revision, the next administration could launch a National Security Council-led review of the role of ICBMs in U.S. nuclear strategy. In particular, this review would assess the feasibility and cost of a Minuteman III life-extension program. The review would also consider whether such a program could be further enabled by reducing the number of deployed ICBMs or the number of annual flight tests, or by pursuing new forms of nondestructive booster reliability testing (see FAQ for more details).
Conclusion
Life-extending the nation’s existing arsenal of Minuteman III missiles instead of immediately pursuing the Sentinel program is the best way to ensure that the United States can continue to field a capable ICBM force without sacrificing funding other critical national-security priorities.
This course of action could buy the United States as much as twenty years of additional time to decide whether to pursue or cancel a follow-on Sentinel program, thus allowing the United States to further spread out costs and reconsider the future role of ICBMs in U.S. nuclear posture.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
While accepting a higher threshold for risk with the ICBM force may sound politically difficult, in reality it has little bearing on strategic stability. The Air Force projects that a 30-year-old missile core has an estimated failure probability of 1.3%, which increases exponentially each year. As long as the expected failure rate did not climb too high, though, an adversary conducting a nuclear first strike would still have to target every silo because there would be no way of knowing which missiles were functional and which were duds. This means that a life-extended Minuteman III force would theoretically produce the same deterrence effect as a brand-new Sentinel force. Additionally, it is extremely unlikely that the United States would ever elect to launch only a small number of ICBMs in a crisis. As a result, even a 10% failure rate across all 400 launched ICBMs would still enable approximately 360 fully functional missiles to reach their targets.
Testing is critical to ensure that the Minuteman III missiles continue to function as designed if they are life-extended. However, there is a limited quantity of Minuteman III boosters that can be used as test assets. This problem was identified early in the Sentinel acquisition process by both internal and external analysts, who noted that increasing the average ICBM test rate from three to four and a half test firings per year – as was done in 2017 – would inevitably exhaust the surplus boosters and lead to a depletion of the currently-deployed ICBM force around 2040., There are several ways to overcome this obstacle without building a brand-new missile force.
One option would be to lower the average test rate from four and a half tests per year back down to three. If the Air Force was prepared to accept a slight additional risk of booster failure––given the fact that, as discussed above, doing so would have no discernible effect on strategic stability––then the number of tests per year could realistically be decreased. To that end, a 2017 Center for Strategic and International Studies report estimated that if the United States chose to re-core its ICBMs and move the firing rate back to three tests per year, then it would be possible to maintain the Minuteman III force at New START levels (400 deployed ICBMs) until 2050.
Another option would be to reduce the number of deployed ICBMs. Again, doing so would not meaningfully affect deterrence but would make a significant quantity of additional missiles available for testing purposes. For example, if the Pentagon reduced its deployed ICBM force from 400 to 300 missiles, it could maintain the current testing rate of four and a half tests per year without the missile inventory dropping below 300 until approximately 2060. A portion of the missiles used for testing could also be converted into commercial or governmental space launch vehicles, thus eliminating the requirement to eventually “re-core” them to ICBM standards.
A third option would be for the Air Force to explore nondestructive methods for testing the reliability of their solid rocket motors. George Perkovich and Pranay Vaddi suggest in their 2021 “Model Nuclear Posture Review” that this could be achieved through technological advances in ultrasound and computed tomography. The Air Force could also consider adapting the Navy’s nondestructive-testing techniques – which involve sending a probe into the bore to measure the elasticity of the propellant – to evaluate the reliability of the Minuteman III force. As Steve Fetter and Kingston Reif noted in 2019, these types of nondestructive testing methodologies “would permit the lifetime of each motor to be estimated on an individual basis. Rather than retire all motors at an age when a small percentage are believed to be no longer reliable, only those particular motors with measurements indicating unacceptable aging could be retired.” Nondestructive testing may be the most effective option, because if successful it would eliminate the attrition problem altogether.
Despite the Pentagon’s repeated claims that the Minuteman III ICBM will become “unviable” after 2030, the Minuteman III’s critical subsystems remain highly reliable with age. There is little evidence to suggest that this will change within the next decade. The Minuteman III’s guidance and propulsion modules were modernized during the 2000s and continue to perform successfully during tests.
A March 2020 Air Force Nuclear Weapons Center briefing to industry partners also acknowledged that the useful life of the Minuteman III force could be extended with “better NS-50 [guidance module] failure data,” because “current age-out on guidance is an engineering ‘best guess’ with no current data.” This suggests that the Air Force’s prediction about the post-2030 “unviability” of these subsystems is based on little actual evidence.
Importantly, the 2030 benchmark for the Minuteman III’s “unviability” appears to have been selected by Congress, not by the Air Force. A consequential amendment inserted into the FY 2007 National Defense Authorization Act directed the Secretary of the Air Force to “modernize Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missiles in the United States inventory as required to maintain a sufficient supply of launch test assets and spares to sustain the deployed force of such missiles through 2030.” This amendment ultimately had a significant impact on the timeline of Sentinel because, as Air Force historian David N. Spires describes, “Although Air Force leaders had asserted that incremental upgrades, as prescribed in the analysis of land-based strategic deterrent alternatives, could extend the Minuteman’s life span to 2040, the congressionally mandated target year of 2030 became the new standard.”
It is telling that the Navy is not currently contemplating the purchase of a brand-new missile to replace its current arsenal of Trident submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and instead plans to conduct a second life-extension to keep them in service until 2084. This life-extension is enabled in large part by the Navy’s unique nondestructive method of testing its boosters, described above. In January 2021, Vice Admiral Johnny Wolfe Jr., the Navy’s Director for Strategic Systems Programs, remarked that “solid rocket motors, the age of those we can extend quite a while, we understand that very well.”
To demonstrate this fact, in 2015 the Navy conducted a successful Trident SLBM flight test using the oldest 1st-stage solid rocket motor flown to date (over 26 years old), as well as 2nd- and 3rd-stage motors that were 22 years old. Rather than replace these missiles as they exceed the planned design life of 25 years, the Navy stated in 2015 that they “are carefully monitoring the effects of age on our strategic weapons system and continue to perform life extension and maintenance efforts to ensure reliability.”
Rather than conduct similar life-extension operations, the Air Force has elected to completely replace its Minuteman III force with the brand-new, highly expensive Sentinel.
A 2016 report to Congress reveals that the Air Force baked multiple flawed assumptions into its cost-assessment process, the most influential of which was the presumption that the United States would continue deploying 400 ICBMs until 2075. However, as researchers from the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace explained in a January 2021 report, “Basing analysis on a straight-line requirement projected all the way to 2075 practically predetermines the outcome.” Rather than prematurely selecting these benchmarks, the Pentagon’s analysis could have considered which options were most cost-effective under a variety of circumstances.
In reality, ICBM force posture is neither sacred nor immutable, and there is little security rationale behind the Pentagon’s selections of the number 400 and the year 2075. The year 2075 a relatively arbitrary timeframe that is not codified in either the Nuclear Posture Review or in other key strategic documents. Moreover, a 2013 inter-agency review—featuring the participation of the Department of State, the Department of Defense, the National Security Council, the intelligence community, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, U.S. Strategic Command, and then-Vice President Joe Biden’s office—ultimately found that U.S. deterrence requirements could be met by reducing U.S. nuclear forces by up to one-third.
Yet despite their lack of strategic rationale, these pre-selected force requirements and exaggerated timelines heavily bias the Pentagon’s cost-assessment process in favor of Sentinel. In particular, if the Pentagon had selected a different ICBM retention timeline – 2050, for example, or even 2100 – then a revised cost assessment would have suggested that life-extending the Minuteman III force would be significantly more cost-effective than building an entirely new Sentinel missile force from scratch.
Federation of American Scientists Releases Latest United Kingdom Edition of Nuclear Notebook
Washington, D.C. – November 12, 2024 – The United Kingdom is modernizing its stockpile of nuclear weapons and delivery systems, as detailed today in the Federation of American Scientists latest edition of its Nuclear Notebook, “United Kingdom Nuclear Forces, 2024”. The researchers estimate that the United Kingdom has maintained its stockpile of 225 nuclear warheads and predict an eventual increase based on shifting posture to counter Russia, modernization, and alliance efforts. The Notebook is published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists and available here.
“Budget overruns remain a constraint for the UK nuclear modernization program, significant parts of which are done in close collaboration with the United States, and efforts are underway to expand the nuclear warhead stockpile,” observes Hans Kristensen, Director of the FAS Nuclear Information Project and one of the Nuclear Notebook authors.
Modernization and nuclear infrastructure construction
The United Kingdom is replacing its sole nuclear platform––the aging Vanguard-class ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs)––with the new Dreadnought-class that is currently under construction.
Additionally, the FAS report includes satellite imagery of ongoing construction at the Atomic Weapons Establishment (AWE) facilities at Aldermaston and Burghfield, including a new warhead assembly facility, enriched uranium storage facility, and plutonium manufacturing facility.
Challenges for the future
Budget overruns and delays in construction continue to be one of the biggest issues for the United Kingdom’s nuclear program. Projected costs for the UK Navy have gone up by 41 percent due to the Dreadnought SSBN program. Delays in this program could threaten the Navy’s ability to maintain their Continuous At-Sea Deterrent (CASD), as it would put additional stress on the Vanguard fleet that has already been pushed past its service life. Nuclear infrastructure projects, including the MENSA warhead facility, are also behind schedule and over-budget.
Collaboration with the United States
Upgrades at RAF Lakenheath discovered by the Notebook authors signal the return of the United States Air Force nuclear mission to the United Kingdom, although it is unlikely that US nuclear weapons will be permanently stored on UK soil in peacetime. The arrival of the F-35A Lightning II, capable of carrying B61-12 gravity bombs, US budgetary indicators for special storage upgrades, and the construction of a new “surety” dormitory for US Airmen at RAF Lakenheath all indicate preparations for the potential return of US nuclear weapons which have been absent in the United Kingdom since 2008.
The Notebook also outlines cooperation between the UK and US Navy on missile tests. This year, UK ballistic missile submarines conducted test fires off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, and US laboratories evaluated and provided measurements for the test effort.
###
ABOUT THE NUCLEAR NOTEBOOK
The FAS Nuclear Notebook, co-authored by Hans M. Kristensen, Matt Korda, Eliana Johns, and Mackenzie Knight, is an effort by the Nuclear Information Project team published bi-monthly in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. The joint publication began in 1987. FAS, formed in 1945 by the scientists who developed the nuclear weapon, has worked since to increase nuclear transparency, reduce nuclear risks, and advocate for responsible reductions of nuclear arsenals and the role of nuclear weapons in national security.
This latest issue follows the release of the 2024 India Nuclear Notebook. The next issue will focus on the United States. More research is located at FAS’s Nuclear Information Project.
The Federation of American Scientists’ work on nuclear transparency would not be possible without generous support from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, Longview Philanthropy, the Joseph Rowntree Charitable Trust, the Jubitz Family Foundation, the New-Land Foundation, Ploughshares, the Prospect Hill Foundation, and individual donors.
ABOUT FAS
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) works to advance progress on a broad suite of contemporary issues where science, technology, and innovation policy can deliver dramatic progress, and seeks to ensure that scientific and technical expertise have a seat at the policymaking table. Established in 1945 by scientists in response to the atomic bomb, FAS continues to work on behalf of a safer, more equitable, and more peaceful world.
The Federation of American Scientists Urges Support of UN Draft Resolution on Nuclear War Effects
The last resolution producing similar scientific research was published in 1989
Washington, D.C. – October 24, 2024 – The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) announces its support for the UN General Assembly Draft Resolution on Nuclear War Effects and Scientific Research, announced August 20th, and calls for others to do the same. FAS believes the resolution is a necessary advancement of scientific understanding of the devastating consequences of a nuclear war.
“Whether people support or oppose nuclear weapons, they deserve to know what the consequences of nuclear use are. An independent fact-based expert study is the best way to do that. All member States, including the United States, can and should support this UN resolution,” says Hans Kristensen, Director of the Nuclear Information Project (NIP) at FAS. “FAS believes in the need for science to inform policy, which is why we call for support of this resolution.”
“The UN resolution is an important and timely measure for articulating the toll of nuclear weapons on humans and the environment,” says Eliana Johns, Senior Research Associate at FAS. “It also provides an opportunity to inject science into nuclear weapons policy deliberations so that policymakers, practitioners, and the public have access to updated and accurate data about nuclear weapons, their effects, and the destruction their use would entail.”
Scientific Report Last Updated in 1989
This resolution, introduced by Ireland and New Zealand, would create a scientific panel to conduct the first comprehensive study on the effects of nuclear war since 1989. With major advances in technology and scientific evidence bases, the independent panel of 21 scientific researchers will produce a more accurate and updated report reflecting current global trends.
It has been over 30 years since the last study on the climatic and other global effects of nuclear war was issued by the UN Secretary-General. Since then, globalization has greatly linked human populations; the global population has grown by 50%, and states’ nuclear arsenals have modernized and advanced. At a time when all nuclear weapons states are undergoing efforts to modernize their arsenals, a better technical understanding of how a nuclear war would impact humanity and the environment is vital to informing discussions on nuclear weapons policy and highlighting nuclear weapons effects on impacted communities.
FAS Nuclear Information Project
FAS is a non-partisan, nonprofit organization dedicated to deploying evidence-based policies to address global threats. From its founding by a group of atomic scientists and engineers involved in the Manhattan Project, FAS has worked for the public promotion of science, and the freedom and integrity of scientists and scientific research to benefit humanity. FAS is proud to support a scientific community that communicates the devastating effects of nuclear war on humans and the environment. In addition to ongoing research, published at the FAS website, the NIP team produces the semi-monthly Nuclear Notebook, published in academic journal Taylor and Francis as well as the Bulletin of Atomic Scientists’ website.
##
ABOUT FAS
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) works to advance progress on a broad suite of contemporary issues where science, technology, and innovation policy can deliver dramatic progress and seeks to ensure that scientific and technical expertise have a seat at the policymaking table. Established in 1945 by scientists in response to the atomic bomb, FAS continues to work on behalf of a safer, more equitable, and more peaceful world. More information at fas.org, and more information about the Nuclear Information Project at https://fas.org/initiative/nuclear-information-project/.