NATO Nuclear Weapons Security Costs Expected to Double

Former US Air Force Europe commander General Rodger Brady shakes hands with 703 Munitions Support Squadron personnel at Volkel Air Base in June 2008 during security upgrades to U.S. nuclear weapons storage sites in Europe. More expensive security upgrades are planned.
By Hans M. Kristensen
The cost of securing U.S. non-strategic nuclear weapons deployed in Europe is expected to nearly double to meet increased U.S. security standards, according to the Pentagon’s FY2015 budget request.
According to the Department of Defense NATO Security Investment Program , NATO has invested over $80 Million since 2000 to secure nuclear weapons storage sites in Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Turkey.
But according to the Department of Defense budget request, new U.S. security standards will require another $154 million to further beef up security at six bases in the five countries.

DOD budget document says more expensive security upgrades are needed for nuclear bases in Europe.
After a US Air Force Blue Ribbon Review in 2008 discovered that “most” U.S. nuclear weapons sites in Europe did not meet U.S. security requirements, the Dutch government denied there were security problems.
Yet more than $63 million of the over $80 million spent on improving security since 2000 were spent in 2011-2012 – apparently in response to the Blue Ribbon Review findings and other issues.
The additional $154 million suggests that the upgrades in 2011-2012 did not fix all the security issues at the European nuclear bases.
The budget document – which also comes close to officially confirming the deployment of nuclear weapons in Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Turkey – states:
NATO funds infrastructure required to store special weapons within secure sites and facilities. Since 2000, NATO has invested over $80 million in infrastructure improvements in storage sites in Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Turkey. Another $154 million will be invested in these sites for security improvements to meet with stringent new U.S. standards.
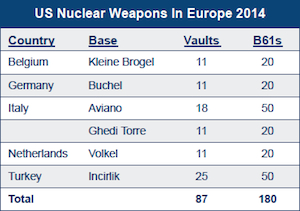
The US Air Force still deploys about 180 nuclear B61 bombs at six bases in five European countries. Despite tight security, the bases are not secure enough.
In addition to the growing security costs, the United States spends approximately $100 million per year to deploy 184 nuclear B61 bombs in the five NATO countries. And it plans to spend an additional $10 billion on modernizing the B61 bombs and hundreds of millions on integrating the weapons on the new F-35A Lightning fighter-bomber.
No doubt the United States and NATO have more urgent defense needs to spend that money on than non-strategic nuclear weapons.
Additional background: Briefing on B61 bomb and deployment in Europe
This publication was made possible by a grant from the Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.