The meteor impacted near large Russian nuclear weapons facilities..
By Hans M. Kristensen
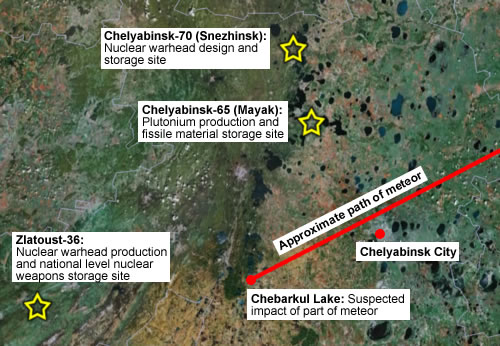
When the news media reported that a meteor had exploded over Chelyabinsk in Russia, the location name sounded familiar: the region is home to some of Russia’s most important nuclear weapons production and storage facilities.
Impact sites still have to be found but one reportedly was Chebarkul Lake, some 72 kilometers (45 miles) southwest of the city of Chelyabinsk. Another piece impacted near the town of Zlatoust some 80 kilometers (49 miles) to the northwest.
Approximately 88 kilometers (55 miles) northeast of Chebarkul Lake is Chelyabinsk-65 (Mayak), a plutonium production and fissile material storage complex. Another 40 miles to the north is Chelyabinsk-70 (Snezhinsk), a nuclear warhead design and storage complex.
Right in the meteor’s path, approximately 115 kilometers (72 miles) southwest of Chebarkul Lake, is Zlatoust-36, one of the two main warhead assembly and disassembly facilities in Russia. Adjacent to the facility is a national-level nuclear weapons storage site.
The odds of a meteor hitting one of these nuclear weapons production or storage site are probably infinitely small, but on a cosmic scale it got pretty close. Just how much damage a direct hit of a sizable chunk of the meteor could have caused is unknown, but the 17-meter (55 feet) meteor reportedly released energy equivalent to nearly 500 kilotons of TNT. That’s roughly the explosive yield of one of the W88 warheads carried on Trident II missiles onboard U.S. ballistic missile submarines.
This publication was made possible by a grant from the Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.