Poor diets present elevated health risks, and Americans need help finding the time and resources to eat nutritiously
Americans get bombarded with promotions for unsubstantiated diet fads on the internet, are exposed to dubious weight-loss branded foods in grocery stores, and often struggle to eat nutritiously. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend a balanced diet of two and a half cups of vegetables, two cups of fruit, six ounces of grains, three cups of dairy, five and a half ounces of protein, and 27 grams of oil every day. This diet is well-balanced, but it is neither practiced by, nor accessible to, all Americans (Figure 1).
Increasing numbers of Americans do not eat healthful diets. In 2018, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that one in three Americans eats fast food on any given day. Moreover, both rural and urban Americans report that lack of time and access to nutritious foods prevents them from cooking healthy meals. Indeed, a 2017 study indicated that the higher prices of healthy foods – nearly double those of unhealthy foods – can play a role in the U.S. population’s failure to achieve a nutritious diet. When healthy food cost even 14 percent higher than unhealthy food, there was a 24 percent decrease in consuming a high-quality diet. Unfortunately, an unhealthy diet can lead to a variety of health issues, such as obesity, type-2 diabetes, heart disease, and an increased risk of some cancers. To reverse poor health metrics such as the 42.4% of American adults over 20 years of age who suffered from obesity in 2018, policymakers and health experts alike hope to make healthy diets more accessible to all Americans.
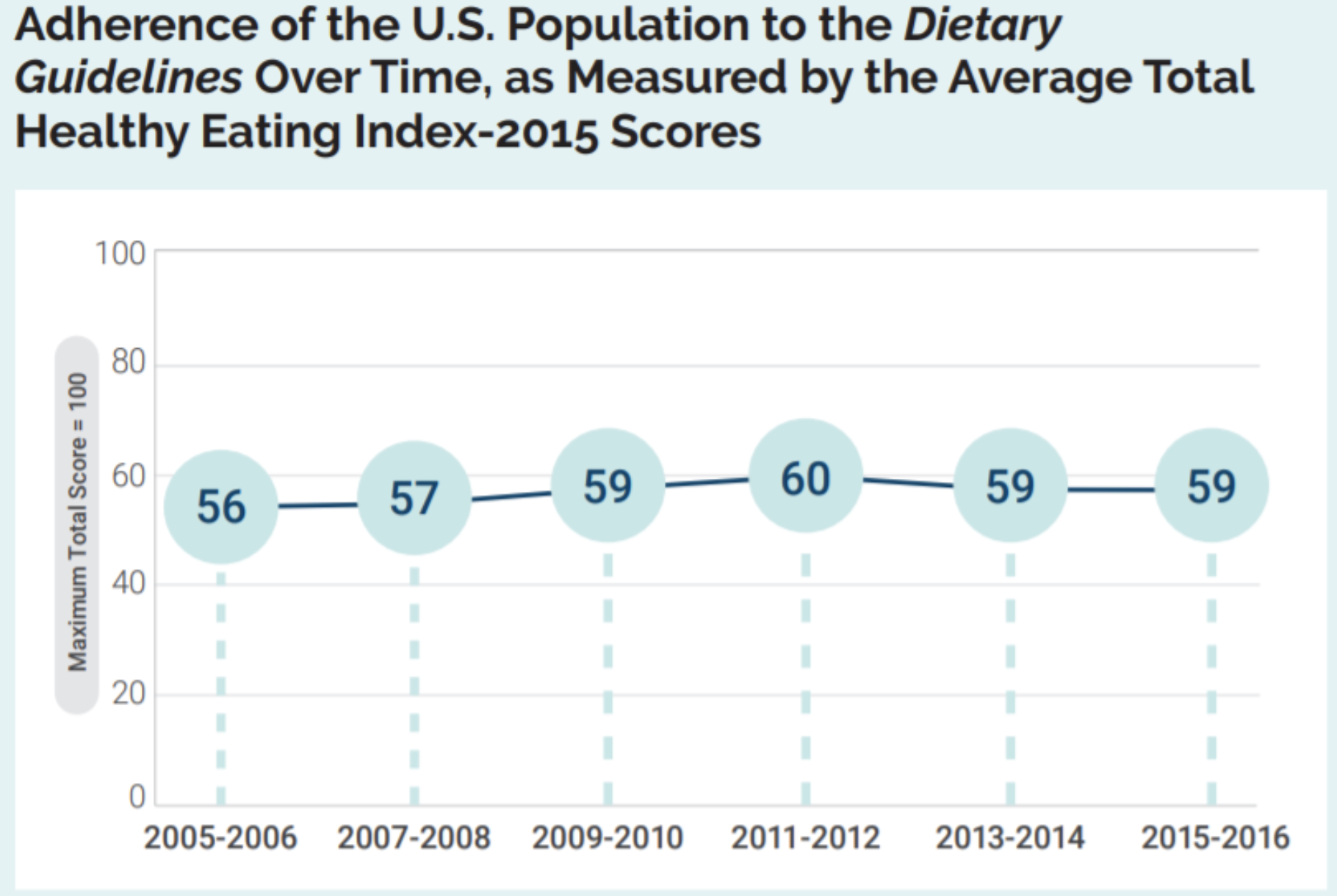
On average, people in the U.S. score between 56 and 60 (out of 100) when evaluated for healthy eating. The maximum test score of 100 points indicates adherence to the American Dietary Guidelines. Figure reproduced from Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025.
To empower people to develop more nutritious eating habits, some experts recommend:
- Teaching better practices for caloric intake, which can increase life expectancy;
- Incentivizing healthy eating with financial rewards, such as coupons, when purchasing fruits and vegetables;
- Teaching and encouraging adults to buy and prepare their own meals; and
- Enabling mutual aid initiatives such as community fridges, food banks, and free breakfast programs for those who are food insecure.
For some, the transition to eating a well-balanced diet will require learning how to cook, carving out time to prepare meals, or gaining an understanding of the nutritional value of various foods. In the U.S., there is no justifiable reason people should not be supported by their local, state, and federal governments in efforts to eat healthy.
To improve American dietary habits, policymakers can learn about and implement public health initiatives for nutritional education, as well as break down systemic barriers to healthy eating lifestyles.
This CSPI Science and Technology Policy Snapshot expands upon a scientific exchange between Congressman Bill Foster (D, IL-11) and his new FAS-organized Science Council.
From California to New Jersey, wildfires are taking a toll—costing the United States up to $424 billion annually and displacing tens of thousands of people. Congress needs solutions.
FAS is launching the Center for Regulatory Ingenuity (CRI) to build a new, transpartisan vision of government that works – that has the capacity to achieve ambitious goals while adeptly responding to people’s basic needs.
This runs counter to public opinion: 4 in 5 of all Americans, across party lines, want to see the government take stronger climate action.
Cities need to rapidly become compact, efficient, electrified, and nature‑rich urban ecosystems where we take better care of each other and avoid locking in more sprawl and fossil‑fuel dependence.