New Nuclear Notebook: British Nuclear Forces 2011
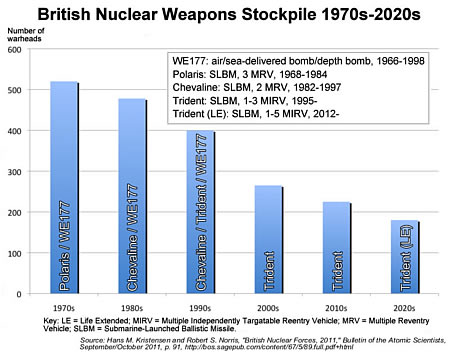 |
| The British Cold War stockpile was bigger than previously thought but will be the smallest of the five original nuclear weapons states by the mid-2020s. Click image for bigger version |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
Britain’s disclosure last year of the size of its nuclear weapons stockpile shows, when combined with official information released earlier, that its Cold War nuclear stockpile was bigger than previously thought – more than 500 nuclear warheads in the 1970s.
Since then, Britain has reduced its stockpile by more than half to approximately 225 warheads and has decided to reduce it further to 180 warheads by the mid-2020s, a reduction of two-thirds compared with the Cold War level.
Modernization and continuous deployment at sea continues, however, and current plans might ironically lead to an increase in the number of warheads carried on each operational missile.
This and more is described in our latest Nuclear Notebook published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
See also: Previous British Nuclear Notebook from 2005
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.