Under ordinary circumstances, the U.S. Army relies on high-speed digital communications. But sometimes that is not an option, and soldiers must revert to more primitive methods.
“When electrical and/or digital means of communication are inadequate, or not available,” a new Army publication explains, messages may be transmitted “through the use of hand-and-arm signals, flags, pyrotechnics, and other visual aids.” Many of those alternate communication methods are described in Visual Signals, U.S. Army Training Circular TC 3-21.60, March 2017.
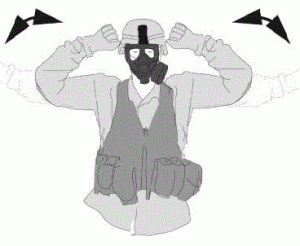
So, for example, “To signal ‘chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear attack,’ extend the arms and fists. Bend the arms to the shoulders. Repeat. (See figure 1-16.)”
Of course, hand and arm signals have limitations. For one thing, they may be misunderstood.
“Visual signals are generally contextual in nature. For example, the hand-and-arm signal for ‘take cover’ and ‘slow down’ are similar in their perspective movements, however the situation in which each is given is completely different.”
Also, “The range and reliability of visual communications are significantly reduced during periods of poor visibility and when terrain restricts observation.”
Finally, visual or gestural communications “are vulnerable to enemy interception and may be used for deception purposes,” the new Army publication said.
Our analysis of federal AI governance across administrations shows that divergent compliance procedures and uneven institutional capacity challenge the government’s ability to deploy AI in ways that uphold public trust.
From California to New Jersey, wildfires are taking a toll—costing the United States up to $424 billion annually and displacing tens of thousands of people. Congress needs solutions.
To secure the U.S. bio-infrastructure, maintain global leadership in biotechnology, and safeguard American citizens from emerging threats to their privacy, the federal government must modernize its approach to human genetic and biological data.
To ensure an energy transition that brings broad based economic development, participation, and direct benefits to communities, we need federal policy that helps shape markets. Unfortunately, there is a large gap in understanding of how to leverage federal policy making to support access to capital and credit.