It’s relatively easy to observe Russian missile bases from above. It’s much harder to do it from inside.
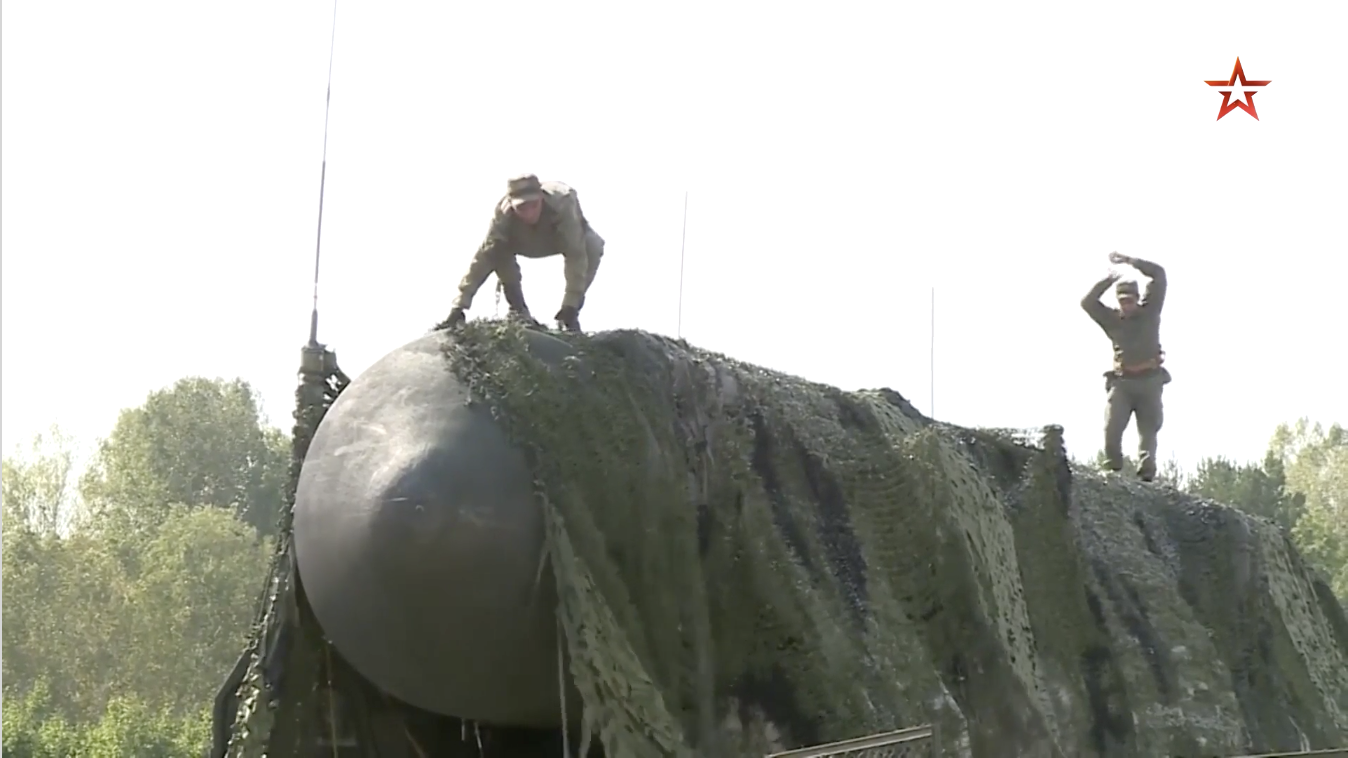
But in September, the Russian Ministry of Defense released a rare video of a command exercise which features mobile SS-27 Mod 2 “Yars-S” ICBMs driving around their base near Novosibirsk.
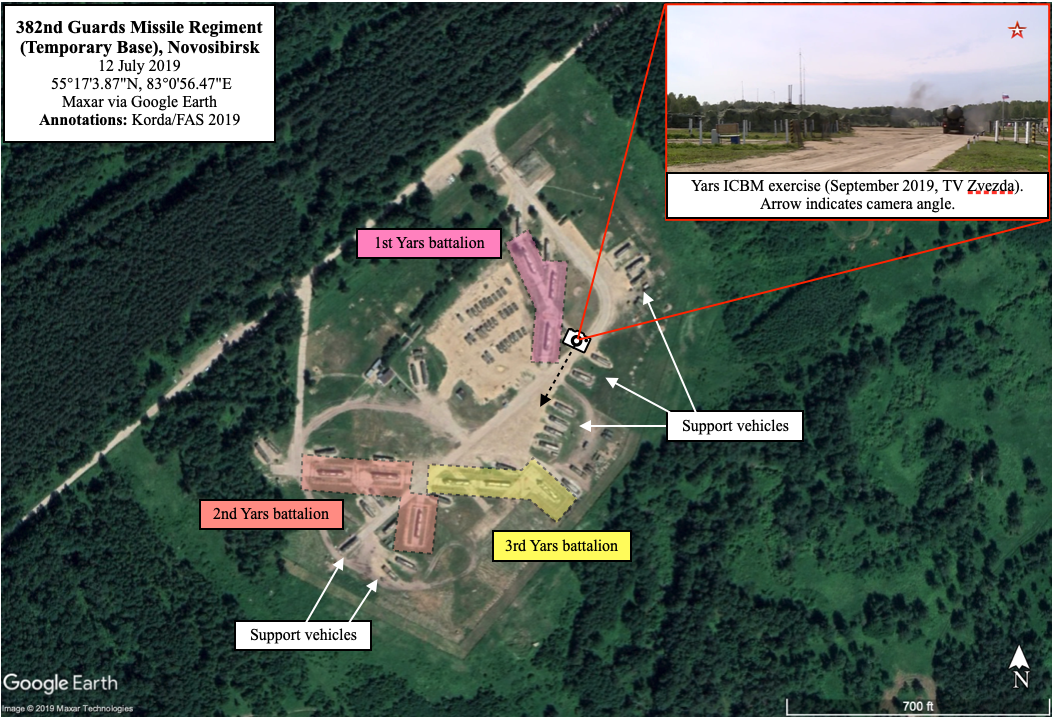
The base itself, which is likely to be the temporary home of the 382nd Guards Missile Regiment, has a relatively strange layout, which makes it significantly easier to identify. Unlike other Yars bases in the 39th Guards Missile Division (which houses the 382nd Regiment)––or even across the region––this base does not have any vehicle garages. Instead, the Yars launchers and support vehicles are simply parked out in the open, usually under camouflage (although they occasionally mix up their camouflage, weirdly replacing the forest green with snowy white well before any snow actually touches the ground!).
The September video shows Russian troops uncovering their ICBMs, taking them out for a spin, and eventually tucking them back in under camouflage blankets.
This regiment––along with the other two Novosibirsk bases associated with the 39th Guards Missile Division––recently completed its long-awaited conversion to Yars ICBMs from its older SS-25 Topol ICBMs. These new missiles are clearly visible in both satellite imagery and in the Ministry of Defense video.
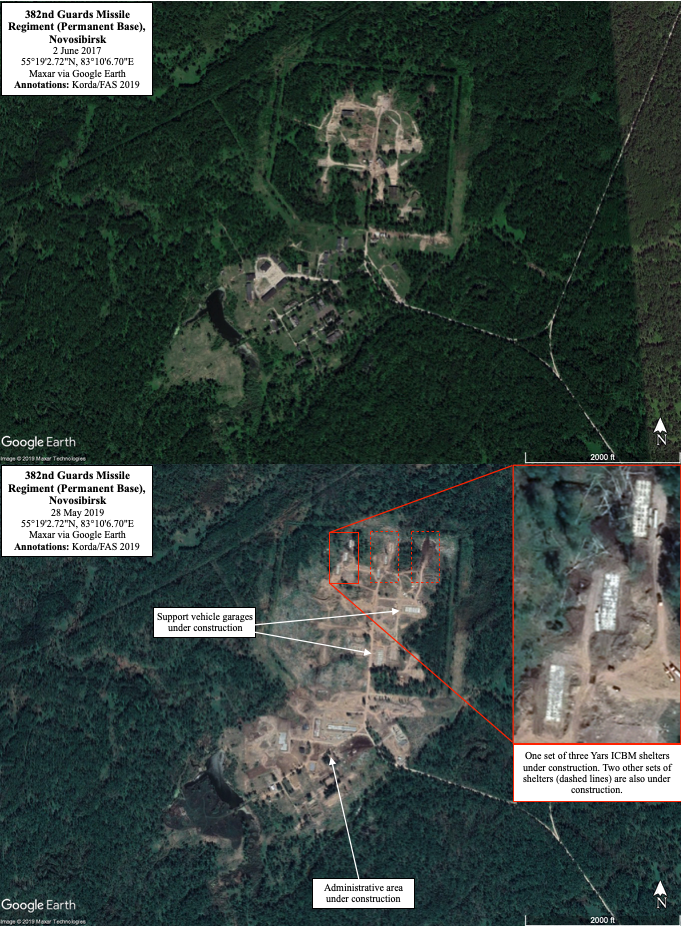
During its conversion, the regiment was moved from its previous base (55°19’2.72”N, 83°10’6.70”E) to this temporary location, while the old base was dismantled in preparation for a substantial upgrade to build new missile shelters for the Yars ICBMs, as well as service and administrative buildings. Construction stalled for several years, possibly because of budget cuts, but has recently picked up again. Once completed, the 382nd Guards Missile Regiment presumably will be relocated back to its old base.
As we write in the Nuclear Notebook, Russia continues to retire its SS-25s at a rate of one or two regiments (nine to 18 missiles) each year, replacing them with newer Yars ICBMs. It is unclear how many SS-25s remain in the active missile force; however, we estimate that it is approximately 54. The remaining two SS-25 equipped divisions will start their upgrades to Yars in 2020, with the SS-25s expected to be fully retired in 2021-2022, according to the commander of Russia’s Strategic Rocket Forces.
Read more about Russia’s nuclear forces in the 2019 Russian Nuclear Notebook, which is always freely-accessible via the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.