B61-12: Contract Signed for Improving Precision of Nuclear Bomb
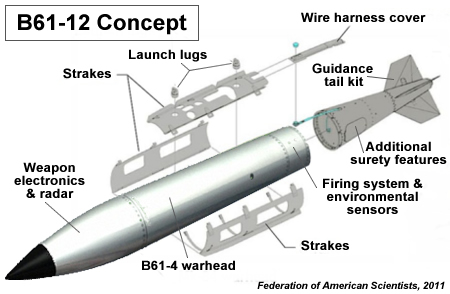 |
| The first contract was signed yesterday for the development of the guided tail kit that will increase the accuracy of the B61 nuclear bomb. This conceptual drawing illustrates the principle of adding a guided tail kit assembly to the gravity bomb. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
The U.S. Air Force’s new precision-guided nuclear bomb B61-12 moved one step closer to reality yesterday with the Pentagon issuing a $178.6 million contract to Boeing. The contract covers Phase 1 (Engineering and Manufacturing Development) to be completed in October 2015. The contract also includes options for a Phase 2 and production.
In a statement on the contract, Boeing said that the tail kit program “further expands Boeing’s Direct Attack weapons portfolio” and that the precision-guided B61-12 would “effectively upgrade a vital deterrent capability.”
The expensive B61-12 project will use the 50-kiloton warhead from the B61-4 gravity bomb but add the tail kit to increase the accuracy and boost the target kill capability to one similar to the 360-kiloton strategic B61-7 bomb.
Because the B61-4 warhead also has selective lower-yield options, the tail kit will also allow war planners to select lower yields to strike targets that today require higher yields, thereby reducing radioactive fallout of an attack. The Air Force tried in 1994 to get a precision-guided low-yield nuclear bomb (PLYWD), but Congress rejected it because of concern that it would lead to more useable nuclear weapons. Now the Air Force get’s a precision-guided nuclear bomb anyway.
The U.S. Air Force plans to deploy some of the B61-12s in Europe late in the decade for delivery by F-15E, F-16, F-35 and Tornado aircraft to replace the B61-4s currently deployed in Europe. The improved accuracy will increase the capability of NATO’s nuclear posture, which will be further enhanced by delivery of the B61-12 on the stealthy F-35 Joint Strike Fighter.
Increasing the capability of NATO’s nuclear posture contradicts the Deterrence and Defense Posture Review (DDPR) adopted in May 2012, which concluded that “the Alliance’s nuclear force posture currently meets the criteria for an effective deterrence and defense posture.” Moreover, improving NATO’s nuclear capabilities undercuts efforts to persuade Russia to decrease its non-strategic nuclear forces.
Instead of improving nuclear capabilities and wasting scarce resources, the Obama administration must re-take the initiative to reduce the role of nuclear weapons and work with NATO to withdraw the nuclear weapons from Europe.
See also: Modernizing NATO’s Nuclear Forces: Implications for the Alliance’s Defense Posture and Arms Control
And: Previous blogs about NATO and nuclear weapons
This publication was made possible by a grant from the Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.