Nuclear Studies and Republican Disarmers
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
A recent report by the Associated Press that the administration is considering deep cuts in U.S. nuclear forces has Congressional Republicans and frequent critics of nuclear reductions up in arms.
The AP report quoted “a former government official and a congressional staffer” saying the administration is studying options for the next round of arms control talk with Russia that envision reducing the number of deployed strategic warheads to 1,000-1,100, 700-800, and 300-400.
Congressional Republicans and right-wing institutions have criticized the administration for preparing reckless unilateral cuts that jeopardize U.S. security.
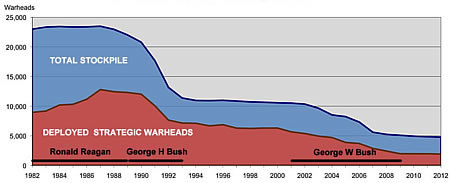
As it turns out, Republican presidents have been the biggest nuclear reducers in the post-Cold War era. Republican presidents seem to have a thing for 50 percent nuclear reductions.
During the George H.W. Bush presidency from 1989-1993, the size of the U.S. nuclear stockpile was cut by nearly 50 percent from 22,217 to 11,511 warheads. The number of deployed strategic warheads dropped from 12,300 to 7,114, or 42 percent, during the same period.
Likewise, during the George W. Bush presidency from 2001-2009, the stockpile was cut by nearly 50 percent from 10,526 to 5,113 warheads. The number of deployed strategic warheads was cut by 65 percent from 5,668 to 1,968 warheads.
A reduction to 1,000-1,100 would be about 30 percent below the New START treaty limit, a drop similar to the 30 percent reduction between the New START treaty and the Moscow Treaty ceiling of 2,200 warheads. A reduction to 300-400 would be a reduction of approximately 77 percent – right up there with the Bush cuts of the past two decades.
Those Bushies must have been reckless liberals in disguise.
Outside Congress, conservative institutions and analysts rally against the administration’s nuclear review saying it’s done in the wrong way, no one will follow, and the U.S. is not modernizing its nuclear forces like other nuclear powers.
A Heritage Foundation blog post mischaracterizes the reduced force levels being studied as “unilateral” cuts and says “there is ample historical evidence” that unilateral reductions will not cause other nuclear powers to follow.
But while there may be no guarantee that other nuclear powers will follow, there certainly is ample historical evidence that they have done so in the past. The unilateral presidential initiative by president George H.W. Bush in 1991 canceled nuclear modernizations, withdrew nonstrategic nuclear weapons from overseas locations and the fleet, retired strategic weapon systems, and stood down bombers from alert with nuclear weapons onboard. The Soviet Union and later Russia followed with significant reductions of their own – reductions that directly benefitted U.S. national security and that of its allies. Britain and France later followed with their own unilateral reductions.
Although I don’t think the current review is about unilateral reductions but about developing potential options for the next round of negotiations with Russia, unilateral initiatives can jumpstart a process by cutting through the fog of naysayers.
The Heritage blog also mischaracterizes the United States as “the only country without a substantial nuclear weapons modernization program.” That’s quite a stretch given that the U.S. has recently converted four SSBNs to carry the Trident II D5 SLBM, has just finished modernizing its Minuteman III ICBM force and replacing the W62 warhead with the more powerful W87, has full-scale production underway of the W76-1 warhead, is preparing full-scaled production of the new B61-12 bomb, is producing a nuclear-capable F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, is studying a new common warhead for ICBMs and SLBMs, is designing a new class of 12 SSBNs, is designing a new long-range bomber, is studying a replacement for the Minuteman III ICBM, and is building new or modernized nuclear weapons production facilities.
That looks like a pretty busy modernization effort to me.
Similarly, an article in The Washington Free Beacon warns that the deepest cut being considered “would leave Pentagon with fewer warheads than China.” Not so. The 300-400 option is for deployed strategic warheads, not the total arsenal. China’s total arsenal includes about 240 warheads, none of which are deployed.
The same article also quotes an unnamed congressional official saying that no president in the past ever told the Pentagon to conduct a review based on specific numbers of warheads. “In the past, the way it worked was, ‘tell me what the world is like and then tell me what the force should be,’” the official said. “That is not happening in this review.”
Well, in this review, as in other reviews intended to reduce nuclear forces, the process begins with the White House asking the Pentagon to examine the options for lower levels. Of course the military is asked to examine implications of a certain range of options; Pentagon reviews have a tendency to be worst-case and the force levels higher than strictly needed. The nice round numbers of arms control treaties are shaped by 1) presidential intent, 2) force structure analysis, and 3) they have to be lower than the previous treaty limit.
During the 1990s, for example, STRATCOM conducted a series of force structure studies in response to – and in anticipation of – future reductions. STRATCOM was created partly to get around the Air Force-Navy rivalry and create a single voice for nuclear force structure analysis. But STRATCOM’s analysis obviously is focused on the needs of the warfighter to meet presidential guidance. As such, there is a tendency to protect force structure and avoid cutting too much too fast. That’s to be expected but it shows that one cannot simply leave it to the military to define what the force should be; it should be an interactive and inter-agency process because the proper nuclear posture is not – and should not be – simply a military matter.
So even if the United States were to cut it’s number of deployed strategic warheads to the lowest number said to be under consideration, those 300-400 warheads would be still more than enough to threaten destruction of Russia. Thousands of additional non-deployed warheads would be in reserve to upload if necessary. Requirements for greater numbers of deployed warheads only emerge when warfighters are asked to use them to hold at risk other nuclear forces, command and control facilities, political and military leadership targets, and war-supporting industry in a myriad of different strike scenarios.
If the administration could convince the Kremlin that it is in Russia’s interest to reduce as well, both countries would be better off.
Further reading:
• “Perspectives on the 2013 Budget Request and President Obama’s Guidance on the Future of the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Program,” briefing to the Fourth Nuclear Deterrence Summit, February 15, 2011.
• “Reviewing Nuclear Guidance: Putting Obama’s Words Into Action,” Arms Control Today, November 2011.
See also: Ivan Oelrich, “Obama’s ‘Radical’ Option for America’s Nuclear Future,” The Atlantic, February 20, 2012.
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.