 |
| Vast inventories of nuclear weapons remain after the Cold War arms race ended. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
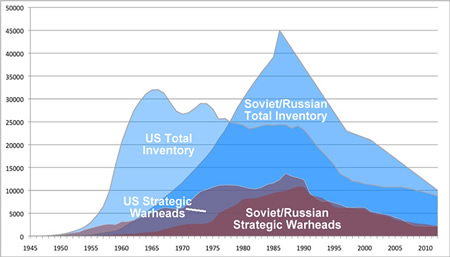
Russia’s nuclear forces are expected to drop well below 500 offensive strategic delivery vehicles within the next five years, less than one-third of what’s permitted by the 1991 START treaty. Unless the next U.S. Nuclear Posture Review significantly reduces the number of land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles, that single leg of the U.S. Triad of nuclear forces alone could soon include more delivery vehicles than the entire Russian strategic arsenal of land- and sea-based ballistic missiles and long-range bombers. With this in mind, Russia is MIRVing its ballistic missile to keep some level of parity with the United States.
This and more from a briefing I gave this morning at the Arms Control Association meeting Next Steps in U.S.-Russian Nuclear Arms Reductions. I was in good company with Ambassador Linton Brooks, the former U.S. chief negotiator on the START treaty, who spoke about the key issues and challenges the START follow-on negotiators will face, and Greg Thielmann, formerly senior professional staffer of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, who discussed how the a new agreement might be verified through START-style verification tools.
Download: Briefing on US-Russian Nuclear Forces
.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.
While advanced Chinese language proficiency and cultural familiarity remain irreplaceable skills, they are neither necessary nor sufficient for successful open-source analysis on China’s nuclear forces.
Satellite imagery has long served as a tool for observing on-the-ground activity worldwide, and offers especially valuable insights into the operation, development, and physical features related to nuclear technology.
This report outlines a framework relying on “Cooperative Technical Means” for effective arms control verification based on remote sensing, avoiding on-site inspections but maintaining a level of transparency that allows for immediate detection of changes in nuclear posture or a significant build-up above agreed limits.