U.S. Nuclear Weapons Withdrawn From the United Kingdom

More than 100 U.S. nuclear bombs have been withdrawn from RAF Lakenheath, the forward base of the U.S. Air Force 48th Fighter Wing. Image: GoogleEarth
The United States has withdrawn nuclear weapons from the RAF Lakenheath air base 70 miles northeast of London, marking the end to more than 50 years of U.S. nuclear weapons deployment to the United Kingdom since the first nuclear bombs first arrived in September 1954.
The withdrawal, which has not been officially announced but confirmed by several sources, follows the withdrawal of nuclear weapons from Ramstein Air Base in Germany in 2005 and Greece in 2001. The removal of nuclear weapons from three bases in two NATO countries in less than a decade undercuts the argument for continuing deployment in other European countries.
Status of European Deployment
I have previously described that President Bill Clinton in November 2000 authorized the Pentagon to deploy 110 nuclear bombs at Lakenheath, part of a total of 480 nuclear bombs authorized for Europe at the time.

US Nuclear Weapons in Europe 2008
President George Bush updated the authorization in May 2004, which apparently ordered the withdrawal of nuclear weapons from Ramstein Air Base in Germany. The withdrawal from Lakenheath might also have been authorized by the Bush directive, or by an update issued within the past three years. This reduction and consolidation in Europe was hinted by General James Jones, the NATO Supreme Commander at Europe at the time, when he stated in a testimony to a Belgian Senate committee: “The reduction will be significant. Good news is on the way.”
Last week I reported that security deficiencies found by the U.S. Air Force Blue Ribbon Review at “most” sites were likely to lead to further consolidation of the weapons, and that “significant changes” were rumored at Lakenheath.
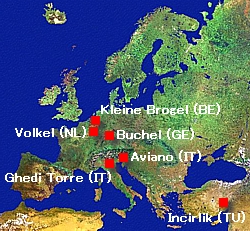
Withdrawal of U.S. nuclear weapons from three European bases since 2001 means that two-thirds of the arsenal is now on the southern flank.
The withdrawal from Lakenheath means that the U.S. nuclear weapons deployment overseas is down to only two U.S. Air Force bases (Aviano AB in Italy and Incirlik in Turkey) plus four other national European bases in Belgium, Germany, Holland and Italy, for a total of six bases in Europe. It is estimated that there are 150-240 B61 nuclear bombs left in Europe, two-thirds of which are based on NATO’s southern flank (see Table 1).
Some Implications
Why NATO and the United States have decided to keep these major withdrawals secret is a big puzzle. The explanation might simply be that “nuclear” always means secret, that it was done to prevent a public debate about the future of the rest of the weapons, or that the Bush administration just doesn’t like arms control. Whatever the reason, it is troubling because the reductions have occurred around the same time that Russian officials repeatedly have pointed to the U.S. weapons in Europe as a justification to reject limitations on Russia’s own tactical nuclear weapons.
In fact, at the very same time that preparations for the withdrawal from Ramstein and Lakenheath were underway, a U.S. State Department delegation visiting Moscow clashed with Russian officials about who had done enough to reduce its non-strategic nuclear weapons. General Jones’ “good news” could not be shared.
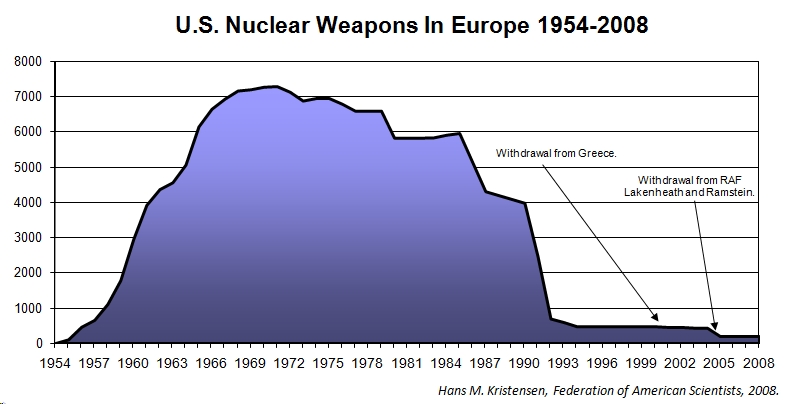
While NATO boasts about its nuclear reductions since the Cold War, the Alliance is more timid about the reductions in recent years.
By keeping the withdrawals secret, NATO and the United States have missed huge opportunities to engage Russia directly and positively about reductions to their non-strategic nuclear weapons, and to improve their own nuclear image in the world in general.
The news about the withdrawal from Lakenheath comes at an inconvenient time for those who advocate continuing deployment of U.S. non-strategic nuclear weapons in Europe. By following on the heels of the withdrawal from Ramstein Air Base in 2004-2005 and Greece in 2001, the Lakenheath withdrawal raises the obvious question at the remaining nuclear sites: If they can withdraw, why can’t we?
What is at stake is not whether NATO should be protected with nuclear weapons, but why it is still necessary to deploy tactical nuclear weapons in Europe. Japan and South Korea are also covered by the U.S. nuclear umbrella, but without tactical nuclear weapons deployed in Asia. The benefits from withdrawing the remaining non-strategic nuclear weapons from Europe far outweigh the costs, risks and political objectives of keeping them there. The only question is: who will make the first move?
Previous reports: USAF Report: “Most” Nuclear Sites in Europe do not Meet US Security Requirements (FAS, June 2008) | United States Removes Nuclear Weapons from German Base, Documents Indicate (FAS, July 2007) | U.S. Nuclear Weapons in Europe (NRDC, 2005)
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.