Most Covid Related Disinformation on Social Media Likely Emanating from Known Influencers and Traditional Media Sources
Key Highlights
- An assessment of the past week’s social media environments indicates traditional media reporting by established news sources such as the New York Times and President Donald J. Trump are most influential by audience reach and volume of engagement.
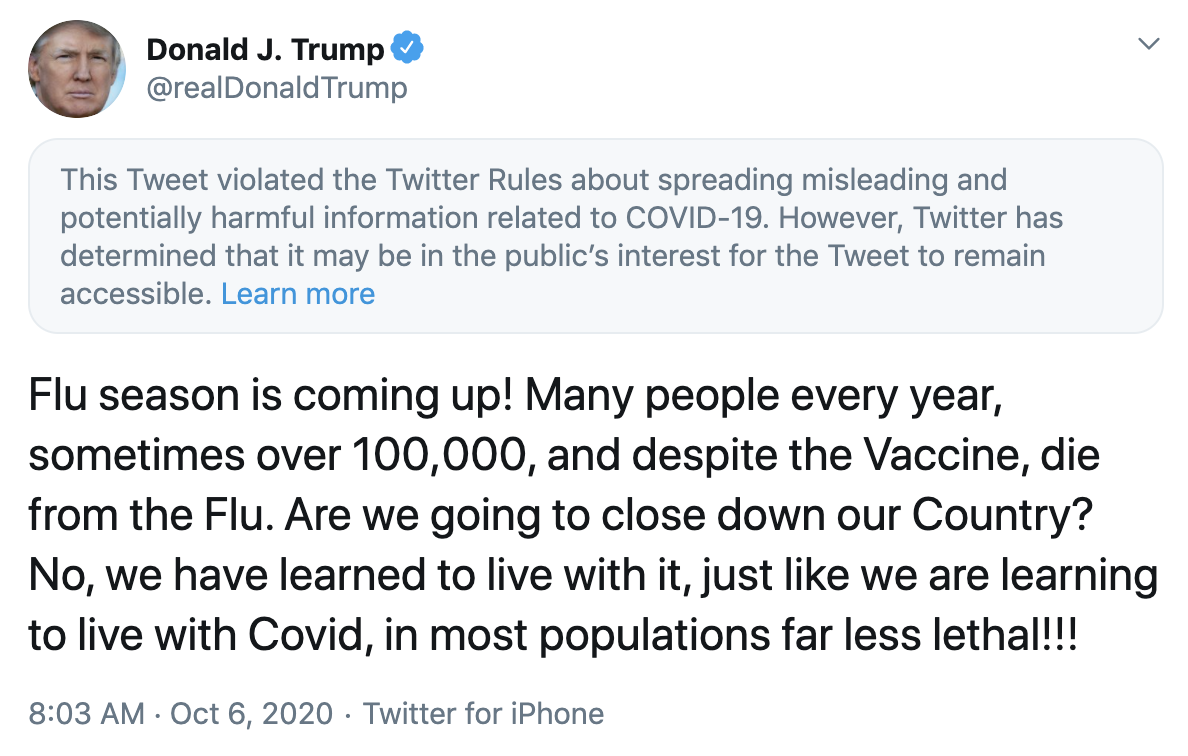
- Donald Trump’s false claim suggesting seasonal flu is comparable to COVID-19 in deaths and lethality had incredibly high reach with an audience of approximately 87M. This same tweet had high audience engagement, amounting to 305K people responding to the message by sharing, liking, or commenting.
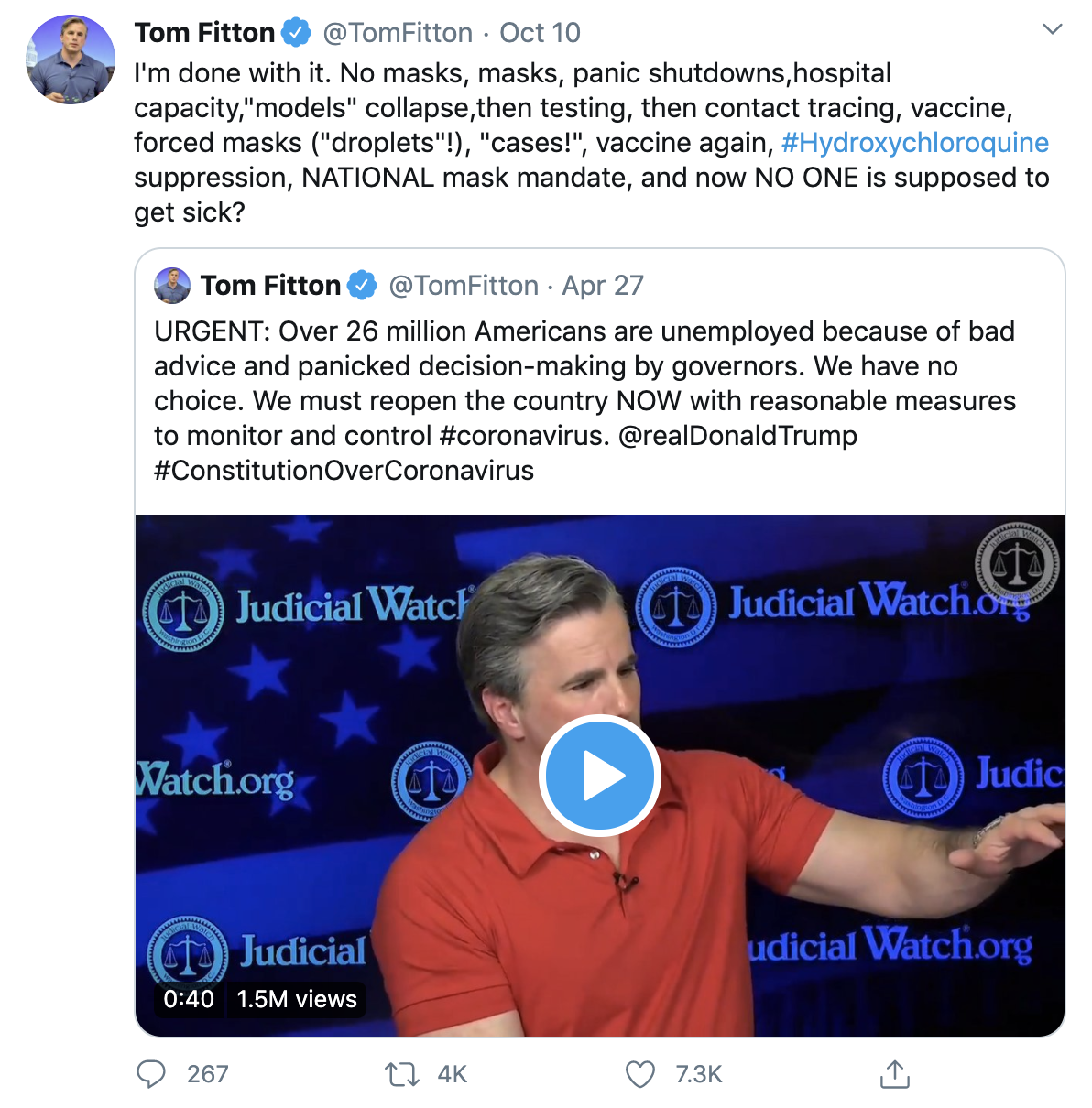
- We also identified a prolific amplifier of disinformation, Tom Fitton, a far right wing conspiracy theorist and climate change denier. In his Tweet, Fitton denounces the use of masks and insinuates the use of hydroxychloroquine is being falsely suppressed. Although the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine has been widely refuted, the narrative that it is an effective treatment persists. A recent false claim by Fitton reached 1.19M people at an audience engagement of 7.5K on Twitter.
Top COVID Related Messages on Social by Reach and Engagement
We conducted an assessment of COVID related messaging on Twitter in the past week (Oct 6th-12th), covering conversations regarding vaccines, masks, treatment, and public health responses. The results indicate traditional media reporting by established news sources such as the New York Times and President Donald J. Trump are most influential by audience reach and volume of engagement. In particular, Donald Trump’s false claim suggesting seasonal flu is comparable to COVID-19 in deaths and lethality had the highest reach of any tweet this week at an audience of approximately 87M. The same tweet had the highest audience engagement, amounting to 305K people responding to the message by sharing, liking, or commenting.
The most significant traditional media posting on Twitter was a New York Times story reporting a substantial shortage of the Regeneron experimental treatment that was administered to President Trump with doses available for only 50,000 patients. This posting had a substantial audience reach of approximately 47.5M; however, it had far less audience engagement compared to influencers with similar reach. This is due to influencer accounts dynamically interacting with their followers compared to the one-way messaging of traditional news sources. Nonetheless, traditional media remains highly influential in spreading both factual and misleading information, as the majority of social media posts share content derived from a linked source typically in the form of a news article.

In our assessment this week, we also identified a prolific amplifier of disinformation, Tom Fitton, a far right wing conspiracy theorist and climate change denier. In his Tweet, Fitton denounces the use of masks and insinuates the use of hydroxychloroquine is being falsely suppressed. Although the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine is widely refuted, the narrative that it is an effective treatment persists. Fitton’s recent false claims ridden tweet reached 1.19M people at an audience engagement of 7.5K.
Methodology
We applied social and traditional media analysis of Twitter across a seven day period covering over 94M Tweets on the topics of vaccines, masks, public health response, and treatments pertaining to COVID-19.
For more about the FAS Disinformation Research Group and to see previous reports, visit the project page here.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.