New Chinese SSBN Deploys to Hainan Island
By Hans M. Kristensen
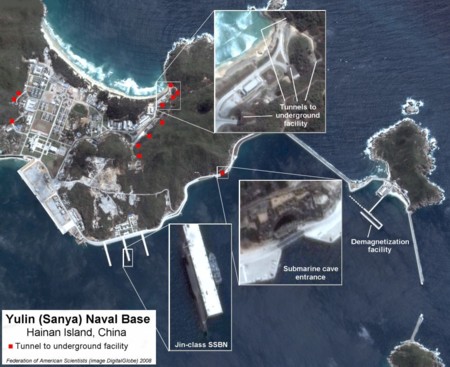
The Chinese navy has deployed a Jin-class (Type 094) ballistic missile submarine to a new base near Yulin on Hainan Island on the South China Sea, according to a satellite image obtained by FAS. The image shows the submarine moored at a pier close to a large sea-entrance to an underground facility.
Also visible is a unique newly constructed pier that appears to be a demagnetization facility for submarines.
A dozen tunnels to underground facilities are visible throughout the base compound.
The satellite image, which has also been described in Jane’s Defense Weekly, was taken by the QuickBird satellite on February 27, 2008, and purchased by FAS from DigitalGlobe.
The Arrival of the Jin-Class Submarine
The dimensions of the submarine in the satellite image are similar to the Jin-class SSBN I spotted at Xiaopingdao Submarine Base in July 2007 and the two Jin-class SSBNs I detected at the Bohai shipyard in October 2007.
China is believed to have launched two Jin-class SSBNs with a third possibly under construction. The U.S. Intelligence community estimates that China might possibly build five SSBNs if it wants to have a near-continuous deterrent at sea. Of course, it is not known whether China plans to operate its SSBNs that way. See Figure 1 for the location of the submarine.
.
Missile loadout of the SSBN will probably take place at pierside at the main pier to the left of the narrow triple-pier where the submarine is seen, unless the underground facility is large enough to permit such operations out of satellite view. Not yet visible at the base is a dry dock large enough to accommodate an SSBN; the Northern Fleet submarine base at Jianggezhuang has a dry dock.
New Demagnetization Facility
One of the most interesting new additions to the base is what appears to be a submarine demagnetization facility (see Figure 2). Located in the southern part of the base and connected by pier to a facility on a small island, the demagnetization facility closely resembles such facilities at U.S. SSBN bases. Demagnetization is conducted before deployment to remove residual magnetic fields in the metal of the submarine to make it harder to detect by other submarines and surface ships. There is no demagnetization facility at the Jianggezhuang base, so this appears to be a new capability for China.
|
Figure 2: |
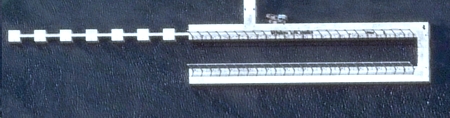 |
| Since 2005, what appears to be a submarine demagnetization facility has been added to the base. Click on image for larger photo. |
.
Underground Facilities
The base has extensive underground facilities. The most obvious is a large portal over a sea-entrance to what is probably an underground facility. The entrance appears to be approximately 3 meters (15 feet) wider than a similar entrance at the Northern Fleet Jianggezhuang Naval Base (see Figure 3 for comparison).
|
Figure 3: |
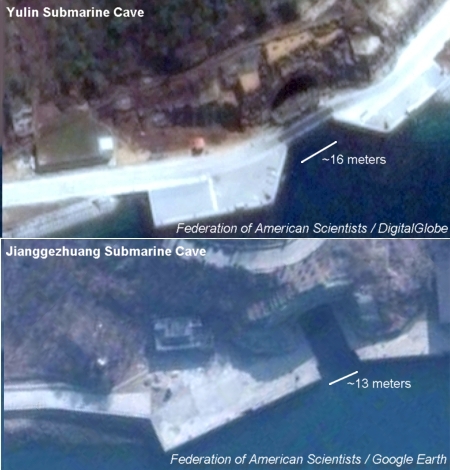 |
| The submarine cave entrance at Yulin Naval Base (top) is approximately 3 meters wider than the one at Jianggezhuang Naval Base. Click on image for larger photo of the Yulin entrance. Description of the Jianggezhuang facility is available here. |
.
Although the interior of the facility is not known, it probably includes a canal at least the length of one submarine as well as halls for handling or possibly storing equipment as well as rooms for personnel. Directly on the other side of the mountain are several land-entrances that might connect to the central facility as well, although none of this is known for sure. Two of those entrances appear from their shadows to be very tall structures (see Figure 4).
.
Some Implications
The SSBN base on Hainan Island will probably be seen as a reaffirmation of China’s ambitions to develop a sea-based deterrent. To what extent the Chinese navy will be capable of operating the SSBNs in a way that matters strategically is another question. China’s first SSBN, the Xia, was no success and never sailed on a deterrent mission. As a consequence, the Chinese navy has virtually no tactical experience in operating SSBNs at sea. Yet the Jin-class and the demagnetization facility on Hainan Island show they’re trying.
The location of the base is important because the Indian government already has pointed to a future threat from Chinese missile submarines operating in the South China Sea or Indian Ocean. The arrival of the Jin-class in Hainan will probably help sustain India’s own SSBN program. For China to sail an SSBN into the India Ocean and operate it there in a meaningful way, however, will be very difficult and dangerous in a crisis. Chinese SSBNs are more likely to stay close to home.
The base on Hainan Island is near deep water and some analysts suggest this will support submarine patrols better that operations from the Northern Fleet base at Jianggezhuang. Of course, if the water is so shallow the submarine can’t submerge fully it will limit operations, but deep water is – contrary to popular perception – not necessarily an advantage. Military submarines generally are not designed to dive deeper than 400-600 meters, so great ocean depth may be of little value. The U.S. navy has several decades of experience in trailing Soviet SSBNs in the open oceans; shallow waters are much more challenging. And the South China Sea is a busy area for U.S. attack submarines, which have unconstrained access to the waters off Hainan Island. And I’d be surprised if there were not a U.S. “shadow” following the Jin-class SSBN when it arrived at Hainan Island.
Additional information: Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning | Chinese Submarine Patrols Rebound in 2007, but Remain Limited | A Closer Look at China’s New SSBNs
This report outlines a framework relying on “Cooperative Technical Means” for effective arms control verification based on remote sensing, avoiding on-site inspections but maintaining a level of transparency that allows for immediate detection of changes in nuclear posture or a significant build-up above agreed limits.
The grant comes from the Carnegie Corporation of New York (CCNY) to investigate, alongside The British American Security Information Council (BASIC), the associated impact on nuclear stability.
Satellite imagery of RAF Lakenheath reveals new construction of a security perimeter around ten protective aircraft shelters in the designated nuclear area, the latest measure in a series of upgrades as the base prepares for the ability to store U.S. nuclear weapons.
It will take consistent leadership and action to navigate the complex dangers in the region and to avoid what many analysts considered to be an increasingly possible outcome, a nuclear conflict in East Asia.