
Ensuring Good Governance of Carbon Dioxide Removal
Climate change is an enormous environmental, social, and economic threat to the United States. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels and other industrial processes are a major driver of this threat. Even if the world stopped emitting CO2 today, the huge quantities of CO2 generated by human activity to date would continue to sit in the atmosphere and cause dangerous climate effects for at least another 1,000 years. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has reported that keeping average global warming below 1.5°C is not possible without the use of carbon dioxide removal (CDR).2 While funding and legislative support for CDR has greatly increased in recent years, the United States does not yet have a coordinated plan for implementing CDR technologies. The Department of Energy’s CDR task force should recommend a governance strategy for CDR implementation to responsibly, equitably, and effectively combat climate change by achieving net-negative CO2 emissions.
Challenge and Opportunity
There is overwhelming scientific consensus that climate change is a dangerous global threat. Climate change, driven in large part by human-generated CO2 emissions, is already causing severe flooding, drought, melting ice sheets, and extreme heat. These phenomena are in turn compromising human health, food and water security, and economic growth.
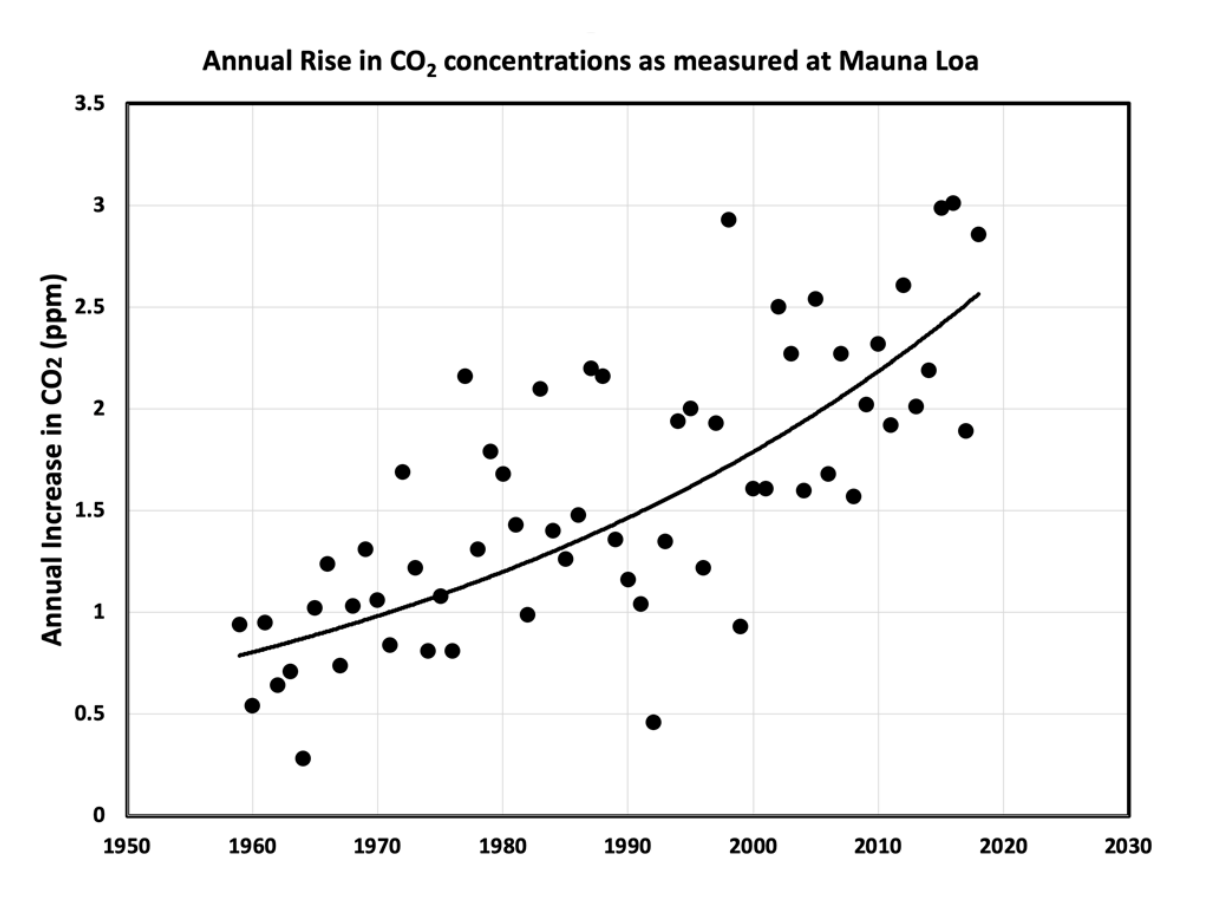
Figure 1. Data collected from observation stations show how noticeably atmospheric CO2 concentrations have risen over the past several decades. (Data compiled by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association; figure by Klaus S. Lackner.)
Morton, E.V. (2020). Reframing the Climate Change Problem: Evaluating the Political, Technological, and Ethical Management of Carbon Dioxide Emissions in the United States. Ph.D. thesis, Arizona State University.
CO2 concentrations are higher today than they have been at any point in the last 3 million years. The contribution of human activity is causing CO2 emissions to rise at an unprecedented rate — approximately 2% per year for the past several decades (Figure 1) — a rate that far outpaces the rate at which the natural world can adapt and adjust. A monumental global effort is needed to reduce CO2 emissions from human activity. But even this is not enough. Because CO2 can persist in the atmosphere for hundreds or thousands of years, CO2 already emitted will continue to have climate impacts for at least the next 1,000 years. Keeping the impacts of climate change to tolerable levels requires not only a suite of actions to reduce future CO2 emissions, but also implementation of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) strategies to mitigate the damage we have already done.
The IPCC defines CDR as “anthropogenic activities removing CO2 from the atmosphere and durably storing it in geological, terrestrial, or ocean reservoirs, or in products.” While becoming more energy efficient can reduce emissions and using renewable energy causes zero emissions, only CDR can achieve the “net negative” emissions needed to help restore climate stability.
Five companies around the world — two of which are based in the United States — have already begun commercializing a particular CDR technology called direct air capture. Climeworks is the most advanced company, and can already remove 900 tons of atmospheric CO2 per year at its plant in Switzerland. Though these companies have demonstrated that CDR technologies like direct air capture work, costs need to come down and capacity needs to expand for CDR to remove meaningful levels of past emissions from the atmosphere.
Thankfully, the Energy Act of 2020, a subsection of the 2021 Consolidated Appropriations Act, was passed into law in December 2020. This act creates a carbon removal research, development, and demonstration program within the Department of Energy. It also establishes a prize competition for pre-commercial and commercial applications of direct air capture technologies, provides grants for direct air capture and storage test centers, and creates a CDR task force.
The CDR task force will be led by the Secretary of Energy and include the heads of any other relevant federal agencies chosen by the Secretary. The task force is mandated to write a report that includes an estimate of how much excess CO2 needs to be removed from the atmosphere by 2050 to achieve net zero emissions, an inventory and evaluation of CDR approaches, and recommendations for policy tools that the U.S. government can use to meet the removal estimation and advance CDR deployment. This report will be used to advise the Secretary of Energy on next steps for CDR development and will be submitted to the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources and the House of Representatives Committees on Energy and Commerce and Science, Space, and Technology.
The Biden administration has clearly shown its commitment to combating climate change by rejoining the Paris Agreement and signing several Executive Orders that take a whole-of-government approach to the climate crisis. The Energy Act complements these actions by advancing development and demonstration of CDR. However, the Energy Act does not address CDR governance, i.e., the policy tools necessary to efficiently and ethically steward CDR implementation. A proactive governance strategy is needed to ensure that CDR is used to repair past damage and support communities that have been disproportionately harmed by climate change — not as an excuse for the fossil-fuel industry and other major contributors to the climate crisis to continue dumping harmful greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The CDR task force should therefore leverage the crucial opportunity it has been given to shape future use of CDR by incorporating governance recommendations into its report.
Plan of Action
The Department of Energy’s CDR task force should consider recommending the following options in its final report. Taken together, these recommendations form the basis of a governance framework to ensure that CDR technologies are implemented in a way that most responsibly, equitably, and effectively addresses climate change.
Establish net-zero and net-negative carbon removal targets.
The Energy Act commendably directs the CDR task force to estimate the amount of CO2 that the United States must remove to become net zero by 2050. But the task force should not stop there. The task force should also estimate the amount of CO2 that the United States must remove to limit average global warming to 1.5°C (a target that will require net negative emissions) and estimate what year this goal could feasibly be achieved. Much like the National Ambient Air Quality Standards enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency, there should be a specific amount of CO2 that the United States should work toward removing to enhance environmental quality. This target could be based on how much CO2 the United States has put into the atmosphere to date and how much of that amount the United States should be responsible for removing. Both net-zero and net-negative removal targets should be preserved through legislation to continue progress beyond the Biden administration.
Design a public carbon removal service.
If carbon removal targets become law, the federal government will need to develop an organized way of removing and storing CO2 in order to reach those targets. Therefore, the CDR task force should also consider what it would take to develop a public carbon removal service. Just as waste disposal and sewage infrastructure are public services paid for by those that generate waste, industries would pay for the service of having their past and current CO2 emissions removed and stored securely. Revenue generated from a public carbon removal service could be reinvested into CDR technology, carbon storage facilities, maintenance of CDR infrastructure, environmental justice initiatives, and job creation. As the Biden administration ramps up its American Jobs Plan to modernize the country’s infrastructure, it should consider including carbon removal infrastructure. A public carbon removal service could materially contribute to the goals of expanding clean energy infrastructure and creating jobs in the green economy that the American Jobs Plan aims to achieve.
Planning the design and implementation of a public carbon removal service should be conducted in parallel with CDR technology development. Knowing what CDR technologies will be used may change how prize competitions and grant programs funded by the Energy Act are evaluated and how the CDR task force will prioritize its policy recommendations. The CDR task force should assess the CDR technology landscape and determine which technologies — including mechanical, agricultural, and ocean-based processes — are best suited for inclusion in a public carbon removal service. The assessment should be based on factors such as affordability, availability, and storage permanence. The assessment could also consider results from the research, development, and demonstration (RD&D) program and the prize competitions mandated by the Energy Act when making its determination. The task force should also recommend concrete steps towards getting a public carbon removal service up and running. Steps could include, for instance, establishing public-private partnerships with prize competition winners and other commercialized CDR companies.
Create a national carbon accounting standard.
The Energy Act directs the RD&D program to collaborate with the Environmental Protection Agency to develop an accounting framework to certify how much carbon different techniques can remove and how long that carbon can be stored. This may involve investigating the storage permanence of various carbon storage and utilization options. This may also involve creating a database of storage lifetimes for CDR products and processes and identification of CDR techniques best suited for attaining carbon removal targets. The task force could recommend to the Secretary of Energy that the framework becomes a standard. A national carbon accounting standard will be integral for achieving carbon removal targets and verifying removal through public service described above.
Ensure equity in CDR.
While much of the technical and economic aspects of carbon removal have been (or are being) investigated, questions related to equity remain largely unaddressed. The CDR task force should investigate and recommend policies and actions to ensure that carbon removal does not impose or exacerbate societal inequities, especially for vulnerable communities of color and low-income communities. Recommendations that the task force could explore include:
- Establishing a tax credit for investing in CDR on private land. This credit would be similar to existing credits for installing solar and selling electricity back to the grid. Some or all of proceeds from the credit should go to help communities previously harmed by environmental injustice (i.e., “environmental justice communities”).
- Launching a CDR technology deployment program that gives environmental justice communities a tax credit or other financial benefit for allowing a CDR technology to be deployed in their communities. This “hosting” compensation would be earmarked for local environmental remediation.
- Incentivizing design of CDR technologies that deliver co-benefits. For instance, planting trees not only helps remove carbon from the atmosphere but also creates shade, provides habitat, and helps mitigate urban heat-island effects. Industrial direct air capture plants can be surrounded by greenspace and art to create public parks.
- Interviewing environmental justice communities to understand their needs and how those needs could be met through strategic implementation of CDR.
Include CDR in international climate discussions.
Because CDR is a necessary part of any realistic strategy to keep average global warming to tolerable levels, CDR is a necessary part of future international discussions on climate change. The United States can take the lead by including CDR in its nationally determined contribution (NDC) to the Paris Agreement. The U.S. NDC most recently submitted in April 2021 does discuss increasing carbon sequestration through agriculture and oceans but could be even more aggressive by including a broader suite of CDR technologies (e.g., engineered direct air capture) and prioritizing pursuit of carbon-negative solutions. The CDR task force could recommend that the Department of Energy work with the Special Presidential Envoy for Climate and the Department of State Office of Global Change on (1) enhancing the NDC through CDR, and (2) developing climate-negotiation strategies intended to increase the use of CDR globally.
Conclusion
Global climate change has worsened to the point where simply reducing emissions is not enough. Even if all global emissions were to cease today, the climate impacts of the carbon we have dumped into the atmosphere would continue to be felt for centuries to come. The only solution to this problem is to achieve net-negative emissions by dramatically accelerating development and deployment of carbon dioxide removal (CDR). As one of the world’s biggest emitters, the United States has a responsibility to do all it can to tackle the climate crisis. And as one of the world’s technological and geopolitical leaders, the United States is well positioned to rise to the occasion, investing in CDR governance alongside the technical and economic aspects of CDR. The CDR task force can lead in this endeavor by advising the Secretary of Energy on an overall governance strategy and specific policy recommendations to ensure that CDR is used in an aggressive, responsible, and equitable manner.
A deeper understanding of methane could help scientists better address these impacts – including potentially through methane removal.
We are encouraged that the Administration and Congress are recognizing the severity of the wildfire crisis and elevating it as a national priority. Yet the devil is in the details when it comes to making real-world progress.
The good news is that even when the mercury climbs, heat illness, injury, and death are preventable. The bad news is that over the past five months, the Trump administration has dismantled essential preventative capabilities.
The Federation of American Scientists supports H.Res. 446, which would recognize July 3rd through July 10th as “National Extreme Heat Awareness Week”.