Calculating the Capacity of Fordow – Updated Issue Brief Posted
by Ivanka Barzashka
We have posted an updated version of our latest Issue Brief “Calculating the Capacity of Fordow” – the technical appendix to our November 23 article “A Technical Evaluation of the Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant” published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
This is the document summary:
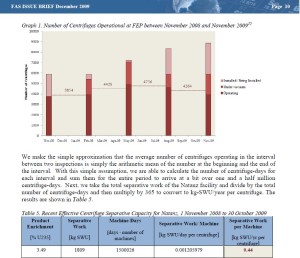
This brief serves as a technical appendix to our November 23 article in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, which premised that Iran’s Fordow enrichment plant is well-sized neither for a commercial nor military program. We concluded that Fordow may be one of several facilities planned. Our estimates of the plant’s capacity are based on current performance of IR-1 centrifuges at Natanz. Underlying our assessment is a calculation of the effective separative capacity per machine of 0.44 kg-SWU/year. This result is based on IAEA data, which we consider as the most credible open-source information on Iran’s nuclear program. Our estimate for the IR-1 performance is significantly lower than values published in the literature, which cannot account for the current performance of Natanz. We argue that, despite Iranian rhetoric, Tehran’s strategic planning for Fordow is based on actual enrichment performance rather than on desired results.
We have made significant layout improvements and have edited the text for clarity. More importantly, we have added detailed explanations on the calculations behind two additional scenarios that we considered in the Bulletin article, namely producing LEU for a commercial reactor from natural uranium and producing a bomb’s worth of HEU from LEU. We have used more precise numbers than the conservative estimates reflected in the Bulletin article, which yield longer timelines and only strengthen our conclusions. Also, version one of the Brief contained numbers only on Fordow’s capability to produce a significant quantity of HEU from natural uranium. This was the only scenario that we have received questions about despite the fact that all three calculations are based on the same premise regarding the effective capacity of the IR-1.
In addition, we have included a section explaining our rationale behind using IAEA’s significant quantity as the amount of uranium required for a bomb. When allowing the Iranians the opportunity to get to a “bomb’s worth” of material faster by assuming less material is needed, one is also assuming a more sophisticated bomb design that will require a longer design phase and will almost certainly require testing, which will be unambiguous. In effect, cutting down on the material production time will result in a longer time to develop a weapon.
We thank everyone for their interest in our work and will address published criticisms directly in an upcoming blog.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.