Retiring Baby Boomers Can Turn Workers into Owners: Securing American Business Ownership through Employee Ownership
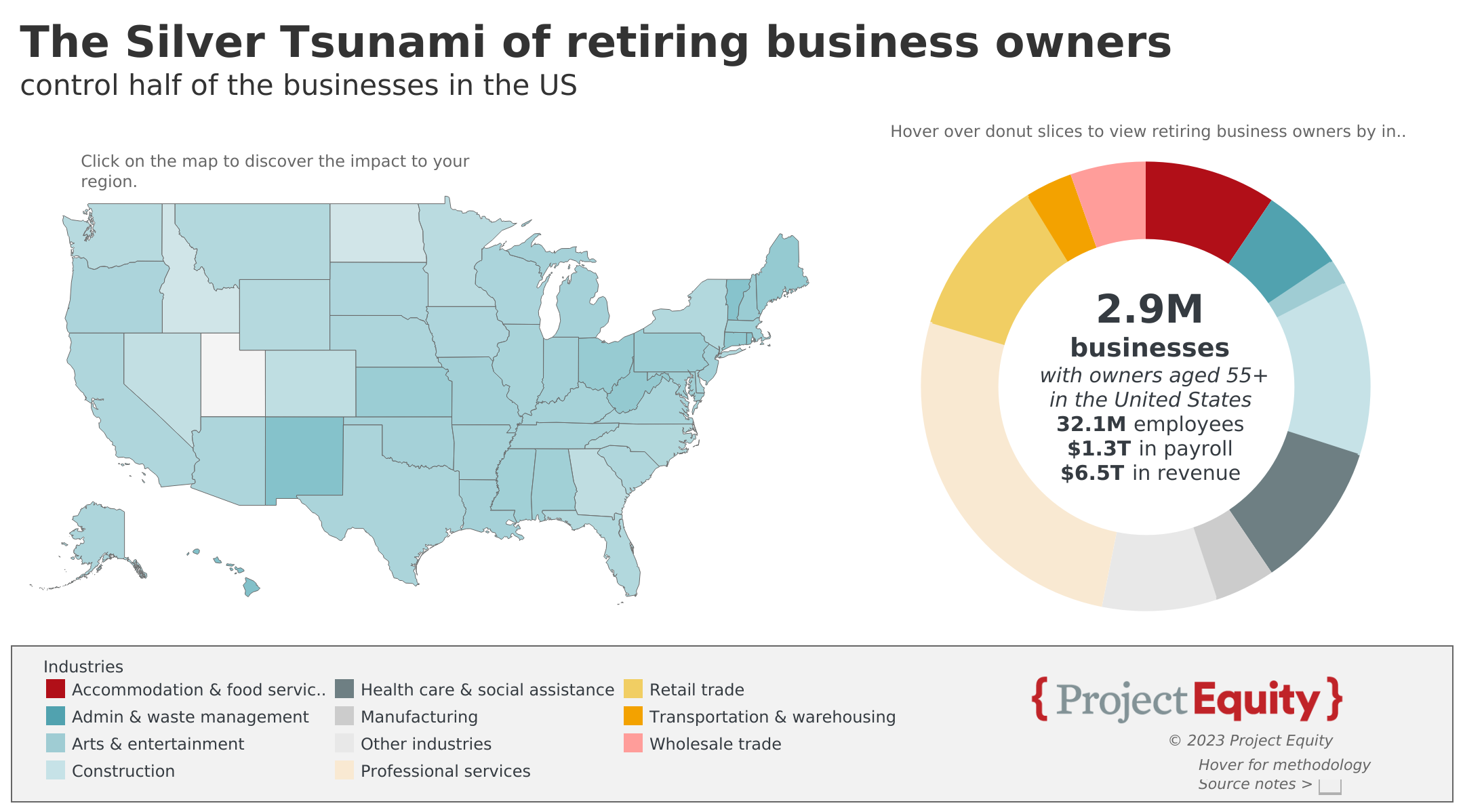
The economic vitality and competitiveness of America’s economy is in jeopardy. The Silver Tsunami of retiring business owners puts half of small businesses at risk: 2.9 million companies are owned by someone at or near retirement age, of which 375,000 are manufacturing, trade, and distribution businesses critical to our supply chains. Add to this that 40 percent of U.S. corporate stock is owned by foreign investors, which funnels these companies’ profits out of our country, weakening our ability to reinvest in our own competitiveness. If the steps to expand the availability of employee ownership were to address even just 10% of the Silver Tsunami companies over 10 employees, this would preserve an estimated 57K small businesses and 2.6M jobs, affecting communities across the U.S. Six hundred billion dollars in economic activity by American-owned firms would be preserved, ensuring that these firms’ profits continue to flow into American pockets.
Broad-based employee ownership (EO) is a powerful solution that preserves local American business ownership, protects our supply chains and the resiliency of American manufacturing, creates quality jobs, and grows the household balance sheets of American workers and their families. Expanding access to financing for EO is crucial at this juncture, given the looming economic threats of the Silver Tsunami and foreign business ownership.
Two important opportunities expand capital access to finance sales of businesses into EO, building on over 50 years of federal support for EO and over 65 years of supporting the flow of small business private capital to where it is not in adequate supply: first, the Employee Equity Investment Act (EEIA), and second, addressing barriers in the SBA 7(a) loan guarantee program.
Three trends create tremendous urgency to leverage employee ownership small business acquisition: (1) the Silver Tsunami, representing $6.5T in GDP and one in five private sector workers nationwide, (2) fewer than 30 percent of businesses are being taken over by family members, and (3) only one in five businesses put up for sale is able to find a buyer.
Without preserving Silver Tsunami businesses, the current 40 percent share of foreign ownership will only grow. Supporting U.S. private investors in the mergers and acquisitions (M&A) space to proactively pitch EO to business owners, and come with readily available financing, enables EO to compete with other acquisition offers, including foreign firms.
In communities all across the U.S., from urban to suburban to rural (where arguably the need to find buyers and the impact of job losses can be most acute), EO is needed to preserve these businesses and their jobs in our communities, maintain U.S. stock ownership, preserve manufacturing production capacity and competitive know how, and create the potential for the next generation of business owners to create economic opportunity for themselves and their families.
Challenge and Opportunity
Broad-based employee ownership (EO) of American small businesses is one of the most promising opportunities to preserve American ownership and small business resiliency and vitality, and help address our country’s enormous wealth gap. EO creates the opportunity to have a stake in the game, and to understand what it means to be a part owner of a business for today’s small business workforces.
However, the growth of EO, and its ability to preserve American ownership of small businesses in our local economies, is severely hampered by access to financing.
Most EO transactions (which are market rate sales) require the business owner to first learn about EO, then to not only initiate the transaction (typically hiring a consultant to structure the deal for them), but also to finance as much as 50 percent or more of the sale. This contrasts to how the M&A market traditionally works: buyers who provide the financing are the ones who initiate the transaction with business owners. This difference is a core reason why EO hasn’t grown as quickly as it could, given all of the backing provided through federal tax breaks dating back to 1974.
More than one form of EO is needed to address the urgent Silver Tsunami and related challenges, including Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs) which are only a fit for companies of about 40 employees and above, and worker-owned cooperatives and Employee Ownership Trusts (EOTs), which are a fit for companies of about 10 employees and above (below 10 is a challenge for any EO transition). Of small businesses with greater than 10 employees, those with 10-19 employees make up 51% of the total; those with 20-49 employees make up 33%. In other words, the vast majority of companies with over 10 employees (the minimum size threshold for EO transitions) are below the 40+ employee threshold required for an ESOP. This underscores the importance of ensuring financing access for worker coops and EOTs that can support transitions of companies in the 10-40 employee range.
Without action, we are at risk of losing the small businesses and jobs that are in need of buyers as a result of the Silver Tsunami.
Across the entire small business economy, 2.9M businesses that provide 32.1M jobs are estimated to be at risk, representing $1.3T in payroll and $6.5T in business revenue. Honing in on only manufacturing, wholesale trade and transportation & warehousing businesses, there are an estimated 375,000 businesses at risk that provide 5.5M jobs combined, representing $279.2B of payroll and $2.3T of business revenue.
Plan of Action
Two important opportunities will expand capital access to finance sales of businesses into EO and solve the supply-demand imbalance created in the small business merger and acquisition marketplace with too many businesses needing buyers and being at risk of closing down due to the Silver Tsunami.
First, passing new legislation, the Employee Equity Investment Act (EEIA), would establish a zero-subsidy credit facility at the Small Business Administration, enabling Congress to preserve the legacy of local businesses and create quality jobs with retirement security by helping businesses transition to employee ownership. By supporting private investment funds, referred to as Employee Equity Investment Companies (EEICs), Congress can support the private market to finance the sale of privately-held small- and medium-sized businesses from business owners to their employees through credit enhancement capabilities at zero subsidy cost to the taxpayer.
EEICs are private investment companies licensed by the Small Business Administration that can be eligible for low-cost, government-backed capital to either create or grow employee-owned businesses. In the case of new EO transitions, the legislation intends to “crowd in” private institutional capital sources to reduce the need for sellers to self-finance a sale to employees. Fees paid into the program by the licensed funds enable it to operate at a zero-subsidy cost to the federal government.
The Employee Equity Investment Act (EEIA) helps private investors that specialize in EO to compete in the mergers & acquisition (M&A) space.
Second, addressing barriers to EO lending in the SBA 7(a) loan guarantee program by passing legislation that removes the personal guarantee requirement for worker coops and EOTs would help level the playing field, enabling companies transitioning to EO to qualify for this loan guarantee without requiring a single employee-owner to personally guarantee the loan on behalf of the entire owner group of 10, 50 or 500 employees.
Importantly, our manufacturing supply chain depends on a network of tier 1, 2 and 3 suppliers across the entire value chain, a mix of very large and very small companies (over 75% of manufacturing suppliers have 20 or fewer employees). The entire sector faces an increasingly fragile supply chain and growing workforce shortages, while also being faced with the Silver Tsunami risk. Ensuring that EO transitions can help us preserve the full range of suppliers, distributors and other key businesses will depend on having capital that can finance companies of all sizes. The SBA 7(a) program can guarantee loans of up to $5M, on the smaller end of the small business company size.
Even though the SBA took steps in 2023 to make loans to ESOPs easier than under prior rules, the biggest addressable market for EO loans that fit within the SBA’s 7(a) loan size range are for worker coops and EOTs (because ESOPs are only a fit for companies with about 40 employees or fewer, given higher regulatory costs). Worker coops and EOTs are currently not able to utilize this SBA product.
The legislative action needed is to require the SBA to remove the requirement for a personal guarantee under the SBA 7(a) loan guarantee program for acquisitions financing for worker cooperatives and Employee Ownership Trusts. The Capital for Cooperatives Act (introduced to both the House and the Senate most recently in May 2021) provides a strong starting point for the legislative changes needed. There is precedent for this change; the Paycheck Protection Program loans and SBA Economic Injury Disaster Loans (EIDL) were made during the pandemic to cooperatives without requiring personal guarantees as well as the aforementioned May 2023 rule change allowing majority ESOPs to borrow without personal guarantee.
There is not any expected additional cost to this program outside of some small updates to policies and public communication about the changes.
Addressing barriers to EO lending in the SBA 7(a) loan guarantee program would open up bank financing to the full addressable market of EO transactions.
The Silver Tsunami of retiring business owners puts half of all employer-businesses urgently at risk if these business owners can’t find buyers, as the last of the baby boomers turns 65 in 2030. Maintaining American small business ownership, with 40% of stock of American companies already owned by foreign stockholders, is also critical. EO preserves domestic productive capacity as an alternative to acquisition by foreign firms, including China, and other strategic competitors, which bolsters supply chain resiliency and U.S. strategic competitiveness. Manufacturing is a strong fit for EO, as it is consistently in the top two sectors for newly formed employee-owned companies, making up 20-25% of all new ESOPs.
Enabling private investors in the M&A space to proactively pitch EO to business owners, and come with readily available financing will help address these urgent needs, preserving small business assets in our communities, while simultaneously creating a new generation of American business owners.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
There are an estimated 7,500+ EO companies in the U.S. today, with nearly 40,000 employee-owners and assets well above $2T. Most are ESOPs (about 6,500), plus about 1,000 worker cooperatives, and under 100 EOTs.
For every 1% of Silver Tsunami companies with more than 10 employees that is able to transition to EO based on these recommendations, an estimated 5.7K firms, $60.7B in sales, 260K jobs, and 12.3B in payroll would be preserved.
Congress and the federal government have demonstrated their support of small business and the EO form of small business in many ways, which this proposed two-pronged legislation builds on, for example:
- Creation of the SBIC program in the SBA in 1958 designed to stimulate the small business segment of the U.S. economy by supplementing “the flow of private equity capital and long-term loan funds which small-business concerns need for the sound financing of their business operations and for their growth, expansion, and modernization, and which are not available in adequate supply [emphasis added]”
- Passage of multiple pieces of federal legislation providing tax benefits to EO companies dating back to 1974
- Passage of the Main Street Employee Ownership Act in 2018, which was passed with the intention of removing barriers to SBA loans or guarantees for EO transitions, including to allow ESOPs and worker coops to qualify for loans under the SBA’s 7(a) program. The law stipulated that the SBA “may” make the changes the law provided, but the regulations SBA initially issued made things harder, not easier. Over the next few years, Representatives Dean Phillips (D-MN) and Nydia Velazquez (D-NY), both on the House Small Business Committee, led an effort to get the SBA to make the most recent changes that benefitted ESOPs but not the other forms of EO.
- Release of the first Job Quality Toolkit by the Commerce Department in July 2021, which explicitly includes EO as one of the job quality strategies
- Passage of the WORK Act (Worker Ownership, Readiness, and Knowledge) in 2023 (incorporated as Section 346 of the SECURE 2.0 Act), which directs the Department of Labor (DOL) to create an Employee Ownership Initiative within the department to coordinate and fund state employee ownership outreach programs and also requires the DOL to set new standards for ESOP appraisals. The program was to be funded at $4 million in fiscal year 2025 (which starts in October 2024), gradually increasing to $16 million by fiscal year 2029, but it has yet to be appropriated.
EO transitions using worker cooperatives have been happening for decades. Over the past ten years, this practice has grown significantly. There is a 30-member network of practitioners that actively support small business transitions utilizing worker coops and EOTs called Workers to Owners. Employee Ownership Trusts are newer in the U.S. (though they are the standard EO form in Europe, with decades of strong track record) and are a rapidly growing form of EO with a growing set of practitioners.
Given the supply ~ demand imbalance of retiring business owners created by the Silver Tsunami (lots of businesses need buyers), as well as the outsized positive benefits of EO, prioritizing this form of business ownership is critical to preserving these business assets in our local and national economies. Capital to finance the transactions is central to ensuring EO’s ability to play this important role.
The SBA 7(a) loan program has been and continues to be, critical to opening up bank (and some CDFI) financing for small businesses writ large by guaranteeing loans up to $5M. In FY23, the SBA guaranteed more than 57,300 7(a) loans worth $27.5 billion.
The SBA 7(a) loan program’s current rules require that all owners with 20% or more ownership of a business provide a personal guarantee for the loan, but absent anyone owning 20%, at least one individual must provide the personal guarantee. The previously mentioned May 2023 rule changes updated this for majority ESOPs.
Just as with the ESOP form of EO, the SBA would be able to consider documented proof of an EO borrower’s ability to repay the loan based on equity, cash flow, and profitability to determine lending criteria.
Research into employee ownership demonstrates that EO companies have faster growth, higher profits, and that they outlast their competitors in business cycle downturns. There is precedent for offering loans without a personal guarantee. First, during COVID, the SBA extended both EIDL (Economic Injury Disaster Loans) and PPP (Paycheck Protection Program) loans to cooperatives without requiring a personal guarantee. Second, the SBA’s May 2023 rule changes allow majority ESOPs to borrow without personal guarantee.
The overlap of the EO transaction value with the $5M ceiling for the 7(a) loan guarantee has the largest overlap with transaction values that are suitable for worker coops and EOTs. This is because ESOPs are not viable below about $750K-$1M transaction value due to higher regulatory-related costs, but the other forms of EO are viable down to about 10 or so employees.
A typical bank- or CDFI- financed EO transaction is a senior loan of 50-70% and a seller note of 30-50%. With a $5M ceiling for the 7(a) loan guarantee, this would cap the EO transaction value for 7(a) loans at $10M (a 50% seller note of $5M alongside a $5M bank loan). If a sale price is 4-6x EBITDA (a measure of annual profit) at this transaction value, this would cap the eligible company EBITDA at $1.7-$2.5M, which captures only the lowest company size thresholds that could be viable for the ESOP form.
Supply chain fragility and widespread labor shortages are the two greatest challenges facing American manufacturing operators today, with 75% of manufacturers citing attracting and retaining talent as their primary business challenge, and 65% citing supply chain disruptions as their next greatest challenge. Many don’t realize that the manufacturing sector is built like a block tower, with the Tier 1 (largest) suppliers to manufacturers at the top, Tier 2 suppliers at the next level down, and the widest foundational layer made up of Tier 3 suppliers. For example, a typical auto manufacturer will rely on 18,000 suppliers across its entire value chain, over 98% of which are small or medium sized businesses. In fact, 75% of manufacturing businesses have fewer than 20 employees. It is critical that we preserve American businesses across the entire value chain, and opening up financing for EO for companies of all sizes is absolutely critical.
The manufacturing sector generates 12% of U.S. GDP (gross domestic product), and if we count the value of the sector’s purchasing, the number goes to nearly one quarter of GDP. The sector also employs nearly one in ten American workers (over 14 million). Manufacturing plays a vital role in both our national security and in public health. Finally, the sector has long been a source of quality jobs and a cornerstone of middle class employment.
Though we aren’t certain the reasoning, it is most likely because ESOPs have the largest lobbying presence. Given the broad support by the federal government of ESOPs through a myriad of tax benefits designed to encourage companies to transition to ESOPs, it is the biggest form of EO, enabling its lobbying presence. As discussed, their size threshold (based on the costs to comply with the regulatory requirements) put ESOPs out of reach for companies with below $750K – $1M EBITDA (a measure of annual profit), which leaves a large swath of America’s small businesses not supported by the SBA 7(a) loan guarantee when they are transacting an employee ownership succession plan.
Likely, the lack of lobbying presence by parties representing the non-ESOP forms of employee ownership has resulted in the rule change not applying to the other forms of broad-based employee ownership. However, the data (as outlined above) clearly shows that worker cooperatives and EOTs are needed to address the full breadth of Silver Tsunami EO need, given the size overlap of loans that fit the size guidelines of the 7(a) loan guarantee and the fit with the form of EO. As such, legislators that are focused on American business resiliency and competitiveness are in the good positions to direct the SBA to mirror the ESOP personal loan guarantee treatment for worker cooperatives and EOTs.
Our analysis of federal AI governance across administrations shows that divergent compliance procedures and uneven institutional capacity challenge the government’s ability to deploy AI in ways that uphold public trust.
To secure the U.S. bio-infrastructure, maintain global leadership in biotechnology, and safeguard American citizens from emerging threats to their privacy, the federal government must modernize its approach to human genetic and biological data.
From use to testing to deployment, the scaffolding for responsible integration of AI into high-risk use cases is just not there.
The Federation of American Scientists supports Congress’ ongoing bipartisan efforts to strengthen U.S. leadership with respect to outer space activities.