Obama Asks UN De-Alerting Resolution to Wait
 |
| President Barack Obama, here shown speaking to the United Nations in September, is seeking to delay a UN Resolution calling for De-Alerting Nuclear Forces. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
The Obama administration has asked four countries to postpone a resolution at the United Nations calling for reducing the alert-level of nuclear weapons.
The intervention apparently is intended to avoid the Obama administration having to vote against the resolution before the important Non-Proliferation Treaty Review Conference in May 2010 — on an issue Barack Obama promised to support when he ran for president.
The resolution, which was last adopted by the U.N. General Assembly with overwhelming support on December 2, 2008, calls for “further practical steps to be taken to decrease the operational readiness of nuclear weapons systems, with a view to ensuring that all nuclear weapons are removed from high alert status.”
Obama’s De-Alerting Pledge
During the presidential election campaign, Barack Obama pledged that as president he would “work with Russia to take nuclear weapons off hair-trigger alert.” This pledge was part of the foreign policy agenda of the Obama for America campaign, and for several months after the election was part of the White House web site:
“The United States and Russia have thousands of nuclear weapons on hair-trigger alert. Barack Obama believes that we should take our nuclear weapons off hair-trigger alert – something that George W. Bush promised to do when he was campaigning for president in 2000. Maintaining this Cold War stance today is unnecessary and increases the risk of an accidental or unauthorized nuclear launch. As president, Obama will work with Russia to find common ground and bring significantly more weapons off hair-trigger alert.”
Apparently Russia has shown little interest in de-alerting, and the pledge has since disappeared from the White House web site and was not mentioned in President Obama’s speech in Prague in April this year.
The Nuclear Posture Review
The Obama administration is more than halfway through a Nuclear Posture Review (NPR) that is analyzing, among other issues, what alert level is appropriate for U.S. nuclear forces in the future.
Currently, virtually all of the 450 Minuteman III land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles are on alert with approximately 500 warheads. Another 96 Trident II sea-launched ballistic missiles with nearly 400 warheads are on alert onboard four of the nine-ten Ohio-class nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines that are at sea at any given time.
Why U.S. national security 20 years after the Cold War ended still depends on the ability to launch nearly 900 nuclear warheads with 12 minutes (actually only four minutes for the ICBMs) is one of the great mysteries the NPR has to answer.
 |
| The EastWest Institute de-alerting report is worth reading. |
The long-range bombers were removed from nuclear alert in 1991 and – despite recent attempts to increase their readiness – will remain off alert with no detrimental impact on U.S. national security.
Reframing Nuclear De-Alert
The EastWest Institute has, with the support of the Swiss and New Zealand governments, just published a highly-recommendable study Reframing Nuclear De-Alert: Decreasing the Operational Readiness of U.S. and Russia Arsenals.
The study, which was briefed to the United Nations yesterday, does a good job of trying to elevate the de-alerting debate from whether or not nuclear alert should be called “hair-trigger alert” to actually considering practical steps for lowering the operational readiness of nuclear forces.
Whether the Obama administration’s request to postpone the U.N. resolution indicates that the NPR will recommend lowering the readiness of U.S. nuclear forces remains to be seen. But it will be truly disappointing if it does not.
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
Pentagon Misses Warhead Retirement Deadline
 |
| Retirement of the W62 warhead, seen here at Warren Air Force Base, has been been delayed. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
The Pentagon has missed the deadline set by the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review for the retirement of the W62 nuclear warhead.
Retirement of the warhead, which arms a portion of the 450 U.S. Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missiles, was scheduled for completion in Fiscal Year 2009, which ended on September 30th.
But the Department of Defense has been unable to confirm the warhead has been retired, saying instead earlier today: “The retirement of the W62 is progressing toward completion.”
The 2001 Nuclear Posture Review decided that, “the W62 will be retired by the end of Fiscal Year 2009.” The schedule was later reaffirmed by government officials and budget documents. But the February 2009 NNSA budget for Fiscal Year 2010 did not report a retirement but a reduction in “W62 Stockpile Systems” – meaning the warhead was still in the Department of Defense stockpile, adding that a final annual assessment report and dismantlement activities will be accomplished in FY2010.
Offloading of the W62 from the Minuteman force has been underway for the past several years. First deployed in 1970, the W62 has a yield of 170 kilotons and is the oldest and least safe warhead in the U.S. stockpile. It is being replaced on the Minuteman III by the 310-kiloton W87 warhead previously deployed on the MX/Peacekeeper missile.
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
State Department Confirms FAS Warhead Estimate
 |
| Retirement of the W62 warhead will be completed in 2009. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
The U.S. State Department has confirmed the estimate made by FAS on this blog in February that the United States had already reached the limit of 2,200 operationally deployed strategic nuclear warheads set by the 2002 Moscow Treaty. The confirmation occurred earlier today in a fact sheet published on the State Department’s web site: “As of May 2009, the United States had cut its number of operationally deployed strategic nuclear warheads to 2,126.”
This is a reduction of 77 warheads from the 2,203 operationally deployed strategic nuclear warheads deployed on February 5, 2009, and probably reflects the ongoing retirement of the W62 warhead from the Minuteman III ICBM force, scheduled for completion later this year.
The total U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile includes approximately 5,200 warheads.
Not Getting It Right: More Bad Reasons to Have Nuclear Weapons
A recently released report, U.S. Nuclear Deterrence in the 21st Century: Getting It Right, by the ad hoc New Deterrent Working Group with a forward by James Woolsey, is an interesting document. I believe this report is significant because it might typify the arguments that will be used against arms control treaties in the upcoming Senate debates.
Much of what is written in support of existing nuclear policies is such a logical muddle that one hardly knows where to start in a critique. As a statement of the pro-nuclear position, this paper is clearer than most so worth addressing. It makes the errors that others do when arguing for nuclear weapons, specifically, making statements about the “requirements” for nuclear weapons that imply missions left over from the Cold War, but the report is particularly blunt in its demands and might serve as a good example of the pro-nuclear arguments. The report is almost seventy pages long, so I can’t touch on every point in a blog and I think I will leave the arguments about nuclear testing for a separate blog to follow.
The report starts out with one fundamental mistake contained in almost every discussion on nuclear weapons: It conflates nuclear weapons with deterrence. Nuclear weapons are so thoroughly equated with deterrence—they are often simply called “the deterrent” —that we seldom stop to think about the details of how this deterrent is supposed to work. What is being deterred, whom, how, for what purpose? If we do not know what nuclear weapons are for, what their missions are, what their targets are, then it is impossible to pin down what their performance characteristics ought to be.
Uncertainty, Reliability, and Safety
The report argues that we need nuclear weapons in part because the world and the future are very uncertain. The report admits no one knows the answers to any of the questions above so the United States simply has to make certain that it has sufficient numbers of nuclear weapons with a variety of capabilities and hope for the best. The problem with this approach is that planning for uncertainty is never finished; we never reach an endpoint. For example, the heading on p. 25, “U.S. nuclear weapons are deteriorating and do not include all possible safety and reliability options” is not only true but always will be true. The “deteriorating” fear has been refuted: parts in weapons age, and these parts are being replaced when needed so the weapons remain within design specifications. This is not cheap or simple but neither is it impossible and can continue for decades. But admittedly, nuclear weapons do not have “all possible safety and reliability options.” There are, no doubt, “options” no one has even thought of yet. So how much reliability and safety is enough? When can we stop?
The answer depends on the missions for nuclear weapons. If nuclear weapons had only the mission of retaliating against nuclear attack, to inflict sufficient pain to make such an attack seem pointless in the first place, then one could plausibly argue that 90% reliability is adequate. If the United States needs to destroy, say, ten targets to inflict sufficient pain to deter, then which ten is not absolutely critical and it could fire at eleven targets and accept that one might escape. Even if the United States wanted to use nuclear weapons to attack and destroy stocks of chemical and biological weapons, it could fire a nuclear weapon at the target and, if one in ten does not go off, it could fire off another bomb an hour later. It is not as though we will not know whether a nuclear bomb actually went off, that will be pretty obvious. If, on the other hand, the United States wants to conduct a surprise, disarming first strike against Russian central nuclear forces, destroying its missiles on the ground, then there is a huge difference whether the attack is 90%, 95%, or 99.9% successful. If the Russians have a thousand warheads, that is the difference between 100, 50, or 1 surviving, obviously significant. So, to say that nuclear warheads need a certain reliability, specifically a high reliability, is to imply certain missions. But these are missions that nuclear advocates rarely want to acknowledge explicitly because they know what a hard sell it will be while “reliability” seems like an obvious, inarguable good quality to have.
What about safety? Certainly we should have nuclear weapons that are as safe as possible and no effort should be spared to make them safer, right? In fact, the Working Group does not agree. The safest nuclear weapons are the ones that do not exist, so ultimate safety calls for nuclear abolition, an option explicitly rejected by the Working Group. If we are going to have actual nuclear weapons, they could be made safer by storing them disassembled. If we need assembled warheads, they could be made safer by removing them from their missiles. Warheads on missiles could be made safer by taking the missiles off alert. All of these options are explicitly rejected by the Working Group. What the report really means when it says we should have “all possible” safety options is that we should fund the National Labs at high levels forever but not change deployments one iota in the interest of safety, hardly my definition of “all possible.”
How Much Is Enough?
The rest of the report makes claims that are unproven and often unprovable and sets requirements for nuclear weapons that sound as though the Cold War never ended. I understand that even in a report of seventy pages not every statement can be fully analyzed and supported but, even so, there are a score of amazing claims for nuclear weapons that are supported mostly by lots of quotes.
The report makes the error of discussing the numbers of nuclear weapons in terms of reductions, specifically since the Cold War (p. 11). All references to reductions imply the Cold War is a benchmark by which current arsenals are measured. But the world has been turned on its head since then and comparison to Cold War numbers is neither relevant nor enlightening. (The Navy also has fewer battleships than it did in World War II. The point is?)
The report states (p. 11), “In a number of cases, a robust American nuclear arsenal has proven to be effective not only in deterring attacks on the United States and its allies from adversaries using weapons of mass destruction.” This may be true but it is very hard to know. Failures of deterrence are obvious but, if some action does not happen, then why did it not happen? Was the action every really considered? Was it considered but rejected for some other reason? Or was it deterred? Arguments about the effectiveness of deterrence are inevitably going to be speculative and based on absence of evidence. As Donald Rumsfeld pointed out while Secretary of Defense, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence. There is no doubt that deterrence is real in many cases, it really works in many cases, but it is very difficult to be certain when and where. We should all (me included) be very cautious when making arguments about deterrence. I believe that general discussions of deterrence almost always go off the rails. When we talk about deterrence, we should at least try to use concrete examples for discussion. In the case of nuclear weapons, going to some example, any example, almost always demonstrates that the arguments in favor of nuclear weapons are simply incredible.
The report states (p. 12), “In short, the available evidence suggests that an American nuclear deterrent that is either qualitatively or quantitatively insufficient will have the effect of encouraging the very proliferation of nuclear forces we seek to prevent.” This might be tautologically true if the definition of “insufficient” is chosen to make it true. But there is no “available evidence” for the simple reason that the “American nuclear deterrent” (note again how nuclear weapons are thoughtlessly referred to as the “deterrent”) has never been anywhere near “insufficient” since 1945. So exactly when was this experiment conducted? Later (p. 51) the reports states, “To the contrary, history has clearly shown that unilateral US reductions, far from causing a similar response, actually stimulate nuclear buildups by adversaries.” What can they be talking about? Russia, Britain, France, and China went nuclear while the U.S. arsenal was expanding or just plain huge. The nuclear arsenal of the United States declined from its peak because of the retirement of thousands of battlefield nuclear weapons made obsolete by modern precision conventional alternatives. Did South Africa, India, Israel, Pakistan, or North Korea really go nuclear because of “unilateral US reductions”? These confident statements are based on a “history” of some parallel universe.
The report asserts that China has “its own extensive military modernization program.” China, with a growing economy is naturally increasing its overall budget but its nuclear ambitions continue to appear quite restrained. Hans Kristensen has written extensively on this.
Hydronuclear Alert
The report asserts that Russia is conducting hydronuclear tests, that is, nuclear weapon tests with very small nuclear yields, tests that the United States would consider in violation of the Comprehensive Test Ban. This is a common claim from pro-nuclear people, based, apparently on highly classified reports that are repeated here in this unclassified document. Some of the authors of the report have or had security clearances so any claim to the contrary is met with “if only you knew what I know.” All I can say is that I have asked people who do know what the authors know and apparently the evidence is unclear, specifically, the United States does not have good enough detection capability to prove that the Russians are not conducting such tests. If the Russians are conducting such tests, and the pro-nuclear lobby has already let the cat out of the bag, the intelligence community should present testimony in Congress confirming the tests. As far as I know, they have not done so. Even so, note that the fuss is about a treaty that the United States has not ratified. Upon ratification, the United States and Russia (and perhaps China) could agree in parallel to place instruments at each other’s tests sites and resolve this ambiguity.
Nuclear Weapons Ready to Fly.
The report advocates, even assumes, an aggressive nuclear stance, with weapons constantly ready to go. For example, (p. 15): “Finally, the continued credibility and effectiveness of the U.S. nuclear deterrent precludes de-mating of warheads on operational systems or otherwise reducing the alert rates or alert status of U.S. forces.” Again, we should apply this general statement to a few concrete examples. First, by arguing against reducing alert rates they are endorsing current alert rates. While the report objects to the term “hair trigger alert,’ U.S. nuclear weapons are, in fact, ready to launch on a few minutes’ notice. At any given moment, many are deployed on submarines off the coast of China and Russia, atop missiles just a few minutes flight time from their targets. Do they really mean that an enemy will not be deterred if these conditions are relaxed? We have to imagine a scenario in which the leader of China, Russia, or maybe North Korea want to use nuclear weapons against the United States but, knowing that they will be hit back 40 minutes later are deterred. Then their head of military intelligence comes in and reports that the American nuclear bombs won’t arrive until eight hours later, or perhaps the next day, or whatever, and as a result the enemy leader says, “Well, in that case, let’s attack.” Perhaps someone else can think of a case in which this is plausible but I cannot.
Later (p. 59), the report does try to give some further justification for high alerts: “They [nuclear weapons] must be known to be ready and useable to have deterrent effect. No START follow-on agreement can be deemed in the national security interest if it would require downgrading of that condition and, thereby, potentially leave the United States vulnerable to coercion based on the threat of second or third strikes before we could respond to an attack.” This actually makes some sense but we have to think about what it really means. It means keeping a constant counterforce attack capability. The statement above says that, if Russia (in the context of START, we are talking about Russia) attacks the United States with nuclear weapons, the next act of the United States should be to attack all remaining Russian nuclear weapons so they can’t do any more damage. That sounds plausible but let’s think this though. The Russians can safely assume the Americans will be more than a little upset after a nuclear bomb has gone off. The Russians will know that their vulnerable weapons could be attacked so they would either disperse their weapons to make them invulnerable or they would use them. It might be that keeping a counterforce capability results in the Russians throwing everything they can throw at the United States in the first wave, actually increasing the damage to the United States in a contest that would otherwise have smaller stakes. I have written elsewhere how high U.S. alert rates make reductions in nuclear forces more difficult for Russia. Moreover, the report completely neglects the costs of high alert rates, not just the financial costs but the risks of accidental nuclear launch, either by the United States or Russia, and the danger of Russian mitigating tactics, and the loss of escalation control. The authors fail to imagine that the United States and Russia might negotiate mutual force postures that include weapons off alert that are mutually invulnerable, creating a much more stable nuclear environment. The authors seem to believe that a Cold War Lite is the only way the world can be. They cannot see over the hill into the next valley.
The report makes a series of other remarkable and unsupportable claims, but I want to address those in a separate blog about nuclear testing.
START Follow-On: What SORT of Agreement?
 |
| Presidents Obama and Medvedev sign a joint understanding on a START follow-on treaty. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
The Joint Understanding for the START Follow-on Treaty signed by President Obama and Medvedev on July 6, 2009, commits the United States and Russia to “reduce their strategic warheads to a range of 1500-1675, and their strategic delivery vehicles to a range of 500-1100.”
Negotiators will still have to hammer out the details and draft a new treaty that the presidents can sign, hopefully by the end of the year, to be implemented in seven years.
The Summit was a good effort to revive U.S.-Russian relations, but seven years is a very long timeline for a START follow-on that doesn’t force either side to change very much. Does it rule out deeper cuts for the rest of the Obama administration?
Perceived and Actual Cuts
Although the actual treaty has yet to be written up, the Joint Understanding indicates that it will be a hybrid between the 1991 START treaty and the 2002 SORT agreement: limits on strategic delivery vehicle and deployed strategic warheads. It adopts the range-limit of the SORT agreement and continues some form of verification regime.
The lower limits of 1,500 strategic warheads and 500 delivery vehicles are meaningless because neither country is prohibited from going lower if it chooses to do so. The only real limit is the upper limit of 1,675 deployed strategic warheads and 1,100 strategic delivery vehicles.
Unfortunately, and this often happens when arms control agreements are covered, the news media has widely misreported what has been agreed to. Here are some examples:
* Washington Post: The agreement would “cut the American and Russian nuclear arsenals by as much as a third” by reducing the “the number of deployed nuclear warheads in each country to between 1,500 and 1,675….”
* Associated Press: The agreement would “slash nuclear stockpiles by about a third….”
* Washington Times: The agreement “would reduce nuclear warheads to between 1,500 and 1,675….”
In fact, the agreement only reduces deployed strategic warheads. It does not affect warheads held in reserve, non-strategic warheads, the size of the total stockpile, nor does it require dismantlement of any nuclear warheads.
The number of warheads in each country is secret and projections fraught with considerable uncertainty, but here is how the proposed START follow-on treaty might affect the nuclear arsenals of Russia and the United States:
Compared with the forces deployed as of 2009, the effect of the START follow-on appears to be a reduction of Russian deployed strategic warheads by approximately 40 percent, and a U.S. reduction of roughly 24 percent. The estimated effect on the total stockpile of either country is more modest: 14 percent fewer warheads for Russia and 10 percent for the United States. But that assumes the warheads cut by the START follow-on treaty would be retired rather than placed in the reserve, something the agreement does not require. The treaty itself requires no change in the size of the total stockpiles.
The reduction to 500-1,100 strategic delivery vehicles represents a significant reduction from the START ceiling of 1,600, at least on paper. In reality, however, the upper limit exceeds what either country currently deploys, and the lower level exceeds what Russia is expected to deploy by 2017 anyway. Therefore, a 500-1,100 limit doesn’t force either country to make changes to its nuclear structure but essentially follows current deployment plans.
The United States currently deploys approximately 798 strategic delivery vehicles; Russia approximately 620. But many of the Russian systems are being retired and not being replaced on a one-for-one basis so the entire force could shrink to less than 400 strategic delivery vehicles by 2016. To put in perspective; that would be less than the United States deploys in its ICBM force alone.
It is clear that claims that the Kremlin got everything while Washington gave away at the store are not accurate. Because Russia deploys more strategic warheads than the United States it also has to reduce more under the new treaty. And even after implementation, the United States will still have more – and better – strategic delivery vehicles than Russia.
So What?
Just like President Bush set a force level of 1,700-2,200 “operationally deployed strategic warheads” before the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review was completed, President Obama has now set what probably will be the overall force level of the ongoing Nuclear Posture Review. Not only will that review cut the number of warheads, it will probably also cut the number of delivery vehicles, perhaps a couple of the SSBNs and some of the ICBMs.
Yet some planners will probably argue against such cuts because Russia is compensating for its lower number of strategic delivery vehicles by deploying more warheads on each missile than the United States. In the minds of some, details like that still matter.
One architect of the Bush administration’s nuclear policy recently argued that the START follow-on agreement is a sellout by the Obama administration because it will “control or eliminate many elements of U.S. military power in exchange for strategic force reductions [Russia] will have to make anyway,” make the United States more vulnerable to a nuclear first strike, and make it harder to direct the nuclear force against other potential adversaries. Another warned that it would right-out “compromise” the U.S. nuclear deterrent.
Such arguments are both well known from the Cold War and out of sync with the 21st Century because they represent a cocooned form of strategic thinking that is preoccupied with Cold War scenarios. It is precisely because Russia is reducing that the United States should also trim its force; anything else will cater to those elements in Russia who want to stop and reverse the reduction. How could such a future possibly be in the interest of the United States or its allies (and, for that matter, Russia)?
And just why a U.S. arsenal of several thousand nuclear weapons would not be able to deter any other realistic adversary – to the extent anything can – is beyond me.
Internally the START follow-on will no doubt help the United States and Russia at the 2010 Review Conference of the Non-Proliferation Treaty. Yet even when the new treaty has been implemented in seven years, the two countries will still possess more than 90 percent of the world’s nuclear weapons, each with over 20 times more weapons than the next-largest nuclear power: China.
What’s Next?
Where does the new agreement fit in? It is explicitly described as a follow-on agreement to START, and U.S. and Russian officials have spoken of a step-by-step process that would initially extend START, produce a follow-on treaty, and also address non-strategic weapons and reserve warheads.
Yet the long timeline of the START follow-on agreement – seven years from the date of signing, five years after the SORT deadline – raises the question of whether this is as deep as they want to go in deployed strategic weapons. Since the limit of 1,100 delivery vehicles liberates either country from having to change their force structure, the agreement could be implemented very quickly – probably in a few months. So why set a timeline of seven years? I hope it does not rule out deeper cuts during even a second Obama administration.
Is the START follow-on the umbrella structure and the other steps – reserve weapons, counting rules, and non-strategic weapons – intended to follow underneath while it is being implemented?
Time will tell, but a couple of clarifying statements from the administration would be helpful.
Background Information: Full Text of Joint Understanding | U.S. Nuclear Forces 2009 | Russian Nuclear Forces 2009
US-Russia Summit Nuclear Weapons Information
 |
By Hans M. Kristensen
Can they do it? Expectations are high for the July Moscow Summit to produce an agreement to extent the START Treaty and commit to additional nuclear weapons reductions in the future. The following provides quick access to information about nuclear weapons numbers:
Overview of World Nuclear Forces
Global Nuclear Stockpiles, 1945-2006
US and Russian Total Nuclear Arsenals:
– Russia
– Briefing slides on history of US and Russian nuclear arsenals
US and Russian Non-Strategic Nuclear Weapons:
– US Nuclear weapons in Europe
– History of US nuclear weapons in South Korea
– Russian Tactical Nuclear Weapons
Other Nuclear Weapon States (Most Recent Overviews):
– France, China, United Kingdom, India, Pakistan, Israel, North Korea
Japan, TLAM/N, and Extended Deterrence
 |
| PACOM Commander Admiral Keating is “unaware” of the Japanese interest in the nuclear Tomahawk cruise missile reported by the Congressional Strategic Posture Commission. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
Admiral Timothy J. Keating, who is Commander of U.S. Pacific Command, said Monday that he is “unaware of specific Japanese interests in the” nuclear-armed Tomahawk Land-Attack Missile.
That’s interesting because the Congressional Strategic Posture Commission recently pointed explicitly to such a Japanese interest in the role that the missile – known as the TLAM/N – provides in extending a U.S. nuclear umbrella over Japan to deter nuclear attacks against it from China and other potential adversaries in the region.
We would expect the commander of Pacific forces to be in close contact with the highest levels of the Japanese government and military. Shouldn’t he be aware of a specific Japanese interest in specific weapons for the U.S. nuclear umbrella? So statements to the contrary in the recent Congressional Commission report seem odd and worth investigating.
The Claims
The final report of the Congressional Commission on the Strategic Posture of the United States of America makes several claims about Japan and the TLAM/N, primarily that:
“extended deterrence [in Asia] relies heavily on the deployment of nuclear cruise missiles on some Los Angeles class attack submarines—the Tomahawk Land Attack Missile/Nuclear (TLAM/N). This capability will be retired in 2013 unless steps are taken to maintain it. U.S. allies in Asia are not integrated in the same way into nuclear planning and have not been asked to make commitments to delivery systems. In our work as a Commission it has become clear to us that some U.S. allies in Asia would be very concerned by TLAM/N retirement.”
Indeed, the report states that the TLAM/N is “primarily relevant to extended deterrence to allies in Asia.”
According to several sources, Japanese government officials provided the Commission with a written list of requirements for the nuclear umbrella. Neither the list not the wording of the Japanese statements are included in the report, which provides the following statement without mentioning Japan by name: “One particularly important ally has argued to the Commission privately that the credibility of the U.S. extended deterrent depends on its specific capabilities to hold a wide variety of targets at risk, and to deploy forces in a way that is either visible or stealthy, as circumstances may demand.”
The U.S. Nuclear Posture in the Pacific
The United States has approximately 300 nuclear-armed TLAM/N, of which about half are stored in igloos at Strategic Weapons Facility Pacific (SWFPAC) near Bangor, Washington (the other half or so are at Strategic Weapons Facility Atlantic (SWFLANT) at Kings Bay, Georgia).
Only about 100 of the TLAM/N warheads are active with limited-life components installed, but none of the missiles are deployed on attack submarines under normal circumstances. Less than a dozen of the 53 U.S. attack submarines are capable of firing the TLAM/N, and although the boats and crews periodically undergo training and inspections to certify them for the mission, they are de-certified again to focus on real-world non-nuclear missions. It would take several months to ready the missiles, recertify the submarines, and deploy the missiles at sea.
The approximately 150 TLAM/N at SWFPAC represent but a fraction of the U.S. nuclear posture in the Pacific, which includes well over 1,000 W76 and W88 warheads for Trident II sea-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) on eight Ohio-class nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) patrolling the Pacific Ocean. Five-six of the eight Pacific SSBNs with an estimated 480-570 warheads onboard are deployed at any given time. Hundreds of additional warheads stored at SWFPAC are available for increasing loading on the SSBNs to an estimated 1,300 warheads if necessary.
| USS Henry M. Jackson (SSBN-730) in Hawaii |
 |
| The nuclear umbrella over Japan is supported by a huge nuclear arsenal in the Pacific region, including SSBNs such as this one that continuously patrol the Pacific and occasionally make their presence known by visiting Hawaii and other Pacific ports. |
In addition to this sea-based force, a portion of the 500 warheads on 450 Minuteman III Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) also cover strike options in the PACOM region, as do B-2 and B-52H bombers with nuclear bombs and cruise missiles. Moreover, F-15Es of the 4th Fighter Wing at Seymour-Johnson Air Force Base in North Carolina have contingency a nuclear strike mission in the Pacific (and elsewhere).
In addition to these nuclear forces, the U.S. Navy is moving 60 percent of its carrier battle groups and nuclear attack submarines into the Pacific. One of these battle groups is even homeported in Japan. Naval exercises in the Pacific are now bigger than even during the Cold War. The Air Force is rotating long-range bomber squadrons to Guam more or less continuously.
Why, given these extensive U.S. forces earmarked for the Pacific region, anyone in Tokyo, Washington, Beijing or Pyongyang would doubt the U.S. capability to project a nuclear umbrella over Japan – or see the TLAM/N as essential – is puzzling. While not all of these warheads are necessarily intended for the defense of Japan per ce, just how many are is probably irrelevant for the purpose of deterrence and assurance. Even if the posture were cut by fifty percent, more than three times the entire Chinese nuclear stockpile would still remain, enough to deter any real-world adversary – to the extent anything can.
The Nuclear Lobby: Articulating a Persuasive Nuclear Mission
So why do we suddenly hear all this talk of Japan being deeply worried about the future of a few hundred TLAM/Ns? After all, nearly all U.S. presidents since Kennedy have called for the elimination of nuclear weapons. As a nuclear target in World War II Japan has always called for the elimination of nuclear weapons, perhaps a little disingenuous given its reliance on the U.S. nuclear umbrella and Japanese officials privately saying that elimination probably wouldn’t happen anyway. Yet the growing international momentum across the traditional political trench-lines for moving convincingly down the nuclear ladder toward zero appears to have caught some in the Japanese government by surprise. Now they suddenly have to think about what it means to move toward zero, and change is always hard.
Another reason appears to be that the end of the Cold War and a growing momentum toward a nuclear free world – even supported by even the presidents of the United States and Russia – have left defense hawks and nuclear proponents on the defensive. Chinese modernization, rogue states, and terrorism haven’t quite been able to sustain the nuclear vigor after the demise of the Soviet threat. In that void, obscure and confidential statements from Japanese and other allied officials about extended deterrence have suddenly become essential tools in an attempt to articulate a persuasive – even positive – enduring role for nuclear weapons. The essence of the message is: nuclear weapons prevent proliferation of nuclear weapons and without them more will come.
It’s tempting to see a collusion. In December 2006, the Defense Science Board (DSB) task force on nuclear capabilities warned that “entrenched views” of arms control advocates had robbed the United States of its “national consensus” on the role of nuclear weapons. The White House and senior leaders had to “engage more directly to articulate the persuasive case” for how modern nuclear weapons serve U.S. national security policy.
After clumsy attempts to get Congressional approval for Complex 2030 and the Reliable Replacement Program backfired and instead caused Congress to ask for a review of nuclear policy, a four-page joint DOD-DOE-State Department statement in July 2007 attempted to articulate one but fell short. And although the loss of control of six nuclear warheads at Minot Air Force Base the following month initially put the nuclear enterprise in doubt, the incident has since become an important vehicle for arguing the case urged by the DSB. During the past 12 months, a series of reports by government agencies and defense institutes have emerged that echo the same basic themes of an enduring role for nuclear weapons, need for modernizations, and continued nuclear threats. The extended deterrence mission underpins these themes:
* September 2008: Schlesinger Task Force Phase I report on the Air Force’s nuclear mission
* September 2008: joint DOD-DOE report on nuclear weapons in the 21st century
* October 2008: Air Force Task Force report on reinvigorating the Air Force nuclear enterprise
* January 2009: Schlesinger Task Force Phase II report on the DOD nuclear mission
* May 2009: Congressional Commission report on the strategic posture of the United States.
These reports, authored by agencies and individuals that are or have been deeply involved in the nuclear business (and many of which “ran the Cold War”), argue for a reaffirmation – even strengthening – of extended deterrence as a “good” and enduring mission for nuclear weapons to prevent proliferation in the 21st Century. They argue that since the U.S. nuclear umbrella is extended to some 30 countries (one report even says 30-plus countries; I can only count 30) it prevents them from acquiring nuclear weapons themselves. Yet for the overwhelming majority of those countries, the function of the extended deterrent is not about nonproliferation but about the ultimate security guarantee. The number of those countries that could potentially be expected to develop nuclear weapons if the U.S. nuclear umbrella disappeared is very small, perhaps a couple, and whether they would actually do so depends on a wide spectrum of factors, most of which have nothing to do with nuclear weapons. Yet the reports paint the role of nuclear weapons as alpha omega.
| James Schlesinger |
 |
| James Schlesinger, who like many other key contributors to recent nuclear studies helped shape Cold War nuclear planning, has been granted a powerful role in articulating post-Cold War policy. |
The September 2008 Schlesinger report describes a “daily” contribution of nuclear weapons, a theme that is echoed by many of the other reports and has been used in testimony before Congress: “Though our consistent goal has been to avoid actual weapons use, the nuclear deterrent is ‘used’ every day by assuring friends and allies, dissuading opponents from seeking peer capabilities to the United States, deterring attacks on the United States and its allies from potential adversaries, and providing the potential to defeat adversaries if deterrence fails.”
One has to be very careful about such nuclear dogma because it quickly can balloon the perceived contribution, mission, and requirements beyond reality. Since the end of the Cold War, which country can we actually say has been deterred by nuclear weapons from attacking anyone, which country has been dissuaded by nuclear weapons from pursuing advanced military capabilities, and which allied or friendly country has been assured by nuclear weapons from pursuing nuclear weapons? This list is very small and the evidence dubious and circumstantial even in the best cases.
Yet the combined effect of these studies and the lobbying that accompany them appears to be setting the tone, at least at the outset, for the Obama administration’s Nuclear Posture Review. Extended deterrence has risen to the top of the agenda and has been assigned to one of only four working groups in the review (International Dimensions), instead of incorporating analysis of that mission into the Policy and Strategy working group like the other missions.
Concluding Remarks
It is impossible to say to what extent Admiral Keating was aware of the public relations battle that is raging on the nuclear extended deterrence front when he gave his answer at the Atlantic Council. I think he was. He certainly looked like he was choosing his words very carefully.
Nuclear advocates and defense hawks appear to be milking the extended deterrence mission for all it’s worth to secure funding for pet projects such as the TLAM/N, a replacement missile, and a nuclear role for the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, capabilities that are not needed. Yet the Congressional Commission report concludes that assuring allies that the U.S. extended deterrent remains credible and effective “may require that the United States retain numbers or types of nuclear capabilities that it might not deem necessary if it were concerned only with its own defense.” Indeed, the Commission said, echoing the January 2009 Schlesinger report, the extended deterrence mission has “design implications for the posture” and nuclear weapons “modernization is essential to the non-proliferation benefits derived from the extended deterrent”.
| Admiral Timothy J. Keating |
 |
| The head of PACOM, Admiral Timothy Keating, says he is “unaware of specific Japanese interest in that particular system” (TLAM/N) described recently by the Congressional Strategic Posture Commission. |
The issue is not whether there should be an extended deterrent or not but what characteristics it needs to have and for what purpose. Nuclear cruise missiles and dual-capable fighter aircraft are characteristics of what nuclear extended deterrence looked like the Cold War, but they might not be necessary or even appropriate today. Long-range systems might be sufficient. Whatever Japanese officials have said about the composition and role of the U.S. nuclear umbrella, there is probably more to the story than meets the eye. Even if some Japanese express a unique value in the TLAM/N – the U.S. military certainly does not share that view – what they say might tell us more about what deterrence literature and Cold War history they have read and which U.S. officials they meet with.
To that end I find it curious that the Japanese government apparently has not brought its alleged interest in the TLAM/N to the attention of PACOM even though that command works with Japanese officials on a daily basis to provide the military capabilities that make up the U.S. security guarantee to Japan. And it is not because PACOM is not aware of their interest in the nuclear umbrella. In the words of Admiral Keating, responding to a question from Miles Pompers from the Center for Nonproliferation Studies:
“As I move around the [PACOM Area of Responsibility]…sooner or later many of the folks with whom we have discussions will get around to asking ‘is your nuclear deterrent umbrella going to continue to extend over’ fill-in-the-blank country? So our capabilities in this area are not taken for granted all throughout our area of responsibility. Everywhere I go, sooner or later – not just in mil-to-mil – the conversation comes up.
I am unaware of specific Japanese interest in that particular system [TLAM/N] you describe. I am, as I said, aware of Japanese interest in the nuclear umbrella.”
It is important for the quality and credibility of the nuclear extended deterrent debate here in the United States and elsewhere to see what the Japanese officials have said and provided, what status and function the officials have within the Japanese government (the Commission report only identifies four individuals from the Japanese embassy in Washington, D.C.), and exactly what they were asked and by whom. The reason is, as all officials know, that questions asked and answers given are always influenced by such factors. It would serve neither the United States nor its allies if the future U.S. nuclear extended deterrence policy and capabilities were to fall victim to bias and special interests.
No U.S. Nukes in South Korea
 |
|
North Korea mistakenly believes there are U.S. nuclear weapons in South Korea. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
The North Korean newspaper Rodong Sinmun reportedly has issued a statement saying the U.S. has 1,000 nuclear weapons in South Korea. In this regional war of rhetoric it is important to at least get one fact right: The United States does not have nuclear weapons in South Korea. It used to – at some point close to 1,000 – but the last were withdrawn in 1991.
The only nuclear weapons the United States has in the Pacific today are the hundreds of warheads deployed on Trident II D5 sea-launched ballistic missiles on board eight Ohio-class nuclear-powered submarines patrolling in the Pacific Ocean. Some of them may be earmarked for potential use against targets in North Korea. Other weapons for bombers could be moved into the region if necessary, but they’re not today.
The North Korean obsession with the U.S. nuclear “threat” might be seen as confirmation that the nuclear deterrent works and hopefully will deter North Korea from attacking anyone. But the flip side of the coin is to what extent the U.S. nuclear posture in the Pacific – past and present – helps feed the North Korean nuclear rhetoric and perhaps even ambitions.
Additional information: A history of U.S. nuclear weapons deployment to and withdrawal from South Korea.
Strategic Failure: Congressional Strategic Posture Commission Report
 |
| The final report from the Congressional Strategic Posture Commission seems focused on hedging rather than leading. |
By Ivan Oelrich and Hans M. Kristensen
The Congressional Strategic Posture Commission report published today is definitely not the place that the President or the nation should look for new ideas on how to reduce the role of nuclear weapons and lead the world toward a world free of nuclear weapons.
Even for a compromise document written by a diverse group, it is a work of deeply disappointing failure of imagination. The recommendations can be summarized as: the nuclear world should stay pretty much the way it is but at slightly lower force levels, incrementalism is the most we can hope for, and even that should be approached very cautiously.
The report comes close to dismissing the President’s vision of a world free of nuclear weapons – and the enthusiastic support it has generated worldwide – as a utopian dream: “The conditions that might make the elimination of nuclear weapons possible are not present today and establishing such conditions would require a fundamental transformation of the world political order.” The United States should retain a viable nuclear deterrence “indefinitely.” The Commission surrenders to the nuclear problems of the world rather than recommending a proactive way forward out of the mess.
Of course, the Commission is not opposed to nuclear reductions per se and supports them under certain conditions, but it recommends that the approach “balances deterrence, arms control, and non-proliferation. Singular emphasis on one or another element,” the report says, apparently hinting at disarmament, “would reduce the nuclear security of the United States and its allies.”
If the Commission’s report is any preview of the Pentagon’s Nuclear Posture Review, we should expect minimal changes in nuclear forces, structure, or mission. The report recommends a nuclear policy of “leading and hedging” but seems to be focused on hedging.
The Nuclear Mission and Deterrence
While President Obama believes the United States should “put an end to Cold War thinking” and “reduce the role of nuclear weapons in our national security strategy, and urge others to do the same,” the Commission offers little support for this approach or analysis of what it would mean.
Indeed, while the report concludes that, “…as long as other nations have nuclear weapons, the U.S. must continue to safeguard its security by maintaining an appropriately effective nuclear deterrent force,” the Commission fails to ask fundamental questions about what nuclear weapons are for and what their character should be. This is probably because there was no consensus on these matters, but better to ask the question and admit they have no answer than to simply state over and over again that nuclear weapons are for “deterrence.” Since some will believe that “appropriately effective” is two thousand nuclear weapons and others think it will be twenty, what does the statement mean?
But it is also an assertion that should be, but is not, challenged. Does this really mean that if North Korea has one nuclear bomb, intended to counter our overwhelming conventional capability, we need to have nuclear weapons to counter it? That may be true but it is certainly not clear to us and should not be asserted as though it needs no explanation. Elsewhere the report says the United States faces decisions about how to reduce “nuclear weapons to the absolute minimum.” Again, two honest people could agree on this goal and differ by a factor of a hundred or a thousand on what an “absolute minimum” is. When the United States had 32,000 nuclear weapons, that was also considered the “absolute minimum” needed for national security.
Without examination of the mission of nuclear weapons, how can we say what their characteristics should be? Even if nuclear weapons are for deterrence, how do they deter? What are their targets? How should those targets be attacked? If we do not answer, or even ask, those questions, how can we say that we need high levels of reliability? How can we say we need land-based missiles that can be launched on a moment’s notice? How can we say we need a vast nuclear weapons complex to design complex two-stage thermonuclear weapons with hundreds of kilotons of yield? There are other examples as well, about reliability, safety, and so on, that presume missions for nuclear weapons that simply should not be presumed.
The Commission acknowledges that it is difficult to replicate the “relatively simple” deterrence calculus of the Cold War, determined by the damage inflicted, in today’s much more complex and fluid security environment. Even so, the report states, the United States still “needs a spectrum of nuclear and non-nuclear force employment options and flexibility in planning along with the traditional requirements for forces that are sufficiently lethal and certain of their result to threaten an appropriate array of targets credibly.” The justification for this sweeping conclusion about capabilities is that “the security environment has grown more complex and fluid.”
As with so many discussions of nuclear weapons, the use of the term “deterrence” in particular is confused and the logic self-referencial. Throughout the report, in too many places to cite, are repeated explicit declarations that nuclear weapons are for deterrence. The report frequently makes the mistake of talking about nuclear weapons and deterrence and then slipping into the error of assuming that deterrence must be nuclear deterrence, or the report makes true statements about deterrence but then implies that the deterrence must be effected with nuclear weapons. It repeatedly refers to our nuclear forces as our “deterrent” or our “deterrent forces” as though they were the same thing. Nuclear weapon designers are maintaining their “deterrent skills.”
In describing the role of deterrence, the Commission glosses over many important developments that have shaped U.S. nuclear policy, strategy, and doctrine over the years. “In a basic sense, the principal function of nuclear weapons has not changed in decades: deterrence. The United States has these weapons in order to create the conditions in which they are never used,” the report declares. Yet we recall hugely important developments ranging from Mutual Assured Destruction, flexible response, adaptive planning, Global Strike, and preemptive strike options, all of which changed the policies and conditions under which the weapons might be used. The report’s more accurate statement would be: “Presidents have not changed their reluctance in decades to authorize use of nuclear weapons.”
Likewise, the report does not describe the important development after the end of the Cold War, where U.S. nuclear targeting policy expanded from Russia and China and their satellite states to deterring all forms of weapons of mass destruction use by six individual countries today (some of which do not have nuclear weapons).
Non-Use and First Strike
One of the most important conclusions in the Commission report is that the “tradition of non-use serves U.S. interests and should be reinforced by U.S. policy and capabilities.” But what that implies for policies and capabilities is not explained.
Even so, the Commission concludes that not only must U.S. nuclear forces be able to retaliate against an attack, “the United States must also design its strategic forces with the objective of being able to limit damage from an attacker if a war begins.” Such damage-limitation capabilities “are important because of the possibility of accidental or unauthorized launches by a state or attacks by terrorists,” and can be achieved “not only by active defenses, such as missile defenses, “but also by the ability to attack forces that might yet be launched against the United States or its allies.”
Such first strike planning might be relevant with conventional forces against rogue states and terrorists, but first strike planning of course can also be used against other nuclear weapon states as it was during the Cold War against the Soviet Union and China. For the Commission to advocate such a mission for nuclear forces today, however, is deeply troubling because it is a primary reason why Russia insists it must have large numbers of nuclear weapons on alert – a dangerous posture that is a direct threat to the interest of the United States or its allies.
Extended deterrence
The Commission report echoes many of the points raised in the Schlesinger report from December last year about extended deterrence and views expressed by officials from some allies about the importance and mission of nuclear weapons. The good news is that the Commission report makes clear that those allies are not all of the same mind concerning the requirements for extended deterrence and assurance, and that substantive and high-level consultations are needed.
But the Commission does not explain the different capabilities that contribute to extended deterrence, but instead equates “extended deterrence” with nuclear weapons and implicitly non-strategic nuclear weapons. This after NATO for almost two decades has insisted that the U.S. non-strategic nuclear weapons deployed in Europe have no military – only a political – role.
The Commission reports that “some allies located near Russia” are saying that “U.S. non-strategic forces in Europe are essential to prevent nuclear coercion by Moscow and indeed that modernized U.S./NATO forces are essential for restoring a sense of balance in the face of Russia’s nuclear renewal.” Yet the Commission does not say that the German foreign minister has called publicly for the withdrawal of the U.S. weapons from Europe, the Belgian Senate has unanimously called for the same, and that the overwhelming majority of Europeans want the weapons to go.
Worst-case analysis is to reference only what is a concern, but that is not the full picture.
The Influence of Russia
After nearly two decades of the Clinton and Bush administrations insisting that Russia is not an adversary and not an immediate contingency for setting U.S. nuclear force levels, the Commission at least admits that Russia largely is what drives U.S. nuclear posturing, saying, “The sizing of U.S. forces remains overwhelmingly driven by the requirements of essential equivalence and strategic stability with Russia.”
In doing so, combined with numerous other references to Russia throughout the report, the Commission essentially reinstates Russia as a central pillar in U.S. nuclear posture planning. The report seems to accept that we are locked in an arms race with Russia and it is surprisingly cautious about how to free ourselves from it. It even concludes that, “the United States should not abandon strategic equivalency with Russia,” because overall equivalence is important to many allies in Europe, and that the “The United States should not cede to Russia a posture of superiority in the name of deemphasizing nuclear weapons in U.S. military strategy.”
While the commission says there is no risk of such an imbalance emerging in strategic weapons in the near-term, the situation is different with non-strategic weapons. The Commission doesn’t know how many Russia has and it can’t say how many the United States has, but while acknowledging that strict U.S.-Russian equivalence in non-strategic force numbers is unnecessary the Commission concludes that the current imbalance is stark and will become apparent as strategic weapons are reduced. This, the report correctly concludes, “points to the urgency of an arms control approach” involving non-strategic weapons.
Overall, the Commission concludes, the United States should “retain enough capacity, whether in its existing delivery systems and supply of reserve warheads or in its infrastructure, to impress upon Russian leaders the impossibility of gaining a position of nuclear supremacy over the United States by breaking out of an arms control agreement.”
Rising China
China looms in the background in many places of the report, reflecting uneasiness among the Commission members about the direction China is taking. But how that direction relates to the U.S. nuclear posture is not analyzed well. Even so, the Commission concludes, in addition to being able to deal with Russian and regional scenarios, the United States “should also retain a large enough force of nuclear weapons that China is not tempted to try to reach a posture of strategic equivalency with the United States or of strategic supremacy in the Asian theater.”
Curiously, the Commission is so concerned about China’s potential nuclear capacity that it urges that Russia – which it is otherwise concerned about – not reduce its nuclear forces too much. This is a mild reversed version of the Reagan administration’s policy that sought China as a nuclear deterrence partner against the Soviet Union.
Therefore…
Based on all of these assumptions (and many more we don’t have room to mention here), the Commission lands on a conclusion that the United States should retain the Cold War nuclear force structure of the Triad. All three legs have unique characteristics that are all needed, the Commission concludes, and because two will be left if one fails, and because “resilience and flexibility of the triad have proven valuable as the number of operationally deployed strategic nuclear weapons has declined.”
Yet the Commission could not come up with a specific force structure or a specific number for the correct size of the U.S. nuclear force, even though it was asked to do so by Congress. The issue is too complex, the authors concluded, and really should be left to deal with by the President in consultation with the military.
The United States should reduce nuclear forces only in bi-lateral negotiations with Russia (and others later), but not pursue unilateral reductions except in reserve warheads — and only if the nuclear warhead production capacity is increased.
Conclusion
In conclusion we were greatly disappointed with the Commission’s report because we see it preoccupied with hedging and failing to offer the leading that is necessary to change status quo.
Indeed, the report seems strangely detached from the President’s vision and the widespread support it and the “gang of four” op-eds have received worldwide.
It would be ironic if the Pentagon’s Nuclear Posture Review ends up recommending bigger changes than the Commission. That shouldn’t be hard.
The task at hand is how to challenge the role of nuclear weapons, we agree with the President, not perpetuate it.
Briefing on US-Russian Nuclear Forces
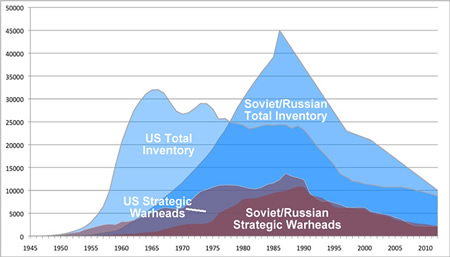 |
| Vast inventories of nuclear weapons remain after the Cold War arms race ended. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
Russia’s nuclear forces are expected to drop well below 500 offensive strategic delivery vehicles within the next five years, less than one-third of what’s permitted by the 1991 START treaty. Unless the next U.S. Nuclear Posture Review significantly reduces the number of land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles, that single leg of the U.S. Triad of nuclear forces alone could soon include more delivery vehicles than the entire Russian strategic arsenal of land- and sea-based ballistic missiles and long-range bombers. With this in mind, Russia is MIRVing its ballistic missile to keep some level of parity with the United States.
This and more from a briefing I gave this morning at the Arms Control Association meeting Next Steps in U.S.-Russian Nuclear Arms Reductions. I was in good company with Ambassador Linton Brooks, the former U.S. chief negotiator on the START treaty, who spoke about the key issues and challenges the START follow-on negotiators will face, and Greg Thielmann, formerly senior professional staffer of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, who discussed how the a new agreement might be verified through START-style verification tools.
Download: Briefing on US-Russian Nuclear Forces
.
Russian Foreign Ministry Responds to FAS/NRDC Study
By Hans M. Kristensen
Russia’s Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs, Sergey Ryabkov, gave a lengthy reaction to the FAS/NRDC report From Counterforce to Minimal Deterrence during a press conference Wednesday.
The transcript from the press conference shows that in response to a question that the “report [is] suggesting a possible retargeting of US missile from Russian cities to key economic facilities,” Ryabkov correctly stated: “I have read the report and think that in the Russian media the thesis mentioned by you was taken our of context. That is not the essence of the report.”
Instead, Ryabkov said correctly described that the report “contains an analysis of the hypothetical consequences of the use of nuclear weapons against large industrial and infrastructure facilities, as well as of what the losses might be in the case of the use of warheads of varying yield.” The rest of Ryabkov’s response is reproduced below:
| Question: The Federation of American Scientists has published a report suggesting a possible retargeting of US missiles from Russian cities to key economic facilities. How can you comment on this?
Sergey Ryabkov: I have read this report and think that in the Russian media the thesis mentioned by you was taken out of context. That is not the essence of the report. It contains an analysis of the hypothetical consequences of the use of nuclear weapons against large industrial and infrastructure facilities, as well as of what the losses might be in the case of the use of warheads of varying yield. It is deplorable and regrettable that the really existing facilities on Russian territory were chosen for such an analytical and speculative work. In my opinion, this evidences the authors’ somewhat detached attitude to the fact that much has changed in Russian-US relations in recent years. Considering Russia as a target for potential use of nuclear weapons is not a good idea. This only adds arguments to those who stick to Cold War thinking. In addition, undoubtedly, the very fact of the appearance of that report bears out our thesis that we cannot approach the question of existing potentials abstractly. Intentions, however positive and constructive today, may change tomorrow. The Federation of American Scientists is perfectly aware of this. And the very fact of the appearance of this material suggests that there needs to be serious negotiation, and that the logic of strategic equilibrium and a super-responsible approach to this sphere cannot be sacrificed to any, even the most constructive political intentions or a general favorable disposition. Intentions and dispositions are very ephemeral magnitudes, and the potentials and capacity to deal a blow, as the Association writes quite cynically and coldly about this in its report, enumerating the exponentially increasing millions of victims and speculating about how many more and what kind of warheads are needed for this knockout, are a wake-up call and a reminder to us that we live in a harsh world, whose realities can’t be disregarded.” |
.
Russian Reactions to Minimal Deterrence Study
If you have followed Russian news media recently, you might have gotten the impression that FAS and NRDC are in charge of U.S. nuclear strike planning and are recommending increasing nuclear targeting of Russia.
Of course, neither is true.
Yet major Russian news media – and apparently also the chairman of the Russia’s parliament’s international affairs committee – have so misread and misrepresented the FAS/NRDC study From Counterforce to Minimal Deterrence that we are compelled to publish this rebuttal.
Pravda Article Gets It Wrong
A Pravda article under the headline “U.S. retargets nuclear missiles to 12 Russian economic facilities” misrepresents the study as saying that the United States has already developed a new doctrine that is “going to retarget their nuclear missiles from large Russian cities to 12 most important economic facilities.”
 |
| The headline and first paragraph of this Pravda article misrepresent what the FAS/NRDC study From Counterforce to Minimal Deterrence actually says. |
.
Rather, our study does not say U.S. nuclear weapons are targeted at Russian cities. In fact, we believe cities are explicitly off-limit to U.S. nuclear strike plans unless vital military targets are present.
Nor does the study conclude it has to be 12 industrial targets. Rather, it includes a nominal list of 12 industrial targets for illustrative purposes.
Nor does the study say the U.S. has developed or is implementing a doctrine to retarget nuclear weapons at Russia’s 12 most important economic facilities. Rather, based on U.S. government documents, which we reference in the study, we estimate that U.S. nuclear strike plans already hold at risk nuclear (and other WMD) forces, command and control facilities, military and political leadership, and war-supporting infrastructure. What we’re proposing is to end nuclear planning against the first three of those target categories and limit the remaining effort – in a transition period toward elimination of nuclear weapons – against a sharply curtailed subset of the fourth target category.
Our correction sent to Pravda has so far been ignored.
|
Konstantin Kosachev Interview |
 |
|
Konstantin Kosachev, the chairman of the International Affairs Committee of the Russia Duma, misrepresents the FAS/NRDC report. |
Duma Committee Chairman Also Gets It Wrong
In an interview with Russia Today, Konstantin Kosachev, who is chairman of the Russian parliament’s international affairs committee, said he had discussed the study with Carl Levin, chairman of the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee, “in the presence of the U.S. ambassador to Moscow.” Their reaction, Kosachev said, “was something like, ‘strange, we should detarget not retarget our missiles’….”
The interviewer then suggested, and Kosachev agreed, that “reports such as this” can have the effect of “scaremongering” people and “derail relations between the United States and Russia.” Kosachev added that, “This type of reports make [Russian hawks who oppose disarmament] even stronger.”
Yet the U.S. nuclear war plan already contains strike options against facilities in Russia (and other countries with WMD) – and it’s surprising if the chairman of the International Affairs Committee is not aware of this. Russia is not an “immediate contingency,” but it’s very much a contingency because of its large numbers of nuclear weapons and history. The recommendations in the FAS/NRDC report would not “retarget” but significantly curtail existing planning.
“Detargeting” is a controversial word that refers to the 1994 bilateral agreement between Russia and the United States (a similar arrangement was made between China and the United States) according to which the two countries pledged not to store targeting coordinates for the other country in their respective missiles. As a result, U.S. Trident SLBMs and Peacekeeper ICBMs were said no longer to store target coordinates in their onboard computers, and the Minuteman III ICBMs, which for technical reasons had to store some coordinates, were targeted on the oceans.
The objective was to avoid an accidental launch of a missile striking the other country. It was a symbolic “detargeting” agreement, not a constraining “nontargeting” agreement, and both countries continue to design and maintain detailed strike plans against each other. Close to 2,000 warheads are on alert, ready to fly within minutes, despite the “detargeting” agreement.
Our report is proposing that we replace that form of planning with a much more constrained policy during the transition period where the United States and Russia figure out how to retain national security without nuclear weapons.
Vice-Chairman of Russian Council Foreign Affairs Committee Also Gets it Wrong
Vasily Likhachyov [Lykhachev], the Vice-Chairman of the Russian Council’s Foreign Affairs Committee told RIA Novosti that our proposal to go to a minimal deterrence posture represents “an infringement on the fundamental principles of international law.” The basis for this assessment apparently was the 1994 detargeting agreement that he said Russia “strictly adheres to,” and that targeting of facilities in Russia demonstrate “disrespect for the soverignty of the Russian Federation.”
Again, the 1994 detargeting agreement is not a nontargeting agreement (see above), but it is particularly interesting if a member of the Russian Council indicates that it would be against international law if the Russian military targeted the United States with nuclear weapons.
Mr. Likhachyov also questioned our calculations of expected casualties from strikes on Russian infrastructure targets arguing that “anyone who knows what a nuclear weapon is also understands that the effect of an atomic explosion spreads over tens and even hundreds of kilometers.”
But as we explain in the report, the selection of “soft” surface targets such as industry allows the Optimum Height of Burst to be set high above the surface, thus avoiding the generation of large amounts of fallout that Mr. Likhachyov appears to assume comes from any nuclear detonation.
Resources: FAS/NRDC Press Release and Full Report
