FDA: COVID-19 vaccine candidates should meet a higher bar for an emergency authorization than other medical products. Trump: Maybe, maybe not.
The disconnect between assurances from federal health and science agencies and President Trump’s words continues. Before Wednesday’s hearing in the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP) Committee, news broke that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has plans to implement special Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) requirements for COVID-19 vaccine candidates. The vaccine EUA requirements proposed by FDA are reported to be more stringent than those for non-vaccine products like hydroxychloroquine or COVID-19 convalescent plasma. FDA Commissioner Hahn alluded to the application of the more stringent standards in his testimony during the hearing, but later in the day the president indicated that his administration may decide to reject the FDA’s proposal.
President Trump may reject FDA COVID-19 vaccine candidate guidelines
On Wednesday, President Trump cast doubt on whether the White House would greenlight FDA’s proposed rules for evaluating COVID-19 vaccine candidates that pharmaceutical companies could submit for approval via the EUA mechanism. An EUA is a temporary clearance for medical products that can be conferred more rapidly and with less documentation than a full approval, which can take six to nine months. Standard EUAs require only that a product “may be effective,” and that the likely benefits to people outweigh the harms. In 2005, the anthrax vaccine was granted an EUA so military personnel considered at high risk of anthrax attack could receive the product, the only instance of an EUA being issued for a vaccine.
Because the vaccine would be administered to a broad population to prevent illness, as opposed to patients suffering from COVID-19, FDA has proposed to strengthen the EUA process. That proposal is now awaiting review in the White House Office of Management and Budget. In a shocking televised press conference, the president characterized the FDA proposal as a “political move.” FDA officials believe a different standard for EUAs for vaccine safety and efficacy, as opposed to EUAs for medical products like hydroxychloroquine (since revoked) and convalescent plasma, is appropriate since vaccines are given to healthy people, not to those who are sick. To earn an EUA, reports indicate the FDA plans to require clinical trial data for COVID-19 vaccine candidates that are close to what is required for a full approval. Specifically, the standards would require monitoring participants in late-stage clinical trials for a median of at least two months, starting after they receive a second vaccine shot (if the vaccine requires two shots), as well as reaching at least five severe cases of COVID-19 in the placebo group for each trial, and some cases of the disease in the elderly. Regardless, any EUA would be based on less safety data than the standard approval track, so clinical trial participants would be monitored well after an EUA, if one were to be issued.
The public will be able to evaluate FDA-reviewed COVID-19 vaccine candidates
As part of its COVID-19 vaccine candidate evaluation process, FDA plans to get the advice of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC), made up of experts in “immunology, molecular biology, recombinant DNA, virology, bacteriology, epidemiology or biostatistics, vaccine policy, vaccine safety science, federal immunization activities, vaccine development including translational and clinical evaluation programs, allergy, preventive medicine, infectious diseases, pediatrics, microbiology, and biochemistry.” These experts are screened for ethical conflicts, and are independent of both the US Government and vaccine-making companies. Notably, the VRBPAC chair recently recused herself from the review of COVID-19 vaccine candidates because she is running Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine candidate clinical trial.
FDA Commissioner Hahn, pressed by Senator Maggie Hassan (D, NH; 2:29:32 mark in video), made it clear that when a vaccine-making company either submits a COVID-19 vaccine candidate application for full approval or requests an EUA, clinical trial data and the FDA summary assessing the data will be provided to VRBPAC as well as to the entire American public. Dr. Hahn also noted that VRBPAC’s discussion, vote, and recommendations will all be public. The public will then have an opportunity to provide comments. FDA will incorporate feedback from VRBPAC into its process, and make a final decision on approval or EUA.
It is important to note, however, that the VRBPAC recommendations are not binding. In other words, the FDA commissioner, Department of Health and Human Services secretary, or possibly even the president have the authority to grant an EUA, irrespective of VRBPAC’s recommendations.
Even so, the opportunity for the entire science and medical community to review COVID-19 vaccine candidate data should help ensure that the public can learn the extent to which COVID-19 vaccine candidates are known to be safe and effective.
The outlook for COVID-19 vaccine availability
At Wednesday’s hearing, Dr. Anthony Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, told the Committee (2:37:41 mark in video) that if all goes well with vaccine-makers’ COVID-19 vaccine candidate clinical trials, that in November, there possibly could be 50 million doses available, about 100 million more doses in December, and roughly 700 million total doses by April. He said that the vaccines will likely be given to healthcare providers and those who are vulnerable due to underlying conditions first. However, Paul Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and a member of VRBPAC, recently told the Washington Post that “It’s hard to imagine how an [emergency use authorization] could possibly occur before December,” indicating the availability of COVID-19 vaccines in November is not certain.
FAS is tracking this situation closely; for an opportunity to contribute to oversight over the COVID-19 vaccine candidate evaluation process, click here.
Additional hearing highlights
Dr. Fauci pushes back on Senator Rand Paul in an exchange about herd immunity
Attention called to head of Operation Warp Speed’s potential conflicts of interest
More than 90 percent of Americans remain susceptible to the coronavirus
To review the entire hearing, click here.
Concerns over political interference in the COVID-19 vaccine candidate evaluation process addressed during Senate hearing
The Oval Office, biopharmaceutical executives, and federal agencies have signaled that COVID-19 vaccines could be ready to go this fall; however, leading experts believe that proof of a safe and effective vaccine before Election Day is unlikely. President Trump has said that “we can probably have [a COVID-19 vaccine] sometime in October.” Pfizer and BioNTech executives think they could know whether their joint COVID-19 vaccine candidate works by the end of October, and that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will grant it an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) wants states ready to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as late October, with distribution sites operational by November 1st. While it is certainly important to be primed to distribute life-saving vaccines, a more realistic scenario is that thorough analyses determining the safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine candidates should be possible at the very end of this year, or beginning of next year.
Nevertheless, extremely optimistic COVID-19 vaccine approval timelines that converge with Election Day are being broadcast to the American public, and during Wednesday’s Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions (HELP) Committee hearing, lawmakers demanded assurances that scientific data, not political agendas, will drive the COVID-19 vaccine approval process.
The path forward for phase III COVID-19 vaccine candidates
Three COVID-19 vaccine candidates that could be made available to Americans are currently in phase III clinical trials, and their paths forward rely on the actions that are taken by the vaccine-makers, FDA, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS, FDA’s parent agency), and the President.
Whereas vaccine candidate clinical trials have historically been designed and executed by biopharmaceutical companies alone, COVID-19 vaccine candidate trials have been overseen by the US Government. To gauge if any of the vaccine candidates prevent or decrease the severity of disease with at least 50 percent efficacy – the bar FDA set at the end of June – tens of thousands of people are being enrolled in each COVID-19 vaccine candidate phase III clinical trial. In fact, on Saturday, Pfizer proposed to FDA that it enroll up to 44,000 participants, almost 50 percent more than the initial target of 30,000. Half are dosed with the vaccine candidate, the other half are dosed with placebo, and, to prevent bias, only a select group of experimentalists – not the trial participants, not the professionals administering the doses – know who gets what. During Wednesday’s hearing, Dr. Francis Collins, the director of the National Institutes of Health, asserted (2:26:10 mark in video) that once 150 people in the entire trial have developed symptomatic disease, it should be possible to determine whether a vaccine candidate is 50 percent effective. However, some experts say that even the point at which the trial reaches 150 cases of disease is unlikely to provide enough time to prove vaccine candidate safety.
Each individual COVID-19 vaccine candidate trial is tracked by a unique Data Safety and Monitoring Board (DSMB). DSMBs are multidisciplinary groups, independent of both the vaccine-maker and the federal government, composed of clinical trials specialists, biostatisticians, bioethicists, immunologists, vaccinologists, and virologists. As trials progress, DSMBs regularly review the data as they accumulate, and make recommendations to the company and to FDA about whether a vaccine has met safety and efficacy standards. Ultimately, DSMBs are only advisory groups, and it is up to the company as to whether it submits a Biologics License Application (BLA) to FDA for their COVID-19 vaccine candidate.
FDA will review the clinical trial data in the BLA for safety and efficacy. Following FDA’s review, the company and the FDA have the option of presenting their findings to FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC), another expert body independent of both the federal government and the vaccine-maker. If consulted, VRBPAC would provide advice to FDA regarding the safety and efficacy of the vaccine. Regardless, FDA could then approve or deny the vaccine candidate for use.
Alternatively, a vaccine-maker could request an EUA from FDA, which opens up the possibility of a vaccine being approved for use before the conclusion of the clinical trial, which could complicate the trial’s full evaluation of safety and efficacy. Another tool FDA could possibly use is Accelerated Approval, a process that could base vaccine approval only on antibody levels or another surrogate biochemical marker produced in trial participants, rather than measuring actual protection from disease. Notably, HHS, or possibly President Trump, could even overrule an FDA rejection of a request for an EUA.
Dr. Anthony Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, believes there would be a moral obligation to end a trial early and make a vaccine accessible if the data from the trial were to be overwhelming that the vaccine candidate is safe and effective.
Federal officials testify that COVID-19 vaccine decisions will be based only on science
During the hearing, Senator Bernie Sanders (D, VT) pressed (1:14:27 mark in video) the witnesses to affirm that the COVID-19 vaccine approval process will only be driven by science. Dr. Collins pledged that he and all US Government scientists will be basing COVID-19 vaccine candidate evaluations and assessments only on science, or else he would have no part in the process. He also expressed cautious optimism that the US will produce a safe and effective vaccine by the end of the year, adding “certainly to try to predict whether it happens on a particular week before or after a particular date in early November is well beyond anything that any scientist right now could tell you and be confident that they know what they’re saying.”
Vice Admiral Jerome Adams, the US Surgeon General, concurred with this sentiment, stating that a COVID-19 vaccine will not be moved along unless it is proven to be safe and effective, that shortcuts will not be taken, and that once approved or authorized by FDA, he and his family would not hesitate to receive the vaccine.
Will words translate into action as Election Day approaches?
Dr. Collins and Vice Admiral Adams are not the only ones giving assurances that science, not political influence, will drive COVID-19 vaccine approval. Career civil servants at FDA reiterated their resolve to working “with agency leadership to maintain FDA’s steadfast commitment to ensuring our decisions will continue to be guided by the best science.” The head of Operation Warp Speed (the US effort to accelerate COVID-19 vaccine development), Dr. Moncef Slaoui, says he will “immediately resign if there is undue interference in this process.” And nine COVID-19 vaccine-making companies have pledged to “uphold the integrity of the scientific process as they work towards potential global regulatory filings and approvals of the first COVID-19 vaccines.”
We will be tracking this issue closely as Election Day nears, and will be sure to alert the community to new developments. To review the entirety of this week’s hearing, click here.
Senate Commerce Committee homes in on consumer protection and enforcement in an era of rampant COVID-19-related scams
Consumer protection and data privacy have come into focus on Capitol Hill over the past few weeks. One week after the leaders of Apple, Google, Amazon, and Facebook testified in front of the House Judiciary Committee, the Senate Commerce Committee held a hearing with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) on this topic. The FTC aims to protect consumers and businesses from “anticompetitive, deceptive, and unfair business practices through law enforcement, advocacy, and education.” The hearing, titled “Oversight of the Federal Trade Commission” focused on the rise in online scams during the COVID-19 pandemic and how to make it easier for the FTC to protect consumers. The senators’ discussion with the FTC chair and commissioners was informed by expert questions provided by the Day One Project, a science and technology policy project that is developing policy proposals for the next Administration. These questions focused on how the FTC plans to keep up with the consumer risks brought by rapidly changing technology, especially from the major tech companies, and risks brought on by scams from current events, such as the pandemic.
There are numerous scams related to COVID-19 and they can be hard to detect. They range from price gouging and selling defective products to people pretending to be contact tracers, those who claim to provide “miracle” cures, and callers pretending to be from the U.S. government. According to the FTC, these pandemic-related scams have cost Americans over $13 million this year and this number is only growing. Out of the 100 million phishing emails blocked by Google each day, it is estimated that about 18 million of them reference the coronavirus. Others attempt to market products that claim to cure COVID-19, like colloidal silver (tiny silver particles suspended in a liquid), which are actually harmful to one’s health.
To combat these scams, the FTC has produced detailed guidance for businesses and consumers. However, enforcement of consumer protection rules can be challenging. Specifically, the FTC’s regulations have not kept up with an evolving internet landscape and scams take advantage of this. Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter acknowledged (1:21:08) that, especially in cases of price gouging, the FTC’s current oversight abilities are an “imperfect tool.”
Typically when a business or individual is caught using predatory tactics on consumers, the FTC sends out a warning letter. The goal of these letters is to notify the business or individual that they are violating consumer protection rules in the Federal Trade Commission Act. They also threaten legal consequences, such as a federal lawsuit, if the predatory behavior continues. The FTC has sent hundreds of letters to companies making misleading claims about COVID-19 treatments and cures, including those pushing treatments with ozone, vitamin C, 5G shields, and ultraviolet light. FTC Chair Joe Simons notes (1:49:25) that these letters tend to be effective. However, Senator Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) expressed (1:50:35) how it would be easier to combat scams if there was a judgement on the books after the first instance of predatory behavior instead of having to wait until the second occurrence to implement harsher punishments.
Through its work in this area, the Day One Project emphasized that FTC’s penalty structure may not provide proper incentives to deter businesses from engaging in predatory tactics or unfair practices in consumer privacy and protection. Experts working with the Day One Project suggested that new regulations could help. During the hearing, Chair Simons and Commissioner Noah Philips agreed and explained (1:32:50 and 2:34:15, respectively) that allowing the FTC to have targeted rulemaking capabilities and the ability to levy civil penalties can help combat scams and protect consumers’ data. This rulemaking authority would allow the FTC, according to Chair Simons, to change its definitions to “account for changes in technology and changes in business methods.”
While this targeted rulemaking authority would need to be passed by Congress, the members of the committee were receptive to the idea. The consumer protection and data privacy landscape is changing rapidly over time and businesses taking advantage of an unprecedented pandemic threaten the security and wellbeing of consumers every day. It is clear from this hearing that FTC is trying its best to combat these threats but needs more help to do so. Input from forward-leaning organizations like the Day One Project are vital to ensure that Congress is informed about the most pressing issues and has the tools it needs to solve them. This will likely not be the last hearing on this topic and the Congressional Science Policy Initiative encourages its readers to get involved in the policymaking process to help Congress protect citizens from predatory business practices.
More information can be found about the Day One Project here: https://www.dayoneproject.org/about.
To get involved with science policy and the U.S. Congress, sign up here: https://fas.org/congressional-science-policy-initiative/.
Hopes are high for safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines to be available in the fall, but the specter of political pressure looms
Come Tuesday, November 3rd – Election Day – Americans will exist in one of two realities: One reality in which COVID-19 vaccines deemed safe and effective are available to the electorate, or a different reality in which vaccines are still unavailable. Biopharma companies are optimistic their COVID-19 vaccines could be available as early as the fall. At the same time, Congress is concerned political interference from the White House could result in the approval of substandard vaccines. This tension was on full display at yesterday’s House Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations hearing featuring leaders from COVID-19 vaccine-makers AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson (J&J), Merck, Moderna, and Pfizer.
The prospect of political interference in COVID-19 vaccine availability
If all goes well, there could be millions of COVID-19 vaccine doses ready to be distributed to Americans this fall. AstraZeneca may have hundreds of millions of doses available as soon as September. Moderna has its sights set on having millions of doses produced by the fall. Pfizer could provide 100 million doses by the end of this year. These hopes are contingent on these companies’ vaccines proving safe and effective in phase three trials involving tens of thousands of people.
But what if US safety and efficacy standards are adjusted, or even disregarded, to serve political interests? That’s the concern Representative Frank Pallone (D, NJ-06), chair of the full committee, raised with the five officials from vaccine-making companies.
At the end of June, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) established guidance for the approval of COVID-19 vaccines. The guidance states that any vaccine must prove at least 50 percent more effective for COVID-19 prevention when compared against placebo. (The flu vaccine varies between 40 and 60 percent efficacy from one year to another.) Efficacy of 50 percent or more for a COVID-19 vaccine must be shown in a clinical trial enrolling at least 30,000 people of all different races and ethnicities.
Chair Pallone raised the possibility that President Trump could pressure FDA to lower official COVID-19 vaccine standards to well below 50 percent efficacy, or to surreptitiously approve a vaccine even if a company’s internal data show it’s less effective than FDA’s public requirements. The Chair was looking for assurances from the vaccine-makers that they will help guard against possible political interference from the White House. Dr. Mene Pangalos, AstraZeneca’s executive vice president of biopharmaceuticals research and development, stressed that all his company’s clinical data will be published openly, and that since the vaccine will be marketed globally, it will be vetted by many countries’ regulators, in addition to FDA. Moderna’s president, Dr. Stephen Hoge, also committed to publishing his company’s data regardless of whether the vaccine succeeds in clinical trials, and added that independent investigators on a National Institutes of Health (NIH) Data Safety Monitoring Board are conducting oversight of Moderna’s trials. Even so, White House influence on FDA is expected to be monitored closely as the US heads toward Election Day.
The White House has not shied away from pressuring federal agencies responding to the COVID-19 pandemic. Earlier this month, President Trump undermined Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for reducing the risk of spreading COVID-19 at schools. In May, the Administration shelved CDC recommendations “with step-by-step advice to local authorities on how and when to reopen restaurants and other public places.” In April, a research grant funding the study of coronaviruses’ transmission from bats to people was terminated because the White House told NIH to cancel it. And finally, FDA is not immune to pressure from the Administration: A whistleblower alleges the since-rescinded emergency use authorization permitting treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine was granted as a result of political interference, and there is evidence FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn took unusual steps to assist a New York medical doctor in obtaining the drug. Congress finds the possibility of political interference from the White House in FDA’s COVID-19 vaccine approval process very worrisome.
Keys to expediting vaccine-making
Vaccines are rarely developed in even less than five years. The development of a safe and effective vaccine and the beginnings of its distribution in less than a year since the emergence of a novel disease would be revolutionary. To expedite COVID-19 vaccine-making, three key tactics have been implemented.
For one, bureaucratic steps are being streamlined to move the vaccine testing process along faster. Unnecessary delays between trial phases have been eliminated, while rigorous studies on vaccine safety and effectiveness have been maintained.
Second, some “plug-and-play” technologies developed in prior vaccine work have been applied to SARS-CoV-2 (the coronavirus that causes COVID-19). For example, Moderna’s vaccine development platform had been used previously to produce influenza virus and Zika virus vaccine candidates, and during the hearing, J&J’s Janssen Vaccines head of clinical development and medical affairs, Dr. Macaya Douoguih, cited her company’s accelerated program that produced an Ebola vaccine as critical to J&J’s efforts to produce 100 million COVID-19 vaccine doses by March 2021.
And third, companies are already scaling up the manufacture of potential COVID-19 vaccines in parallel with the testing phases, so that if a COVID-19 vaccine candidate proves successful in trials, millions of doses will be immediately available. Called at-risk manufacturing – if vaccine candidates do not pass muster, millions of doses would be worthless – vaccine-makers are implementing this capital intensive tactic because of the urgent need for safe and effective COVID-19 vaccines to be available for protection of the public.
Vaccine-makers are optimistic that tens of millions of COVID-19 vaccine doses will be available by the end of this year; however, the US government’s plan for fair and equitable vaccine distribution is yet to be released. CDC has the lead on planning for COVID-19 immunization infrastructure and vaccine distribution to the American people, and the Department of Defense is supporting CDC on logistics. Ensuring all Americans can be vaccinated against COVID-19 demands intensive local-state-federal coordination, as well as cooperation between the public and private sectors. While biopharma companies continue their rapid pursuit of vaccines against COVID-19, there is good reason for both hope and vigilance.
To review the full House Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations hearing, click here.
Transforming Infant Nutrition to Give Every Baby a Strong, Healthy Foundation
Breastfeeding can provide important health and financial benefits for new families. But insufficient healthcare coverage, underlying medical conditions, and economic obstacles can make breastfeeding difficult or impossible for many parents. In this memo, a three-pronged approach is proposed—facilitated by an interagency collaboration through the National Advisory Council on Maternal, Infant, and Fetal Nutrition—to transform infant nutrition. First, to increase breastfeeding rates in the United States, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) should alter reimbursement policy by reimbursing tele-lactation and nutrition support for all babies covered under Medicaid. Second, the government should partner with the private sector to launch a “Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Innovation Challenge” to catalyze new extramural R&D and innovation efforts to accelerate commercialization of breast-milk alternatives for those that cannot breastfeed. And finally, the government should enact paid parental leave policies to give parents financial flexibility and dedicated time after birth to breastfeed.
Challenge and Opportunity
To ensure that all babies begin their lives on equal footing, swift action should be taken to give as many babies as possible access to breastmilk and high-quality breastmilk alternatives. Though breastfeeding and breastmilk represent only 0.04% of the National Institute of Health (NIH) budget, access to breastmilk and infant nutrition are issues that affect the health and finances of all American families with very young children. For babies, access to breastmilk has been shown to protect against respiratory illnesses, ear infections, gastrointestinal diseases, eczema, and sudden infant death syndrome. For mothers, breastfeeding may help reduce postpartum blood loss and may lower risk of post-partum depression, Type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Economic Research Service has estimated that Medicaid would save at least $172.6 million every year if breastfeeding rates among women, infants, and children increased to medically recommended levels.1 More broadly, one study highlighted by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) estimated that increasing breastfeeding rates could save $3.6 billion annually in the costs of treating some childhood illnesses.2
While breastfeeding can provide important health and financial benefits for new families, not all babies can breastfeed. 1 in 8 mothers in the United States face lactation dysfunction, which means that they cannot produce enough breastmilk to provide sufficient infant nutrition.3 Medical conditions such as Insufficient Glandular Tissue (IGT), mastitis, postpartum depression and anxiety (PPD/A), and infant birth defects—to name just a few—present challenges to breastfeeding. Adoptive parents can only breastfeed in certain circumstances, and birth mothers may be confused about whether they can breastfeed while on certain medications, may dislike the process of breastfeeding, or face difficulty breastfeeding while transitioning back to work.
For these and other reasons, 75% of babies use infant formula instead of breastmilk to some extent by the time they are 6 months old. A 2007 report from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) found that existing formula-feeding solutions are associated with higher risks for chronic diseases including Type 2 diabetes, asthma, and childhood obesity.4 Formula feeding is also linked with higher rates of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) for premature infants. More research is needed to understand the underlying biochemical mechanisms of human breastmilk to develop infant formulas that better mimic breastmilk. In addition, infant formula is a major expense for the federal government. Infant formula is the single most expensive item that the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Woman, Infants, and Children (WIC) provides, and the program spends more on formula than any other food—a total of $927 million in FY 2010.
It is also important to note that paid parental leave is a critical part of the postnatal experience for mothers and babies. Increases in paid parental leave are consistently associated with better infant and child health, particularly in terms of lower infant mortality rates.5 Paid parental leave also gives parents the opportunity and flexibility to focus on breastfeeding, which can be extremely time-consuming. The children of educated, well-off mothers are more likely to breastfeed because they have access to paid parental leave, careers with access to breaks for breast pumping, and disposable income to hire support such as night nurses. However, according to a national survey of employers conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), only 18% of private industry U.S. employees had access to paid family leave through their employers. Paid parental leave in the private sector is voluntary and more prevalent among managerial and professional occupations.
Plan of Action
CMS, USDA, NIH, state WIC agencies, and the private sector should work together through the National Advisory Council on Maternal, Infant, and Fetal Nutrition to transform U.S. infant nutrition for the better. The following specific actions are recommended:
First, to increase breastfeeding rates in the United States, CMS should alter its reimbursement policy to reimburse bi-weekly tele-lactation and nutrition support appointments for any baby covered under Medicaid during the baby’s first three months of life. Currently, the Affordable Care Act requires private insurance plans and Medicaid expansion programs to cover maternity care—including prenatal screenings and lactation consultations—without cost sharing by the patient. But there is no federal requirement to reimburse for telemedicine. Advocates should encourage the Center for Consumer Information and Insurance Oversight (CCIIO) at CMS to expand mandatory maternal-health coverage to include telehealth and for CMS to implement this policy change. This can be done in collaboration with WIC, which already provides breastfeeding support through state agencies.
Second, the federal government should catalyze new R&D and innovation efforts to accelerate commercialization of high-quality breastmilk alternatives such as
- Organizing a national “Synthesizing Human Milk R&D Summit.” This Summit would bring together formula makers, academic researchers, clinicians, parent and infant advocacy groups, representatives of the public-health community, and government stakeholders. Government stakeholders include NIH, CMS, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration [FDA], the U.S. Surgeon General, and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF). The goals for the event include (i) gathering input and commitments from stakeholders to lay the groundwork for a “Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Challenge” (see next bullet); (ii) identifying barriers to developing an infant formula that more closely mimics breast milk; and (iii) generating a white paper to summarize the current understanding of the underlying biochemical mechanisms of human milk.
- Launching a “Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Challenge.” Based on the insights gained by the Synthesizing Human Milk R&D Summit, NIH should launch a “Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Challenge” that awards cash prizes for innovations in development of human breastmilk alternatives. Industry stakeholders should be recruited to match NIH investments in the prize amounts.
- Dedicating extramural academic research funds from NIH as well as funds from the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program to stimulate commercialization of high-quality breastmilk alternatives. These funds would help scale up innovations from the “Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Challenge” and would motivate additional R&D in academic settings to bring infant formula closer to human milk. In addition, a “synthesizing human milk” budget set-aside subpriority should be established as part of the SBIR NIH/NICHD program.
- Only purchasing validated infant formulas with federal funds. WIC should only buy infant formula solutions that demonstrate specific outcomes as outlined by an interagency committee convened by the USDA through the National Advisory Council on Maternal, Infant, and Fetal Nutrition. The committee should include representatives from NIH, CMS, CDC, USDA, FDA, USPSTF, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
Third, in the longer term, the federal government should enact paid parental-leave policies that give parents financial flexibility and dedicated time after birth to breastfeed.
Regarding the federal government’s role as a buyer of infant formula, WIC currently serves half of all infants in the United States and infant formula is the single most expensive item that WIC provides, and the program spends more on formula than any other food — $927 million in fiscal year 2010 as an example. For reference, each year Congress provides USDA FNS with a specific amount of funds for state agencies to operate the WIC program. WIC leads an infant formula bidding process, which is a cost containment approach. It is highly effective because it allows for state WIC programs to receive significant discounts in the form of rebates. These rebates result in up to $2B a year in savings, which means that 2 million more people can participate in this program. The national WIC association provides more details on this breakdown. Surrounding the federal government’s role in research in this arena, breastfeeding, lactation, and breastmilk represent only 0.04% of the NIH’s budget ($85M in 2019) despite the fact that this impacts every single American.
reducing costs for families, employers, health insurers, and taxpayers. As stated in the 2011 Surgeon
General’s Call to Action to Support Breastfeeding, “a study conducted more than a decade ago estimated
that families who followed optimal breastfeeding practices could save more than $1,200–$1,500 in
expenditures for infant formula in the first year alone (Ball et al, 1999). In addition, better infant health
means fewer health insurance claims, less employee time off to care for sick children, and higher productivity,
all of which concern employers (US Breastfeeding Committee, 2002).” By increasing breastfeeding rates
through paid leave and creating an infant formula closer to infant formula, this could save CMS at least
$172.6M in Medicaid costs alone.
item as part of the WIC program funded by the federal government (USDA), the government has a uniquely
high leverage and is incentivized to take action to save both healthcare costs and buyer costs on infant
formula. Specifically, on the healthcare cost front, Medicaid would save at least $172.6M every year if
breastfeeding rates in the WIC population increased to medically recommended levels.
cover maternity care without cost sharing to the patient, including prenatal screenings and lactation
consultations, but there is no federal requirement to reimburse for telemedicine, and lactation support services
are rolled out inconsistently. As a first step as part of our policy proposal, we recommend extending this
policy to cover telehealth services to allow for more even and efficient delivery of lactation support services
to increase breastfeeding adherence rates.
We believe strongly that in order for impact to happen that this needs to be a collaboration between the public and private sector. In particular, we propose NIH to launch the ‘Synthesizing Human Milk R&D Summit’ (linked to NICHD Aspirational Goal identified in their Strategic Plan) to bring together the community to rally around this ambitious goal and build a coalition. The goals for the event include 1) gathering input and commitments from stakeholders to launch a “synthesizing human milk grand challenge” and 2) laying the groundwork to launch and celebrate a future grand challenge. During this Summit, we will identify the specific barriers to developing an infant formula closer to breast milk by bringing together the formula makers, academic researchers, clinicians, parent/infant advocacy groups, and public health community with government stakeholders. Government stakeholders include NIH, CMS, CDC, FDA, US Surgeon General, and US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF). In addition, a white paper will be generated to summarize the current state of our understanding of the underlying biochemical mechanisms of human milk.
In addition, we propose NIH to launch the ‘Synthesizing Human Milk Grand Challenge’ to award prizes to new innovative approaches in human milk, which is jointly funded by the NIH and the private sector, including formula manufacturers.
This effort complements existing efforts identified as part of the NIH’s Pediatric Growth and Nutrition Branch’s strategic priority of synthesizing human milk, the Affordable Care Care Act’s effort requirement that private insurance plans and Medicaid expansion programs to cover maternity care without cost sharing to the patient, including prenatal screenings and lactation consultations, and the USDA funding WIC State Agencies who support breastfeeding and provide WIC lactation experts, WIC peer counselors, WIC breastfeeding classes.
Also this effort complements the existing National Advisory Council on Maternal, Infant, and Fetal Nutrition, and we propose that this effort is led through that council, which was originally specified as part of legislation (Section 17(k) of the Child Nutrition Act of 1966, as amended (S 42 USC 1786). This legislation mandates that the Council authorizes the Secretary of Agriculture to appoint the members.
Expanding the Health Policy Mission of the Veterans Health Administration
Summary
With 1,255 VA medical facilities serving over 9 million veterans each year, the VA — through its Veterans Health Administration — maintains the largest integrated healthcare system in the United States. The VA is a national leader in delivering quality health services and driving innovation in high-priority healthcare issues such as telehealth, precision medicine, suicide prevention, and opioid safety. Yet the VA remains an under-appreciated and underutilized health policy stakeholder, involved in minimal interactions with other federal health agencies and exerting limited influence on the private healthcare system. This is a mistake. The VA is a robust healthcare provider with innovative clinical and operational practices that should be firmly entrenched in the national health policy conversation.
As a remedy, we propose strategically coordinating and consolidating the healthcare innovation, demonstration, and implementation capacities of the VA and HHS in order to ensure care of the highest possible quality across urgent issues. Elevating the VA as a major healthcare policy stakeholder will demonstrate the value of government-run healthcare, promote best practices for building an effective and forward-thinking healthcare system, and advance the VA’s “fourth mission” of supporting national preparedness.
Building Trust In the Health Data Ecosystem
Summary
Pending bipartisan “Cures 2.0” legislation is intended to safely and efficiently modernize healthcare delivery in the wake of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. Such modernization is contingent on access to high-quality data to power innovation and guided decision-making. Yet over 80% of Americans feel that the potential risks of companies collecting their data outweigh the benefits. To ensure the success of Cures 2.0, provisions must be added that bolster public trust in how health data are used.
Addressing the largely unregulated activities of data brokers — businesses that collect, sell, and/or license brokered personal information — offers a budget-neutral solution to the public’s crisis of faith in privacy. Building a well-governed health-data ecosystem that the public can trust is essential to improving healthcare in the United States.
US vaccine manufacturing capacity assessed at Senate HELP Committee hearing
At the Senate Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions Committee hearing on Tuesday, Members of Congress and witnesses evaluated whether the U.S. will be able to manufacture enough COVID-19 vaccines to protect the population, as well as be able to distribute them equitably. Vaccine manufacturers are racing to increase their capacity to produce what will likely be billions of doses, but it might take months to years from when the vaccine is approved to produce enough doses to vaccinate the number of people necessary (about 70% of the world’s population) to achieve herd immunity.
Infrastructure for producing vaccines
Committee Chair Lamar Alexander (R, TN) asked witnesses for recommendations on what type of manufacturing capacity the federal government should have on hand to produce and distribute doses of a potential COVID-19 vaccine. Former Governor of Utah Michael Leavitt explained (1:03:30) that while the infrastructure exists to scale up U.S. vaccine manufacturing capacity, the plants were not effectively maintained after they were built. Additionally, maintaining such manufacturing facilities costs a significant amount of money, and, prior to the pandemic, pharmaceutical companies were reluctant to spend so much on facilities that are specific to only one vaccine, which may not ultimately be approved or sold.
Dr. Julie Gerberding, Executive Vice President of Merck & Co., added (1:05:00) that most pharmaceutical companies manufacturing large quantities of vaccines are nearly at capacity producing doses of other vaccines, such as those for the flu. Moderna’s CEO, Stephane Bancel, who is overseeing one of the leading experimental COVID-19 vaccine efforts, mentioned this problem in a May 12 interview with CNBC. He stated, “The odds that every [vaccine] program works are really low, obviously, but I really hope we have three, four, five vaccines, because no manufacturer can make enough doses for the planet.” To put this in perspective, pharmaceutical companies estimated they provided between 162 to 169 million doses of the flu vaccine for the U.S. during the 2019-2020 flu season. To protect the U.S. population from COVID-19, about 230 million Americans would have to be vaccinated. This also does not account for the possibility that each person may need multiple doses to be fully vaccinated or the fact that many manufacturers in the U.S. supply vaccines to other countries.
Besides overall capacity, one of the largest challenges is that the manufacturing infrastructure will differ depending on which type of vaccine(s) are the most effective. The vaccines may need to be produced by processes requiring large vats of cells or other organisms, such as tobacco plants. If a successful vaccine is based on inactivated virus, vaccine production might require highly secure facilities, of which there are very few. This means that until one or more vaccine candidates are closer to being approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), vaccine manufacturers will have a difficult time tailoring their existing facilities, or building new ones, that have the necessary equipment ready to produce the vaccines.
Some pharmaceutical companies are relying on public-private partnerships to develop and scale their vaccines, such as Johnson & Johnson with the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA). These flexible agreements allow the federal government to help the pharmaceutical companies invest money and talent into the most promising vaccine candidates. They also make it possible for companies to overhaul their production facilities and build new ones to accommodate the new vaccines, a complex and costly process for these organizations by themselves.
Equitable distribution of a potential COVID-19 vaccine
Even if companies are able to develop and produce enough doses of a COVID-19 vaccine, there are concerns that the doses may not be distributed equitably among the global population. For example, during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, Australia was the first to manufacture a vaccine but did not export it immediately because it wanted to inoculate its citizens first. Additionally, wealthier countries have the advantage of being able to purchase large quantities of vaccines at much higher rates than countries with fewer resources.
However, even in wealthy countries like the U.S., care must be taken to ensure that vaccines get to the country’s most vulnerable communities. The pandemic has devastated minority communities in cities across the country due to deep-seated public health disparities. Dr. Joneigh Khaldun, Chief Medical Executive for the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services, noted (1:06:40) during her testimony that people of color are more likely to be impoverished and more likely work in occupations that are deemed essential, but they also have the least access to healthcare. Both Dr. Khaldun (45:25) and former Governor Leavitt (40:20) emphasized that the U.S. should develop a national procurement and distribution strategy not only to reduce the competition for vaccines, but also competition for supplies in future pandemics.
Currently, pharmaceutical companies are working to adapt their vaccine manufacturing facilities to accommodate the production of the large number of doses that will be needed to protect against COVID-19, but they have a long way to go. As Chair Alexander noted (2:50:00), Congress will be reviewing the U.S. response to COVID-19 regularly, so stay tuned for more opportunities to engage with Capitol Hill.
To review the full hearing, click here.
Much-needed supplies for responding to COVID-19 remain limited
Unlike countries such as South Korea, New Zealand, or Germany, the US has not controlled the spread of COVID-19 in a coordinated fashion, and the nation is in danger of a second surge of cases. Some experts already see indicators of the second surge. For instance, COVID-19 hospitalizations rose sharply in several states after Memorial Day, and the percentage of COVID-19 tests that are positive is rising in some parts of the country. Tragically, more than 113,000 Americans have died from COVID-19, about a quarter of all deaths reported globally. This week’s Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee hearing examined key aspects of US preparedness for a second surge of COVID-19.
Status of US availability of medical supplies
From mid March through April, when COVID-19 was first on the rise throughout the country – with cases especially surging in New York City and New Jersey – there were shortages of almost every COVID-19-related medical supply imaginable. N95 respirator masks. Face shields. Cleaning supplies. Drugs for patients on ventilators. Swabs for COVID-19 tests. States scrambled to obtain much-needed supplies, sometimes forced into bidding against one another. This was all due to the combined impacts of the sudden worldwide surge in demand for these goods, deficiencies with US caches of emergency supplies, domestic distribution issues, and a lack of timely, decisive, evidence-based leadership in the White House.
The US should have been ready for the intensified needs brought on by the pandemic, with the health security community recommending for many years that more resources be dedicated to infectious disease preparedness and response, but unfortunately, the country was caught flat-footed. The White House COVID-19 Supply Chain Task Force’s own estimates of US personal protective equipment (PPE) needs and availability – made public because Senator Maggie Hassan (D, NH) pressed the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to release them during the hearing – show US supplies of N95 respirator masks, surgical masks, gowns, and nitrile gloves not meeting demand in March, April, and May. Moving forward, the Task Force projects that beginning in July for N95 respirator masks, surgical masks, and gowns, and beginning this month for nitrile gloves, supply will meet demand for hospitals, long-term care facilities like nursing homes, first responders, and janitorial, laboratory, and correctional workers.
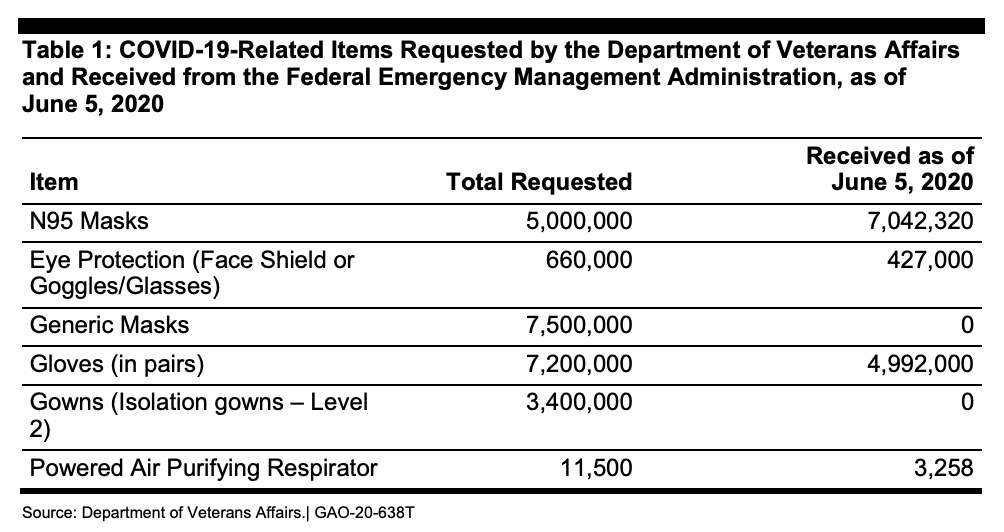
But America’s PPE supply is in flux, and there are clearly inadequacies. For example, the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) says it needs a six-month supply of PPE to handle a second surge of COVID-19. At the height of the initial surge, the VA’s 170 medical centers were using 250,000 N95 respirator masks every day. Right now, the VA only has about a 30-day supply of PPE, and as of June 5th, the VA had not received any of the 7.5 million “generic masks,” nor any of the 3.4 million “isolation gowns,” it had requested from FEMA’s Strategic National Stockpile program back in mid-April.
Strategic National Stockpile
The Strategic National Stockpile was intended to be America’s fallback plan. Through April 1st (the Administration changed the wording on April 2nd), the stockpile was defined as
“…the nation’s largest supply of life-saving pharmaceuticals and medical supplies for use in a public health emergency severe enough to cause local supplies to run out. When state, local, tribal, and territorial responders request federal assistance to support their response efforts, the stockpile ensures that the right medicines and supplies get to those who need them most during an emergency. Organized for scalable response to a variety of public health threats, the repository contains enough supplies to respond to multiple large-scale emergencies simultaneously.”
The stockpile was initially launched in 1999 and managed by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In 2018, responsibility for the stockpile shifted to the HHS assistant secretary for preparedness and response (ASPR). In March, responsibility for the stockpile shifted again, this time to FEMA.
In the face of the coronavirus pandemic, the stockpile did not offer much resilience. Government officials estimated that the US would require 3.5 billion N95 respirator masks for a severe outbreak. There were only 12 million unexpired N95 respirator masks in the stockpile in February. In early March, the stockpile contained only 16,600 ventilators, and on April 3rd, the federal government had just 9,800 ventilators available. It is unlikely that the stockpile is being replenished since PPE that becomes available is generally immediately put to use in COVID-19 hot spots or delivered to medical centers, and it is difficult to gain insight into the current inventory of the stockpile. For instance, after not receiving a response to their Freedom of Information Act request, ProPublica filed a lawsuit against the Administration to get medical stockpile records.
A group of nine former presidential science advisors warned that the US needs to build the stockpile back up by September 1st in order to be prepared for a possible COVID-19 resurgence in the fall, and that state and local supply inventories need to be stocked as well. Their recommendations revolve around increased funding for producing essential medical goods, stockpiling supplies, and improving the coordination of the supply chain and distribution.
Moving forward through the pandemic
During the hearing, the vice director of logistics for the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Rear Admiral John Polowczyk, testified that the US is ramping up domestic production of at least some critical medical supplies. Polowczyk cited the current capacity to manufacture 180 million N95 respirator masks each month, his expectation for the production of an adequate number of reusable gowns by the fall, the beginnings of at least some nitrile glove manufacturing (compared to essentially zero previous domestic capacity), and initiating the process of onshoring the making of some ventilator drugs.
Despite these signs of progress, at the moment, the US does not appear ready for another surge of coronavirus. And that surge may come sooner rather than later.
The Senate Finance Committee questioned FDA officials about US policies on hydroxychloroquine, the World Health Organization, and supply chain security
The coronavirus has killed over 108,000 people, and infected millions, in the US alone. As some areas of the country begin to lift infection control precautions, it is critical for the federal response to the COVID-19 pandemic to improve. An important part of this process is Congressional oversight of the Administration’s response to COVID-19, and during Tuesday’s Senate Finance Committee hearing, Members pressed Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officials on decision-making around the potential COVID-19 treatment hydroxychloroquine, the Administration’s commitment to withdraw from the World Health Organization (WHO), and reliance on China and other foreign countries for drug manufacturing.
Policy on hydroxychloroquine as a treatment for COVID-19
Early in the pandemic, anecdotal reports of COVID-19 patients in China and France who seemed to improve when given hydroxychloroquine, combined with laboratory findings of a possible antiviral effect, raised hopes that hydroxychloroquine, and a closely related drug chloroquine, could serve as treatments for the coronavirus. The drugs had been FDA-approved for the safe and effective treatment of malaria, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis for many years. President Trump began publicly promoting chloroquine as a potential COVID-19 treatment, and later at the end of March, FDA granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for both chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine to be used for COVID-19 patients.
The first study describing a large, controlled clinical trial of hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 was released this week. It was found that people, such as healthcare workers, who experienced high risk exposures to the coronavirus, and who were then given hydroxychloroquine and monitored, developed COVID-19 just like those who experienced high-risk exposures and who were given placebo. Furthermore, the study found that hydroxychloroquine did not impact the severity of illness for these individuals. The question of whether hydroxychloroquine can prevent coronavirus infection if people take it before they are exposed to sick patients is under study in other clinical trials.
During Tuesday’s hearing, Senator Ron Wyden (D, OR), the ranking member of the Committee, said he believed FDA gave in to political pressure when it approved the EUA for hydroxychloroquine. Senator Wyden noted that the EUA led to the production of “tens of millions of pills, including some…manufactured inside facilities in Pakistan and India that have either failed FDA’s inspection or never been inspected by the FDA at all.”
The Government Accountability Office is evaluating the FDA process that resulted in the EUA for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine to learn if the EUA was purely based on the FDA’s science-based best practices.
Plans to terminate relationship with the World Health Organization
Last Friday, President Trump announced his Administration’s intention to withdraw the US from WHO. In the global fight against disease, WHO’s roles in providing assistance, setting health standards, and collecting data are critical. Considering WHO convenes international partners to support the development of COVID-19 drugs, vaccines, and other measures to curb spread, a US withdrawal will weaken our ability to fight the pandemic. Furthermore, US absence from WHO would allow nations like China, which stalled its delivery of essential COVID-19 information to WHO, to have even more influence on the global stage.
When asked about how the US plans to address global health needs, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, or Ebola in Congo, or polio in Yemen, without being a member of WHO, the FDA’s associate commissioner for global policy and strategy Mark Abdoo responded that he had “not been privy to those conversations” and referred the Committee to the National Security Council or the Presidential spokesperson.
Meanwhile, Chinese President Xi Jinping pledged to contribute $2 billion to WHO over the next two years to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as share any coronavirus vaccine developed in China with the world. China’s government or Chinese companies have developed five of the ten coronavirus vaccine candidates currently being tested in clinical trials around the globe.
Reliance on foreign drug manufacturing
Most manufacturing of finished drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients is done outside the US. Throughout the pandemic, there have been shortages of certain drugs. Many members of the Committee, including Senator Pat Toomey (R, PA), asked about the security of the US supply chain for medicines, concerned that countries such as China could withhold drugs or ingredients, or that future global health emergencies could leave the US vulnerable to being without needed drugs.
FDA officials assured the Committee that the US drug supply is safe and supply chains are secure, and that, to their knowledge, no countries had held back medicines. They attributed the limited drug shortages in the US mainly to a sudden surge in demand for drugs as well as domestic distribution issues. They also advised that the US bolster its domestic drug manufacturing capacity now since the US is bound to face future pandemics. Drug companies could move more production back to the US by implementing advanced manufacturing techniques that allow for more rapid production of drugs, while at the same time reducing environmental impacts.
For the full video of the hearing, click here.
Addressing the Organ Donor Crisis
Summary
The organ-donation crisis is one of the most persistent, expensive, and yet solvable public-health challenges of our time. As of January 2020, nearly 115,000 Americans were waitlisted for an organ transplant. The vast majority have kidney failure, which, as one of the rare conditions qualifying patients for Medicare, imposes billions of dollars of costs on taxpayers. In 2016 alone, taxpayers spent an alarming $113 billion on kidney disease — more than the entire budgets of the National Institutes of Health ($39 billion), the Department of Homeland Security ($44 billion), and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, $21.5 billion) combined. The clear solution is to shorten the organ waiting list. For every Medicare patient who receives a kidney transplant, taxpayers save $250,000 in avoided dialysis costs. This proposal presents a discrete set of actions for the federal government to take to quickly and decisively to address the organ-donation crisis.
Creating the Health Advanced Research Projects Agency (HARPA)
Summary
The federal government can directly address the massive market failures at the center of our healthcare enterprise by establishing a new Health Advanced Research Projects Agency (HARPA)1 modeled after the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)—the agency the Department of Defense uses to build new capabilities for national defense.
The need for HARPA is twofold. First, developing treatments for disease is difficult and time consuming. HARPA will provide the sustained drive needed to push through challenges and achieve medical breakthroughs by building new platform technologies. Second, the U.S. healthcare system largely relies on the private sector to leverage national investments in basic research and develop commercially available treatments and cures. This model means that diseases for which investments are risky or downstream profit potential is low are often ignored. HARPA will step in where private companies do not, addressing market failures with direct investments that ensure that all patients have hope for a brighter future.
HARPA will leverage existing basic science research programs supported by taxpayer dollars, as well as the efforts of the private sector, to develop new capabilities for disease prevention, detection, and treatment and overcome the bottlenecks that have historically limited progress. To do this, we have to think and act differently about how we address human health challenges. HARPA would support research that directly affirms, refutes, or otherwise changes current clinical practice. It would do this using milestone-driven, time-limited contracts as the central mechanism for driving innovation. This will ensure efficiency, transparency, and optimize success.
Challenge and Opportunity
Every year, the United States spends more than $3.4 trillion on healthcare and tens of billions of dollars on biomedical research. Yet we only have treatments for around 500 of the approximately 10,000 known human diseases.2 30 million people in the United States—half of whom are children—suffer from a rare disease for which no treatment has yet been developed.3 There are no ongoing efforts to develop treatments or cures for the overwhelming majority of these diseases. That massive market failure is the big secret of the biomedical research enterprise and is simply unacceptable. We need bold action to correct this massive market failure and revolutionize how we attack disease.
In 1958, the United States created the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) at the Department of Defense. This new government agency was designed to make pivotal investments in breakthrough technologies for national security and directly address market failures that were impeding innovation. The establishment of DARPA launched a new era in defense innovation that led to countless innovations, including the Internet, stealth aircraft, GPS-based precision navigation, night vision, autonomous vehicles, speech recognition, and robotic prostheses.
We need to take the same aggressive entrepreneurial approach to health innovation as we have in protecting our nation from foreign threats. Creating a new Health Advanced Research Projects Agency (HARPA) would fundamentally transform the way the United States approaches treating the majority of human diseases, and would directly address many of the shortcomings of our healthcare and biomedical research systems.
Imagine being able to predict and intervene before someone has a mental health crisis; diagnose cancers at their earliest stages when treatments are most effective; end deaths from antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections; and provide treatments for rare genetic diseases. That is the promise of HARPA.
By applying the same tools that DARPA uses to develop new capabilities for defense (Section 3), HARPA would be engineered to close the gap between basic research and real-world needs. HARPA initiatives would target the diseases that affect millions of Americans but are going unaddressed because of risk aversion and short-term, perverse incentives in academia and the private sector. These initiatives would be funded through large milestone-driven timeline limited contracts needed to take on transformational projects, and would be led by top experts recruited for focused stints at the agency. The result will be an institution designed from the ground up to finally solve the most pressing healthcare issues of our time: skyrocketing drug prices, the tragic shortcomings of our mental-health support systems, the opioid crisis, unconscionable waiting lists for organ donations, medical errors, and many more. DARPA enabled the United States to lead the world when it comes to defense innovation. HARPA will do the same for healthcare.
Function
Federal funding for medical research is primarily allocated though the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Through its $41 billion annual budget, NIH funds basic science and clinical research through grants. Grants are typically awarded to individual projects at academic institutions. Collectively, these projects form the bedrock of our knowledge about biology, health, medicine, and disease.
Importantly, NIH is not designed to develop marketable disease treatments or cures or to develop new platform technologies that are intended to revolutionize medicine. NIH funding is used to support therapeutic and technology development, but not in a way that prioritizes quick, efficient commercialization of new discoveries. Moreover, NIH does not include a mechanism for ensuring commercialization. SBIR grants flail at the challenge of commercializing innovations with woefully inadequate funding. Simply put, the current path from NIH-funded basic science to applied research to viable commercial product is too slow, and it does not address massive market failures that define health research and development today, leaving many human diseases without dedicated efforts to uncover solutions. Funds for basic science and clinical research through grants—awarded to academic institutions that pursue particular, individual interests in discovery—are great for uncovering truths about biology, but are an extremely inefficient way to drive toward therapies that make their way into the clinic.
Private companies, on the other hand, only scale up and market economically viable therapies. Therapies that are potentially effective but have a limited market remain inaccessible to the public at large or come with astronomical price tags that patients simply cannot afford.
Effectively bringing new innovations to the market requires alternative approaches to the bottom-up grant funding common to NIH programs. Again, this is not to say that the NIH dollars are poorly spent. The dollars spent on research are essential to understanding health and disease. But an alternative model is needed to advance research toward the development of necessary technologies and treatments to cure disease.
HARPA would close these gaps. Just as NIH brings federal resources to bear on basic science and early-stage research, HARPA would bring federal resources to bear on applied science and later-stage development and deployment. HARPA would have three guiding functions:
- Launch and manage large-scale health-research initiatives. Although multiple federal entities4 work on health research, there is little coordination among these entities regarding research priorities, activities, or progress. HARPA would work with these entities—as well as with the private sector, academia, and states and localities—to launch and carry out targeted, multi-stakeholder research initiatives aimed at our most pressing underserved health challenges. Using milestone driven and timeline limited funding contracts, HARPA will be able to ensure rapid continuous progress. These initiatives would integrate the diverse capabilities of participating institutions to make real progress on persistent and pressing health problems.
- Invest in transformational platform technologies. HARPA’s focus will be on projects that have direct impact on clinical care. Basic science tends to advance methodologically and incrementally. This partly reflects the nature of the field (one set of experiments informs the next) and partly reflects the nature of incentives in academia (moving too far and too fast away from an established knowledge base decreases the likelihood of publishable findings). By contrast, HARPA will only support transformative research that will substantially improve clinical practice and this is how potential impacts will be evaluated. Pushing for such platform technology breakthroughs is a high-risk, high-reward enterprise. HARPA will focus on the uncertain but potentially transformational medical technologies and therapies that tend to go underfunded today.
- Support development of treatments and cures for all diseases. All taxpayers contribute to federally funded medical research. But not all taxpayers reap the benefits. Relying on the private sector to bridge the gap between basic research and commercially available products means that those with rare or difficult-to- treat diseases are often ignored. HARPA will correct this market failure by supporting development of treatments and cures for all diseases—especially those that are being neglected by the existing healthcare ecosystem.
Structure
HARPA would be modeled on DARPA. DARPA is considered the “gold standard” for innovation and accountability within the federal government. DARPA is also distinct from other federal agencies that fund research and development in that it is focused on building capabilities rather than simply advancing knowledge. This unique mission requires DARPA to have a unique set of attributes and operating principles, including the following:
- Contracts large enough to provide a critical mass of funding. While most federal grants for academic research are on the order of tens to hundreds of thousands of dollars annually, DARPA funds projects at $1–$5 million per year. These large contracts enable DARPA affiliates to pursue goals that would simply be out of reach at lower funding levels.
- Minimal bureaucracy. DARPA’s entire staff consists of about 220 government employees. This includes DARPA’s ~100 program managers (PMs), who collectively oversee about 250 research & development projects funded at total of about $3 billion per year. All actual research and development activities are conducted by public, private, and academic affiliates. DARPA’s small staff size and flat organizational hierarchy makes the agency effective and nimble, able to move quickly on priority issues in a limited amount of time. Moreover, the fact that DARPA is not organized around disciplines allows PMs to pursue unconventional but productive cross-disciplinary collaborations.
- No entitled constituencies. While funding from other federal grant programs may only be accessible to certain recipient classes (e.g., academic institutions), DARPA does not predetermine which types of institutions are eligible for funding. Funding projects at a wide variety of institutions—including universities, national labs, public and private companies, state and local government agencies— enables DARPA to access the full breadth of talent, expertise, ideas, and resources that the nation has to offer. For example, DARPA funding in the start- up community has yielded advances that may have been difficult or impossible to achieve in other sectors. DARPA uses flexible procurement tools like “Other Transaction Authority” to make it easy for small businesses and nontraditional defense contractors to participate in the agency’s initiatives.
- “Portfolio approach” to high-risk, high-reward efforts. DARPA understands and accepts that frequent failure is the price of success when it comes to achieving transformational breakthroughs. DARPA PMs have the resources and authority to invest in multiple approaches to a given goal. DARPA proposals are openly competed, but PMs can strategically select the winners in a way that creates a diversified, risk-mitigating project portfolio.
- Government control of contracts. DARPA negotiates contracts that enable control over performance. Contracts specify milestones and “go/no-go” decision points to ensure that scientific progress is made in an efficient and timely manner. This enables PMs to better manage funded projects and to cut funding if a project is not yielding desired results.
- Top-notch talent. DARPA attracts world-class PMs recruited from academia, industry, and government agencies. DARPA benefits from expedited direct hiring authority for science and engineering experts.
- High turnover. PMs are hired for limited stints (generally 3–5 years), and there are no career PMs. This approach keeps DARPA talent fresh—ensuring that the agency is scientifically current and flexible to new avenues of investigation—and fuels an urgency for PMs to “achieve success in less time than might be considered reasonable in a conventional setting.”5
Many, if not all, of these characteristics could be carried over to HARPA. HARPA could also adopt DARPA’s funding-management model. Under this model, all funding allocations would be left to the discretion of the HARPA Director while all funding oversight would be entrusted to HARPA PMs. Funds would be awarded as milestone- driven contracts that give PMs the capacity for early termination if a particular project is not yielding desired results. This almost never happens with traditional federal grants for research and development.
Because HARPA will differ in structure and function from traditional research-funding agencies, it is sensible for HARPA to have a reporting chain of command separate from NIH. We believe that HARPA would be best situated directly under the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) or under the HHS Assistant Secretary for Health. The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) provides precedent for placement directly under the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response.6
Path to Establishment
HARPA could be established under existing authorities, but, ideally, would be established through authorizing legislation and new appropriations. There are several steps the federal policymakers could take to kick-start the establishment process. First, the president could issue a Memorandum or Executive Order directing the HHS Secretary to develop a blueprint for HARPA’s establishment as well as a strategic plan for HARPA’s activities. These documents would include identification of priorities and goals; analysis of global markets, policies and production capabilities; structure and accountability; and initial funding recommendations. Ideally, they would be developed by a short-term Federal Advisory Committee (FAC)—comprised of top physicians, health researchers, and innovative thought leaders. It is important that the FAC include avenues for external input, including providing and promoting a public comments period and convening stakeholder for a across the country. After these documents are developed, the president could urge Congress to deliver a bill establishing HARPA.
Alternatively, the President could include funds for HARPA in an annual budget proposal under the Assistant Secretary for Health or Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response. (If Congress appropriates those dollars, HARPA could be established without authorizing legislation.7) We believe that a minimum budget of $100 million for HARPA in its first year and $300 million in its second year would be sufficient to get the agency started and to establish high-impact programs, but to be truly transformational, the agency should ramp up to several billion in research expenditures annually. Throughout this process, the president should use high-profile speeches and events to publicly explain the need for HARPA, and to advocate for its creation.
Vision
With a DARPA-inspired structure, HARPA would achieve rapid translation of biomedical discoveries into patient-care capabilities. HARPA’s mission and activities would be synergistic—not duplicative or competitive—with existing federal research efforts. In particular, HARPA would use fundamental scientific understanding developed with NIH support as a foundation for developing breakthrough medical advances.
HARPA would operate in a health ecosystem that includes biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and healthcare companies, venture capital and philanthropy, academic institutions, and government and regulatory agencies. HARPA would address two of the most prominent shortcomings of this ecosystem: (1) the aversion to failure that limits the willingness of academics and the private sector to pursue high-risk, high-reward projects, and (2) profit incentives that limit the willingness of the private sector to develop therapies for rare or difficult-to-treat diseases. HARPA would provide the capital and supportive, focused research environment needed for experts from all sectors to demonstrate “proof of principle” for various medical innovations. In doing so, HARPA will drive explosive growth in the number of technologies, treatments, and cures that cross the so-called “valley of death” separating lab-scale insights from commercially available products.
HARPA would focus on developing transformational technologies that fundamentally change the way we do health research and deliver care. By focusing on the development of tools and technologies to transform the way we approach diseases, HARPA can establish mechanisms that ensure wellness and curing disease are prioritized, while correcting the perverse incentives in the market that limit the country’s ability to receive treatment.
There is a rich history of under-funding the development of such technologies even though they are often quickly engrained into the healthcare enterprise, making it difficult to imagine life without them. They enable breakthroughs that even inventors did not anticipate, create entire new fields of research, and often result in Nobel Prizes. They establish jumping-off points and serve as accelerants for progress. Such work is typically high-risk, high-reward and aims to build transformative capabilities rather than incremental discovery-based research that is commonly funded by the NIH. While NIH does a tremendous job of funding basic science and clinical research, HARPA will build new capabilities on the foundation that agencies like NIH and the Department of Veterans Affairs establish through their funding.
For instance, HARPA could drive the following:
- Technologies that allow clinicians to identify and quantify every protein in a drop of blood, completely transforming disease diagnosis, health monitoring, and care.
- A next-generation diagnostic imaging machine that makes it possible to detect a myriad of diseases at much earlier stages that is substantially cheaper, higher-resolution, and more portable than current MRI machines enabling broader use.
- A cortical eye prosthesis that communicates directly with the brain, making it possible to restore sight to the 7 million individuals (including 160,000 veterans)living with a visual disability in the United States.
- New classes of antibiotics to fight the enormous international public-health andeconomic threat posed by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- A series of clinical trials for the most expensive marketed drugs, aimed atdeveloping alternative treatment regimens to improve outcomes by reducing toxicities while dramatically reducing treatment costs. Such de-escalation studies of marketed oncology drugs have been shown to improve outcomes and dramatically reduce costs to save billions of dollars.
- A massive effort to repurpose already approved drugs for new applications. There have only been about 2,400 drugs ever been approved for use in humans. Exploring new applications of drugs that are already known to be safe and effective—instead of only focusing on creation of new drugs—could save billions of dollars on research and development and uncover novel uses for drugs that are already known to be safe and effective for other indications.
Beyond Health
It has not escaped our notice that the same market and institutional failures that created the valley of death and need for DARPA and HARPA exist in other areas of research and development. Our nation is facing unprecedented challenges associated with climate change and the need to provide a better world for all. We feel strongly that the federal government should establish additional Advanced Research Projects Agencies (ARPAs) to complement the efforts of other federal agencies and the private sector. Doing so would enable the government to take a leadership position in tackling monumental challenges.
We believe that, in addition to HARPA, the nation needs to establish capabilities in agriculture (AgARPA), the environment (EnARPA), and transportation/infrastructure (TARPA). Fleshing out the details for establishing each of these entities should fall upon the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy in coordination with the Office of Management and Budget, the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST), and the leadership of the appropriate federal agencies. Creating these new capabilities will kickstart new industries, create the jobs of the future, and improve our ability to be better stewards of the Earth. Without them, the nation risks continuing its piecemeal approach to addressing our most pressing challenges, while slipping further behind other nations investing heavily in innovations aimed at solving these global challenges. Establishing ARPA capabilities across the federal government would create a network of forward-thinking agencies prepared to address intractable challenges, while building an extraordinary, lasting legacy.