US Air Force Decides to Retire Advanced Cruise Missile

The U.S. Air Force has decided to retire the Advanced Cruise Missile, the most modern and capable nuclear cruise missile in the U.S. arsenal, according to information obtained by the Federation of American Scientists.
The decision affects approximately 400 ACMs (AGM-129A) currently deployed at Minot Air Force Base in North Dakota and Barksdale Air Force Base in Louisiana. Each missile carries a W80-1 warhead with a yield of 5-150 kilotons. The ACM is designed for delivery by B-52H strategic bombers.
FAS analyst Hans Kristensen noticed elimination of funding for the ACM in the Air Force’s FY2008 budget request, and a subsequent email to the Air Force confirmed the decision to retire the weapon system. The Air Force has not announced when the retirement will be completed, but it appears to be within the next year.
The decision to retire the ACM is part of the reduction of strategic nuclear warheads under the 2002 SORT agreement (Moscow Treaty), which limits U.S. and Russian operationally deployed strategic nuclear warheads to a maximum of 2,200 by 2012. To meet the treaty limit, the United States already has reduced the number of nuclear warheads on sea-launched ballistic missiles and is in the middle of a download of warheads from land-based ballistic missiles. Confirmation of the ACM retirement is the first public statement about a reduction of warheads on the bomber force.
The ACM is one of two nuclear cruise missiles in the U.S. arsenal, but the only nuclear cruise missile built with stealth technology to evade radar detection. The ACM, which has hard target kill capability, was produced by General Dynamics between 1987 and 1993. The initial plan was to produced nearly 1,500 missiles but the program was cut back to 460 missiles in 1991. The Air Force has not decided what to do with the retired ACM airframes, but is exploring alternative uses such as converting them to carry conventional warheads or use in missile tests.
The Air Force also has an inventory of approximately 1,300 older Air Launched Cruise Missiles (AGM-86B), which also carry the 80-1 warhead. The Air Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM) has just completed a life-extension program, and funding continues through 2013. It is estimated that the ALCM force will be reduced by two-thirds over the next five years.
The United States currently has total stockpile of nearly 9,900 nuclear warheads, of which roughly 4,700 are operationally deployed. Approximately 2,000 warheads are in the Responsive Force, a reserve of extra warheads available to increase the operational force if necessary. The remaining 3,000 warheads are scheduled to be dismantled. After the reductions under the SORT agreement are completed in 2012, the United States will still have a nuclear stockpile of nearly 6,000 warheads.
Background: Status of World Nuclear Forces
Divine Strake Experiment Canceled
 The Defense Threat Reduction Agency announced today that it has canceled the controversial Divine Strake experiment.
The Defense Threat Reduction Agency announced today that it has canceled the controversial Divine Strake experiment.
A 700 tons chemical explosion at the Nevada Test Site was intended to provide data for calibration of nuclear and conventional weapons against underground targets. Local fear that the explosion would kick up and disperse radioactive material from the ground – as well concern about Divine Strake’s role in calibrating the use of low-yield nuclear weapons against underground targets – prompted members of Congress to raise questions about Divine Strake.
The Federation of American Scientists was the first to obtain and publish confirmation from DTRA that Divine Strake was the same experiment described in the FY2006 and FY2007 DTRA budget requests as intended to “improve the warfighter’s confidence in selecting the smallest proper nuclear yield necessary to destroy underground facilities while minimizing collateral damage.” DTRA public affairs officials subsequently denied Divine Strake had any connection to nuclear missions, but were later contradicted by senior DTRA officials saying that it was nuclear related.
Background: Divine Strake
China’s Submarine Fleet Continues Low Patrol Rate

China’s entire submarine fleet conducted only two patrols in 2006, according to information declassified by the U.S. Navy and obtained by the Federation of American Scientists under the Freedom of Information Act. The low patrol rate follows a drop from an all-time high of only six patrols in 2000 to none in 2005. China’s single sea-launched ballistic missile submarine Xia, the data shows, has never conducted a deterrent patrol.
The low level of Chinese submarine patrols is a curious contrast to warnings by the Pentagon, some private institutes and news media that China is expanding its submarine operations deeper into the Pacific. Although Chinese submarines occasionally venture into the waters around Japan and Taiwan, the fleet is surprisingly inactive.
Since 1981, the first year for which patrol data is available, the Chinese submarine force has conducted an average of less than two patrols per year. The highest number of annual patrols conducted since 1981 was six patrols in 2000. In four years (1982, 1990, 1993 and 2005), no patrols were conducted at all. Over the 25-year period, the trend is that patrols have only increased from one per year to approximately 2.8 patrols per year.
|
Chinese Submarine Patrols |
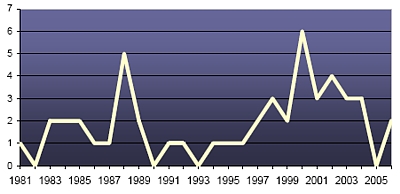 |
| The entire Chinese submarine fleet conducts less than three patrols per year on average. The ballistic missile submarine Xia has never conducted a deterrent patrol. |
So What is a Patrol?
The Navy has refused to tell FAS what a “patrol” is, saying doing so “would divulge methods and sources.” So interpretation of the data comes with a great deal of uncertainty. But the Defense Department’s unclassified Dictionary of Military Terms (JP 1-02) and earlier versions provide some hints by listing the following five definitions:
* Antisubmarine patrol: The systematic and continuing investigation of an
area or along a line to detect or hamper submarines, used when the direction
of submarine movement can be established.
* Inshore patrol: A naval defense patrol operating generally within a naval
defense coastal area and comprising all elements of harbor defenses, the
coastal lookout system, patrol craft supporting bases, aircraft, and Coast
Guard stations.
* Offshore patrol: A naval defense patrol operating in the outer areas of
navigable coastal waters. It is a part of the naval local defense forces
consisting of naval ships and aircraft and operates outside those areas
assigned to the inshore patrol.
* Patrol: A detachment of ground, sea, or air forces sent out for the purpose
of gathering information or carrying out a destructive, harassing, mopping up,
or security mission.
* Submarine patrol area: A restricted area established to allow submarine
operations: a. unimpeded by the operation of, or possible attack from, friendly
forces in wartime; b. without submerged mutual interference in peacetime.
If one assumes that U.S. Naval Intelligence’s use of the term “patrol” follows the DOD’s definitions, then the declassified patrol data suggests that Chinese general purpose submarines in 2006 twice conducted investigations to detect other submarines, participated in naval defense operations in coastal or outside coastal areas, or deployed for the purpose of gathering information or harassing. That implies an almost dormant submarine fleet.
The Song Incident
One of the two patrols conducted in 2006 appears to have been the widely reported surfacing of a Song-class diesel-electric submarine near the U.S. aircraft carrier USS Kitty Hawk in the South China Sea. The news media and pundits dramatized the incident as an example of China expanding its submarine operations, the Chinese government downplayed the reports as inaccurate, and the Pentagon said the media made too much of the incident.
“The bottom line is that […] they’re deploying them further and more frequently,” Defense News quoted an expert on the Chinese Navy at the National Defense University saying. China might even have a decisive submarine surge capability in 20 years, another pundit argued. “They are building a blue-water navy,” yet another expert warned. A politician in Taiwan thought it raises questions about “whether the U.S. in losing its military edge in the Western Pacific,” and commentators in both Taipei and Washington concluded that the incident showed that Taiwan needs to buy more submarines.
The Pentagon’s 2006 report Military Power of the People’s Republic of China stated that China was working on establishing a “first” or “second island chain” strategy for its naval forces, and that “Chinese forces have increased operations beyond China’s borders and coastal waters.” This may be the case for surface ships, but to illustrate the development the Pentagon highlighted “the highly publicized 2004 intrusion of a HAN-class nuclear submarine in Japanese territorial waters during operations far into the western Pacific Ocean.” DOD did not mention that the intrusion was one of only three patrols conducted by the entire Chinese submarine force in 2004, and that no patrols at all were conducted in 2005.
The U.S.-China Commission established by Congress after reports about Chinese spying, stated in 2006 that China is pursuing measures to try to “control” the seas in the Western Pacific, although “controlling” the seas is a daunting technological and operational task, and that China continues to “expand” its submarine force.
The Shrinking Chinese Submarine Fleet
Although China is modernizing its submarine force, it is not “expanding” it. Since the mid-1980s, the force has been in steady decline from nearly 120 boats to roughly 55 operational submarines today. The U.S. Navy expects the force will level out around 40 boats in the next decade.
|
The Shrinking Chinese Submarine Fleet |
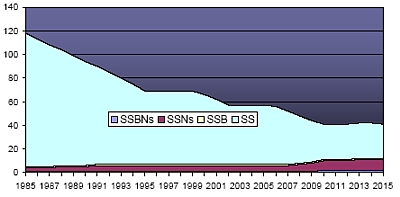 |
| The Chinese submarine fleet has declined by approximately 50 percent since the mid-1980s, mainly due to retirement of old and obsolete classes. Construction of new classes is underway but is not anticipated to lead to an increase, as the U.S. Navy expects the fleet will level out at around 40 submarines in the next decade. |
The decline of the submarine fleet is part of a transition where large older classes are being phased out and replaced with newer but less numerous submarine classes. The new submarines are more capable than the ones they replace, but the modernization has not resulted in an increase in the number of submarine patrols. On the contrary, during the period between 2000 and 2006, when China acquired a dozen new Kilo and Song class submarines, the number of patrols declined from six to two (with no patrols at all in 2005).
Implications
The implications of the low patrol rate are significant. The total operational experience for the entire Chinese submarine force is only 49 patrols in 25 years, corresponding to each submarine conducting an average of one patrol every third year.
As a result, Chinese submarine crews appear to have relatively little operational experience and consequently limited skills in operating their boats safely and competently. It suggests that the tactical skills that would be needed for the Chinese submarine force to operate effectively in a war may be limited.
China continues – at least for now – to use its submarine force as a coastal defense force.
Background: Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
No Need to Replace UK Nuclear Subs Now, FAS Board Member Tells Brits
 (Updated January 26, 2007)
(Updated January 26, 2007)
British Vanguard-class ballistic missile submarines have at least 15 years more service life in them, and the U.K. government does not have to make a decision now on whether to replace them with a new class of submarines, Richard Garwin told BBC radio Tuesday.
Garwin, who is a member of the Federation of American Scientists Board of Directors and a long-term adviser to the U.S. government on defense matters, is in Britain to testify before the House of Commons Defence Select Committee on the future of Britain’s nuclear deterrent.
The U.K. government announced on December 4, 2006, that it had decided to replace its current Vanguard-class sea-launched ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) with a new class to enter operation in 2024. If approved by the parliament, the plan would extend Britain’s nuclear era into the 2050s.
According to the U.K. government, a decision to build a new new class must be made now because the Vanguard-class SSBNs only have a have a design life of 25 years. But Garwin says that the submarines have a minimum design life of 25 years, which can be extended by at least another 15 years. A decision made now is premature and unwise, Garwin told BBC, because the large Trident missiles may not be necessary 15 years from now.
New additions: Garwin testimony / House of Lords debate
Background: BBC Today | Garwin Archive at FAS | Britain’s Next Nuclear Era
Nuclear Missile Testing Galore
 (Updated January 3, 2007)
(Updated January 3, 2007)
North Korea may have gotten all the attention, but all the nuclear weapon states were busy flight-testing ballistic missiles for their nuclear weapons during 2006. According to a preliminary count, eight countries launched more than 28 ballistic missiles of 23 types in 26 different events.
Unlike the failed North Korean Taepo Dong 2 launch, most other ballistic missile tests were successful. Russia and India also experienced missile failures, but the United States demonstrated a very reliable capability including the 117th consecutive successful launch of the Trident II D5 sea-launched ballistic missile.
The busy ballistic missile flight testing represents yet another double standard in international security, and suggests that initiatives are needed to limit not only proliferating countries from developing ballistic missiles but also find ways to curtail the programs of the existing nuclear powers.
The ballistic missile flight tests involved weapons ranging from 10-warhead intercontinental ballistic missiles down to single-warhead short-range ballistic missiles. Most of the flight tests, however, involved long-range ballistic missiles and the United States, Russia and France also launched sea-launched ballistic missiles (see table below).
|
Ballistic Missile Tests |
||
| Date | Missile | Remarks |
| China | ||
| 5 Sep | 1 DF-31 ICBM |
From Wuzhai, impact in Takla Makan Desert. |
| France | ||
| 9 Nov | 1 M51 SLBM | From Biscarosse (CELM facility), impact in South Atlantic. |
| India | ||
| 13 Jun | 1 Prithvi I SRBM |
From Chandipur, impact in Indian Ocean. |
| 9 Jul | 1 Agni III IRBM |
From Chandipur. Failed. |
| 20 Nov | 1 Prithvi I SRBM |
From Chandipur, impact in Indian Ocean. |
| Iran** | ||
| 23 May | 1 Shahab 3D MRBM |
From Emamshahr. |
| 3 Nov | 1 Shahab 3 MRBM, as well as “dozens” of Shahab 2, Scud B and other SRBMs |
Part of the Great Prophet 2 exercise. |
| North Korea*** | ||
| 4 Jul | 1 Taepo Dong 2 ICBM and 6 Scud C and Rodong SRBMs |
From Musudan-ri near Kalmo. ICBM failed. |
| Pakistan | ||
| 16 Nov | 1 Ghauri MRBM |
From Tilla? |
| 29 Nov | 1 Hatf-4 (Shaheen-I) SRBM |
Part of Strategic Missile Group exercise. |
| 9 Dec | 1 Haft-3 (Ghaznavi) SRBM |
Part of Strategic Missile Group exercise. |
| Russia | ||
| 28 Jul | 1 SS-18 ICBM | Attempt to launch satellite, but technically an SS-18 flight test (see comments below). |
| 3 Aug | 1 Topol (SS-25) ICBM |
From Plesetsk, impact on Kura range. |
| 7 Sep | 1 Bulava SLBM |
From Dmitry Donskoy (Typhoon) in White Sea. Failed. |
| 9 Sep | 1 SS-N-23 SLBM |
From K-84 (Delta IV) at North Pole, impact on Kizha range. |
| 10 Sep | 1 SS-N-18 SLBM |
From Delta III in Pacific, impact on Kizha range. |
| 25 Oct | 1 Bulava SLBM |
From Dmitry Donskoy (Typhoon) in White Sea. Failed. |
| 9 Nov | 1 SS-19 ICBM |
From Silo in Baykonur, impact on Kura range. |
| 21 Dec | 1 SS-18 ICBM |
From Orenburg, impact on Kura range. |
| 24 Dec | 1 Bulava SLBM |
From White Sea. Third stage failed. |
| United States | ||
| 16 Feb | 1 Minuteman III ICBM |
From Vandenberg AFB, impact Kwajalein. Final W87/Mk-21 SERV test flight. |
| Mar/Apr | 2 Trident II D5 SLBMs |
From SSBN. |
| 4 Apr | 1 Minuteman III ICBM |
From Vandenberg AFB, impact near Guam. Extended-range, single-warhead flight test. |
| 14 Jun | 1 Minuteman III ICBM |
From Vandenberg AFB, impact Kwajalein. Three-warhead payload. |
| 20 Jul | 1 Minuteman III ICBM |
From Vandenberg AFB, impact Kwajalein. Three-warhead flight test. Launched by E-6B TACAMO airborne command post. |
| 21 Nov | 2 Trident II D5 SLBMs |
From USS Maryland (SSBN-738) off Florida, impact in South Atlantic. |
| * Unreported events may add to the list. ** Iran does not have nuclear weapons but is suspected of pursuing nuclear weapons capability. *** It is unknown if North Korea has developed a nuclear reentry vehicle for its ballistic missiles. |
||
The Putin government’s reaffirmation of the importance of strategic nuclear forces to Russian national security was tainted by the failure of three consecutive launches of the new Bulava missile, but tests of five other missile types shows that Russia still has effective missile forces.
Along with China, Russia’s efforts continue to have an important influence on U.S. nuclear planning, and the eight Minuteman III and Trident II missiles launched in 2006 were intended to ensure a nuclear capability second to none. The first ICBM flight-test signaled the start of the deployment of the W87 warhead on the Minuteman III force.
China’s launch of the (very) long-awaited DF-31 ICBM and India’s attempts to test launch the Agni III raised new concerns because of the role the weapons likely will play in the two countries’ targeting of each other. But during a visit to India in June 2006, U.S. Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, General Peter Pace, downplayed at least the Indian issue saying other countries in the region also have tested missiles. In a statement that North Korea would probably find useful to use, Gen. Pace explained that “the fact that a country is testing something like a missile is not destabilizing” as long as it is “designed for defense, and then are intended for use for defense, and they have competence in their ability to use those weapons for defense, it is a stabilizing event.”
But since all “defensive” ballistic missiles have very offensive capabilities, and since no nation plans it defense based on intentions and statements anyway but on the offensive capabilities of potential adversaries, Gen. Pace’s explanation seemed disingenuous and out of sync with the warnings about North Korean, Iranian and Chinese ballistic missile developments.
The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) seeks to limit the proliferation of ballistic missiles, but that vision seems undercut by the busy ballistic missile launch schedule demonstrated by the nuclear weapon states in 2006. Some MTCR member countries have launched the International Code of Conduct Against Ballistic Missile Proliferation initiative in an attempt to establish a norm against ballistic missiles, and have called on all countries to show greater restraint in their own development of ballistic missiles capable of delivering weapons of mass destruction and to reduce their existing missile arsenals if possible.
All the nuclear weapons states portray their own nuclear ballistic missile developments as stabalizing and fully in compliance with their pledge under the Non-Proliferation Treaty to pursue nuclear disarmament in good faith. But fast-flying ballistic missiles are inherently destablizing because of their vulnerability to attack may trigger use early on in a conflict. And the busy missile testing in 2006 suggests that the “good faith” is wearing a little thin.
President Signs US-India Nuclear Cooperation Agreement
On Monday, President Bush signed into law the Henry J. Hyde United States and India Nuclear Cooperation Promotion Act of 2006. The Federation of American Scientists strongly supports better ties—economic, cultural, technical, even security ties—with India. Specifically with energy production, there are many ways in which U.S. know-how could help India and the technology flow is not all one way, for example, India is, along with the United States, one of the world’s leaders in wind energy. But India made tacit acceptance of their nuclear weapons program the price of better relations. The Federation strongly opposed the nuclear deal because of the proliferation implications. We organized petitions to Congress. Thirty seven Nobel Prize winners from our Board of Sponsors signed a letter to the Congressional leadership opposing the agreement. We had a press conference where Michael Krepon and Len Weiss argued against the agreement and we released the Nobelist letter. In the end, however, the president and the Congress seem to have accepted the price set by India and here we are.
(more…)
Entrenched Views of the Defense Science Board
Hans Kristensen has just posted an excellent analysis of the new Defense Science Board (DSB) report Nuclear Capabilities. The report presents what is known to the military as a “target rich environment” so we might make a few more comments over the next couple of days.
I want to focus here on the section, starting on p. 2, entitled “Some Entrenched Views on Nuclear Capabilities.” I will leave to the reader the analysis of the word “entrenched.” This section of the DSB report sets up some straw men and then knocks them down. But the straw is a bit tougher than they think.
(more…)
U.S. Nuclear Posture at a Crossroad, Defense Science Board Says

The Defense Science Board concludes in a new report that the United States has lost its “national consensus” on what the nation’s nuclear deterrent should look like and the role it should serve. The consensus has been replaced by an “entrenchment” of “sharp differences” of opinion. Therefore, urgent action is needed by the White House and senior leaders to “engage more directly to articulate the persuasive case” for how modern nuclear weapons serve U.S. national security policy.
U.S. nuclear policy has come to a crossroad because the current formula is no longer sustainable.
Perhaps not coincidently, the DSB report comes as the administration is preparing to persuade Congress to pay for a new nuclear weapons complex (Complex 2030) to resume production of nuclear weapons for the first since since the end of the Cold War. To that end, the report presents a wide range of recommendations for how to revitalize the U.S. nuclear posture.
Recommendations for nuclear weapons policy and forces include:
1. Leaders should declare “unequivocally and frequently” that nukes are still needed.
2. Establish a Red Team to look for nuclear enemies.
3. Establish a Deterrence Team to figure out how to better deter current and future adversaries.
4. The missile defense under construction is inadequate to deal with countermeasures and needs to be upgraded.
5. Accelerate development of “a credible Nuclear Leg of the Strike Triad.”
6. Figure out what to do with nuclear forces beyond the SORT treaty, but hedge (it is now called “remain reversible”) against negative developments in Russian and China.
7. Modernize the command and control system.
8. The Nuclear Weapons Council should establish a policy that no single warhead type makes up more than 20 percent of the deployed stockpile (i.e., the stockpile should consist of at least five different warhead types).
9. RRW-1, as the first Reliable Replacement Warhead prototype is called, should be a full weapons program.
Recommendations for the nuclear weapons production complex include:
1. Produce “a predetermined number of RRW-class warheads” per year by 2012.
2. Create a National Nuclear Weapons Agency to support Complex 2030.
3. Retain all three nuclear weapons labs.
4. The Secretary of Defense should figure out which is easier: sustain the current quantities and diversity of nuclear weapons or build new ones.
5. Create an Assistant Secretary of Defense for Strategic Weapons with a Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Nuclear Weapons.
6. Get congressional approval to appoint the Deputy Secretary of Defense as the Nuclear Weapons Council and make the commander of STRATCOM a member of the Nuclear Weapons Council.
Yet Another RRW Vision?
One of the surprises in the report is that the DSB seems to have a different long-term vision for the RRW than the administration. A drawing in the DSB report shows how the composition of nuclear warheads would change with the introduction of RRWs. The drawing a future mix of equal numbers of RRWs and existing life-extended warheads (see figure below).
|
DSB Stockpile Vision |
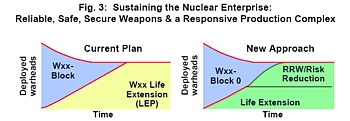 |
| The Defense Science Board report presents a nuclear stockpile vision that includes roughly equal numbers of the RRW and life-extended warheads. |
That vision is very different from the one presented by the Secretary of Energy, Secretary of Defense, and the Nuclear Weapons Council in their joint interim RRW report to Congress in March 2006. A drawing in that report showed a future mix of warheads where RRWs would replace all life-extended warhead types (see figure below).
|
DOD/DOE Stockpile Vision |
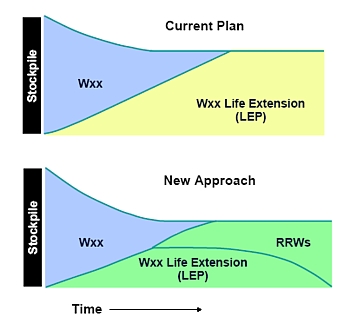 |
| The Department of Energy and Department of Defense vision for the nuclear stockpile includes a phaseout of all life-extended warheads leaving only RRWs. |
Analysis
The DSB report comes across as an attempt to “resell” the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review. It is a report on the defensive that suggests that critics of Cold War nuclear policy and excessive capabilities have had a considerable impact on U.S. nuclear policy and the mood inside the administration and Congress.
A major shortfall of the report is this: Despite lamenting that new thinking is urgently needed, the DSB report offers no new ideas for why it is necessary to revitalize the nuclear posture, except the arguments made in the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review and the 2004 DSB report on the future of strategic forces. Instead of defining the new agenda, the DSB report appears to be defending the current agenda.
This is perhaps not surprising considering that the entire DSB Task Force consisted of people from the nuclear labs, major defense contractors and conservative think tanks. Some were even the architects of the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review. All advisors are from the Pentagon, the nuclear agencies, and the nuclear labs. The DSB report’s primary conclusion is that new thinking is needed, but the list of participants and briefings received strongly suggests that no attempt was made to think “outside the box.”
The failure to involve others and new ideas is perhaps the worst enemy of U.S. nuclear policy, not to mention a disfavor to national and international security.
Background: Defense Science Report | US Nuclear Guidance
Britain’s Next Nuclear Era

After having spent the last several years sending diplomats to Teheran to try to persuade Iran not to develop nuclear weapons, the British government announced Monday that it plans to renew its own nuclear arsenal.
If approved by the parliament, Monday’s decision means that the United Kingdom will extend its nuclear deterrent beyond 2050, essentially doubling the timeline of its own nuclear era.
Doing so is entirely consistent with the United Kingdom’s international obligations under the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and with a policy that favors complete elimination of nuclear weapons, the government insisted in a fact sheet, because the British nuclear arsenal today is smaller than during the Cold War, and because the Treaty does not say exactly when nuclear disarmament has to be accomplished. In fact, the new plan has “the right balance,” the government claims, between working for a world free of nuclear weapons and keeping those weapons.
The Reduction
Probably in acknowledgment that it will be a hard sell domestically and internationally, the $40 billion nuclear plan was sweetened with an announcement that Britain will reduce the number of “operationally available warheads” from fewer than 200 today to fewer than 160 at some future date.
The gesture is somewhat hollow, however, because Britain only has enough Trident D5 missiles to arm three of its four SSBNs with a maximum of 144 warheads anyway. The Blair government previously decided in 1998 to purchase only 58 missiles instead of 65. Since then, eight missiles have been used in operational test launches, leaving 50 missiles in the inventory – barely enough to fill the tubes of three SSBNs.
The British government has stated that the single SSBN on patrol at any given time carries “up to 48” warheads, a statement that partly reflects that some of the missiles have been given a “substrategic” mission, probably with only one warhead each. Depending on the number of substrategic mission missiles carried, the actual loading of the patrolling submarine probably is 36-44 warheads. Assuming a similar loading for the other two SSBNs for which there are missiles available, the estimated number of warheads needed for the British SSBN fleet since the substrategic mission first became operational in 1996 is 108-132 warheads.
The announcement to retain “fewer than 160” operationally available warheads seems to reflect this existing reality rather than an additional operational reduction. But it raises the question why the British government for the past eight years has retained 20 percent more warheads than it actually needed.
The Catch
The plan to replace the submarines comes with a catch: Half-way through their service-life, the missiles will expire, necessitating further investment to purchase new missiles and possibly also new warheads. The U.K. government has already received, the White Paper states, assurance from the U.S. government that Britain can be a partner if the United States later decides to build a successor to the D5 missile, and that such a missile will be compatible, or can be made compatible, with Britain’s new SSBNs.
The Warheads
The type of warhead deployed on Britain’s D5 missiles will last at least into the 2020, according to the White Paper. But the U.K. government says it doesn’t yet know whether the warhead can be “refurbished” to last longer, or whether it will be necessary to develop a replacement warhead. The next Parliament will have to make that decision, the government says, an option that of course will be harder to reject if a decision has already been made to build the new submarines.
How British are the warheads on the British SSBN fleet? The Ministry of Defence stated in a fact sheet that the warheads on the D5 missiles were “designed and manufactured in the U.K.” Even so, rumors have persisted for years that the warheads are in fact modified U.S. W76 warheads.
Now a U.S. Department of Energy document – declassified after eight years of processing – directly links the warhead designs on U.S. and U.K. Trident missiles. The document shows that the “U.K. Trident System,” as the British warhead modification is called, is similar enough to the U.S. W76 warhead to make up an integral part of the W76 engineering, design and evaluation schedule (see figure below).
|
How British is Britain’s Nuclear Warhead? |
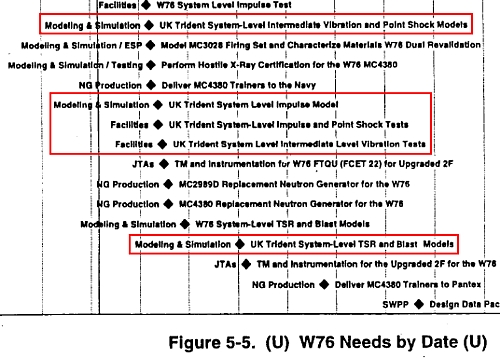 |
| The British Trident warhead is similar enough to the U.S. W76 to form an integral part of the U.S. Department of Energy’s “W76 Needs” schedule, according to this document declassified and released under the Freedom of Information Act. The document directly links the warhead designs on U.S. and U.K. Trident missiles. To download a PDF-copy of the declassified document, click here. |
Specifically, the document shows that between 1999 and 2001, work on five of 13 “W76 needs” involved the “U.K. Trident System.” These activities included vibration and point shock models, impulse models, impulse and point shock tests, vibration tests, as well as “TSR [thermostructural response] and Blast Models.”
The activities listed in the chronology are contained in a detailed database that “maps the requirements and capabilities for replacement subsystem and component modeling development, test, and production to the specific organizations tasked with meeting these requirements.”
The “U.K. Trident System” is thought to consist of a 100-kiloton thermonuclear warhead encased in a cone-shaped U.S. Mark-4 reentry vehicle. The W76 is the most numerous warhead (approximately 3,200) in the U.S. stockpile. Built between 1978 and 1988, about a third of the W76s are being modified as the W76-1 (see figure below) and equipped with a new fuze with ground-burst capability to “enable the W76 to take advantage of the higher accuracy of the D5” against harder targets. Delivery of the first W76-1 is scheduled for 2007 and the last in 2012. The W76 is also the first warhead scheduled to be modified under the proposed Reliable Replacement Warhead program.
|
The W76 |
 |
| This is believed to be the first publicly available picture of the W76. It shows the four First Production Units of the modified W76-1/Mk4A reentry vehicle. The British version of the W76 probably looks similar. Source: Sandia National Laboratories. |
The Nuclear Mission
The U.K. government presents several specific military and political justifications for why it intends to double Britain’s nuclear era.
One is that none of the other nuclear weapon states are even considering getting rid of their nuclear weapons, but instead are modernizing – some even increasing – their nuclear arsenals.
Another justification is that North Korea and Iran are pursuing nuclear weapons too, and that some countries might even “sponsor nuclear terrorism from their soil.”
Finally, the world is an uncertain and risky place, the White Paper concludes, and adds that it is “not possible to accurately predict the global security environment over the next 20 to 50 years.”
Those who question that these justifications are sufficient to retain the nuclear deterrent, Prime Minister Tony Blair writes in the foreword of the White Paper, “need to explain why disarmament by the U.K. would help our security.”
Analysis
The White Paper fails to identify a specific, urgent mission for British nuclear weapons. Instead, the justification to keep them seems like a little of everything: A couple of Cold War leftovers (Russia is still looming on the horizon and China might rise), a little sheep mentality (the other nuclear powers won’t give them up either), a little mission-creep (we might have to use them against proliferators), and a little hype (a role against terrorists). All of this is wrapped in the popular post-Cold War mantra that claims that the world suddenly is very uncertain and impossible to predict. As Prime Minister Tony Blair told the Parliament Monday:
“It is just that, in the final analysis, the risk of giving up something that has been one of the mainstrays of our security since the war [World War II], and moreover doing so when the one certain thing about our world today is its uncertainty, is not a risk I feel we can reasonably take.” The world has changed “beyond recognition,” and “it is precisely because we could not have recognized then, the world we live in now, that it would not be wise to predict the unpredictable in the times to come.”
Of course, it is one thing to argue that Britain needs a nuclear bomb in the basement or a mothballed nuclear production capability just in case. It is quite another to claim that strategic submarines need to continue to hide deep in the oceans much like they did during the Cold War without an urgent threat against the survival of the nation.
That’s for the U.K. Parliament to debate in the next months, followed – presumably – by a decision whether to approve the government’s plan sometime in 2007.
Background: MOD White Paper and Fact Sheets | British Nuclear Forces, 2005
New Report: Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning

An incipient nuclear arms race is emerging between China and the United States, according to a new report published today by the Federation of American Scientists and the Natural Resources Defense Council.
The 250-page report, Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning, outlines the status and possible future development of China’s nuclear weapons, describes the history of U.S. nuclear targeting of China, and simulates nuclear strike scenarios between the two nuclear powers.
Both countries are pointing to the other as an excuse to modernize nuclear forces. In the United States the report finds that the Pentagon, the intelligence community, congressional committees, private institutes and the news media frequently overstate Chinese capabilities or present dramatic new developments out of context to underscore a threat.
China, for its part, cloaks its nuclear forces in a veil of secrecy, which creates suspicion and fear in other countries about Chinese intentions.
The report, which is based on analysis of declassified and unclassified U.S. government documents as well as commercial satellite images of Chinese installations, urges both countries to take steps to halt and reverse the tension and military build-up.
China’s Nuclear Forces
The report estimates that China has a stockpile of approximately 200 nuclear warheads, of which roughly 140 are deployed. About 100 of the warheads are for use by ballistic missiles while 40 are bombs for delivery by aircraft.
Given the almost complete lack of information from Chinese authorities about the size and composition of the stockpile, the FAS/NRDC estimate largely builds on analysis of declassified and unclassified assessments produced by U.S. government agencies over the years. Those assessments have been fraught with inaccuracy and inconsistency, the report finds, with a strong predisposition towards making worst-case predictions for stockpile size, weapons range and deployment.
This tendency continues today, and the report takes issue with the core prediction made by the intelligence community that says that the number of Chinese warheads primarily targeted against the continental United States will increase from 20 today to 75-100 warheads by 2015. The prediction assumes 40-55 new DF-31A missiles will be deployed over the next nine years in addition to the DF-31 and JL-2 missiles, a questionable estimate given that the DF-31A has not even been flight tested.
Chinese Submarines
The report discloses for the first time the number of patrols that Chinese submarines conduct each year. The capability of the Chinese submarines fleet is a hot issue following news media reports earlier this months about a Chinese submarine surfacing undetected near the USS Kitty Hawk carrier battlegroup off Okinawa, claims by the Pentagon that the Chinese navy is expanding its reach deep into the Pacific, and the U.S. Congress’ US-China Commission reporting earlier this month that China “continues to expand” its submarine fleet.
Yet the FAS-NRDC report shows that the Chinese submarine fleet is in steep decline from 120 submarines in the mid-1980s and expected by the U.S. navy to level out around 40 submarines in the next decade. The report shows that Chinese submarines rarely sail on patrol, that the entire submarine fleet in average conducts two patrols per year, that the most patrols conducted in a single year were six (in 2000), and that no patrols were conducted at all in 2005.
The report also reveals that China’s single ballistic missile submarine has never sailed on a nuclear deterrent patrol.
US Nuclear Targeting of China
Through analysis of declassified Pentagon documents, the report finds that U.S. nuclear targeting of China in the past has been considerably more prominent than normally assumed in the public debate. During the 1970s, for example, half of the major nuclear attack options in the U.S. strategic nuclear war plan were aimed at China.
After a hiatus in the 1980s precipitated by a joint U.S.-Chinese stand against the Soviet Union, U.S. nuclear targeting of China has increased after the end of the Cold War. The U.S. navy now bases the majority of its ballistic missile submarines in the Pacific, modernizing their nuclear missiles, and forward-deploying strategic bombers to Guam.
Nuclear Simulations
The report also presents the result of number of simulated nuclear strike scenarios between the two countries, showing that both have more than adequate capability to deter each other. The simulations are striking because they show that regardless of whether the strike is an imprecise Chinese “countervalue” attack on cities, or a highly accurate U.S. “counterforce” attack on military facilities, the result would be tens of millions of innocent civilian casualties.
A Chinese attack with 20 ICBMs would result in as many as 40 million casualties, the report estimates, and blanket large portions of the United States and Canada with radioactive fallout. Likewise, a limited and highly accurate U.S. nuclear attack on China’s 20 long-range ballistic missile silos would result in as many as 11 million casualties and scatter radioactive fallout across three Chinese provinces.
Take Google Earth Trip of Chinese Military Facilities
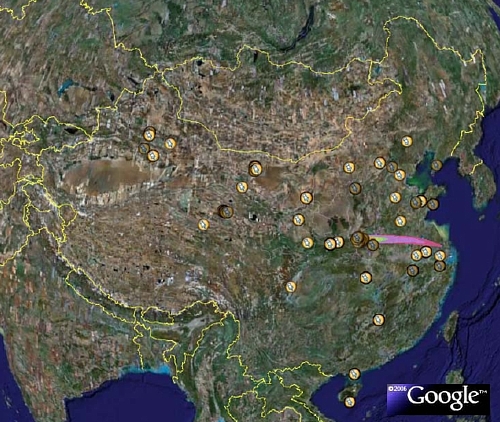 |
|
Download the FAS-NRDC Google Earth file here. |
Making use of the unique capabilities of the free Google Earth program, FAS and NRDC have designed a virtual trip of selected nuclear and military facilities in China. Here is how to use it:
1. Download Google Earth onto your computer.
2. Click here or on the link below the map above to download the FAS-NRDC Google Earth file. The program will ask you to either open in Google Earth or download to your hard drive.
3. When Google Earth has finished loading on your computer, make sure the check-box “Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning” in the “Places” window to the left is checked to activate the placemarks.
4. Click once on the first placemark (“Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning”) to open the text “bubble” with information.
5. If all the placemarks have not opened automatically, click the “plus-box” to the left of the “check-box” in the “Places” window.
6. Those placemarks with an icon that looks like the Google Earth logo or a file-folder contain additional sub-placemarks. Click on the “plus-box” to open each folder. Note that some air bases contain sub-placemarks for each aircraft.
7. Double-click on each consecutive placemark to zoom in on each facility. Don’t forget to use the “tilt” and “rotate” functions of Google Earth to get a better view.
8. The last two folders contain graphic displays of nuclear strike simulations. These simulations are explained in detail in the Chapter 4 of the report (download from here).
Download: Full Report | Individual Chapters | Google Earth Map
US-China Commission Report Toned Down; Errors Remain

The annual report published Monday by the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission is different – kind of toned-down – compared with the report published in 2005. The Commission hasn’t gone soft on China, and the report continues the strong critique of China that has characterized the Commission since it was established in 2000. But much of the stronger language from the 2005 report, and many of the more questionable claims about Chinese nuclear weapons capabilities, did not make it into the new report.
The toning-down of the report follows reports earlier this year that the Pentagon’s annual report on Chinese military capabilities was also softened before publication. A call to the US-China Commission office about why the changes were made was not answered.
Noticeable changes in the 2006 report compared with last year include:
* Deletion of the top recommendation that Congress should “encourage increasing U.S. military capabilities in the Western Pacific in response to growing Chinese capabilities.” This blunt call for an arms race is replaced in the new report with a recommendation that DOD includes in its annual report on China’s military power “an assessment of U.S. weapon systems, force structure, basing, doctrine, and tactics in order to maintain a favorable balance of military power in the region” to ensure that the Pentagon can beat the Chinese in a war.
* Deletion of the erroneous claim that China’s next-generation long-range nuclear ballistic missiles will carry multiple warheads. In last year’s report, this claim was based on two non-authoritative sources: a Heritage Foundation brochure and a Japanese news paper article. The U.S. intelligence community, in contrast, has consistently stated that the missiles will be equipped with single warheads.
* Deletion of the erroneous claim that the Chinese navy has nuclear-armed anti-ship cruise missiles.
* The section “Expansion of China’s Nuclear Forces” is now simply called “Missiles.”
While it is a positive development that the Commission has made these changes, the 2006 report by no means looses sight of the Commission’s mandate to report on China’s military modernization and force deployments. Yet there are several claims in the 2006 report that stand out:
* A big one is that China is said to be pursuing measures to “control” the seas in the “Western Pacific.” But as anyone with just a little knowledge of naval operations understands, gaining “control” over an area requires superior capabilities, something China simply does not have now nor is likely to acquire in the foreseeable future. It is one thing to try to achieve “control” of a limited coastal area between China and Taiwan, but quite another to achieve it in the “Western Pacific” as the Commission says.
* Another claim is that China “continues to improve its older intercontinental ballistic missiles,” which, although true, forgets to mention that this particular improvement of the DF-5 missile has been underway since the 1980s and is now finally nearing completion. Slow and long-term is typical for Chinese nuclear programs.
* The Commission also claims that a new missile currently under development – the DF-31A – “will be the first Chinese ICBM capable of hitting Washington, DC.” Not so, unless the U.S. intelligence community has been wrong or lying for 30 years. According to numerous declassified documents, unclassified official reports and official statements made by the intelligence community, China has been targeting all of the United States with the DF-5 since the early 1980s. But the suggestion that DF-31A has a longer range than DF-5 echoes information contained in the 2006 DOD report on China’s military forces. A map in that report showed a DF-5 range considerably shorter than shown on a map in the 2005 DOD report. Whether the U.S. intelligence community has decreased its estimate for the DF-5 range or simply made an error (that everyone keeps repeating) is unknown.
* The Commission report also claims that China “continues to expand” its submarine fleet, when, in fact, it is not. On the contrary, China’s submarine fleet is in sharp decline, down from approximately 120 boats in the mid-1980s to about 60 today. While the Commission report focuses on highlighting China’s acquisition of new submarines, U.S. Naval Intelligence anticipates that the Chinese submarine fleet will level out at around 40 boats.
Over the past two years, military-to-military contact has increased between China and the United states, not least thanks for the efforts of Admiral William J. Fallon, the commander of U.S. Pacific Command. Likewise, U.S. Strategic Command has begun direct conversions with its Chinese counterpart about the role of nuclear weapons. The U.S.-China Commission report acknowledges this development, but complains that the military-to-military contacts “may disproportionally benefit the” Chinese by increasing their knowledge of U.S. military capabilities.
To ensure that the United States doesn’t t fall behind, the Commission has a solution: increase U.S. spying against China. This is a curious recommendation, given that allegations about Chinese spying against the United States is what gave birth to the U.S.-China Commission in the first place.
The overall impression I get from the Commission’s report is that it spends too much time on reporting dramatic new developments and too little time on analyzing what its all means. To that end it is important not only to get the facts right but also to describe them in context. China is modernizing its military forces – as are virtually all of its neighbors including the United States. All these players are engaged in a dangerous game of deterrence that creates fear and suspicion and triggers requirements for better weapons and bolder war plans.
The challenge for the United States and its allies in the region is not, as the Commission seems to believe, to continue to deploy more and better weapons to counter China’s military modernization, but to figure out how to create a foreign policy that ends the mistrust.
|
New report |
New Article: Where the Bombs Are
 |
| B83 thermonuclear bombs at Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana. Image © Paul Shambroom |
Ever wondered where all those nukes are stored?
A new review published in the November/December issue of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists shows that the United States stores its nearly 10,000 nuclear warheads at 18 locations in 12 states and six European countries.
The article’s authors – Hans M. Kristensen of the Federation of American Scientists and Robert S. Norris of the Natural Resources Defense Council – identified the likely locations by piecing together information from years of monitoring declassified documents, officials statements, news reports, leaks, conversations with current and former officials, and commercial high-resolution satellite photos.
The highest concentration of nuclear warheads is at the Strategic Weapons Facility Pacific in Bangor, Washington, which is home to more than 2,300 warheads – probably the most nuclear weapons at any one site in the world. At any given moment, nearly half of these warheads are on board ballistic-missile submarines in the Pacific Ocean.
Approximately 1,700 warheads are deployed on Ohio-class ballistic missile submarines operating in the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, and about 400 warheads are at eight bases in six European countries – Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Turkey and Great Britain (for more information on U.S. warheads in Europe, go to http://www.nukestrat.com/us/afn/nato.htm). The United States is the only nuclear weapon state that deploys nuclear weapons in foreign countries.
Consolidation of U.S. nuclear storage sites has slowed considerably over the past decade compared to the period between 1992 and 1997, when the Pentagon withdrew nuclear weapons from 10 states and numerous European bases. Over the past decade, the United States removed nuclear weapons from three states – California, Virginia and South Dakota, and from one European country – Greece.
The overview finds that more than two-thirds of all U.S. nuclear warheads are still stored at bases for operational ballistic missiles and bombers, even through the Cold War ended more than 16 years ago. More than 2,000 of those warheads are on high alert, ready to launch on short notice. Only about 28 percent of U.S. warheads have been moved to separate storage facilities. The largest of these, an underground vault at Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico, stores more than 1,900 warheads.
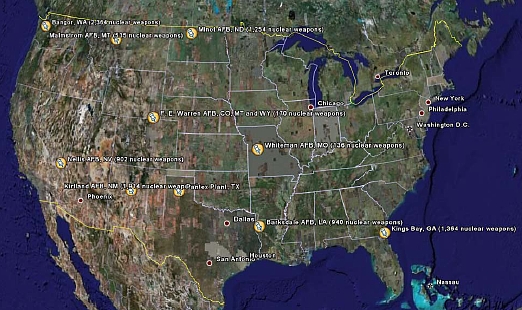
The 10 U.S. sites that currently host nuclear weapons are: the Strategic Weapons Facility Pacific, Bangor, Washington; Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada; Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming; Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico; Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana; Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota; Pantex Plant, Texas; Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana; Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri; and the Strategic Weapons Facility Atlantic, Kings Bay, Georgia. (See map.)
 |
|
Full-size map available here. Full article available from Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists here. |
Go on a Nuclear Google Trip
Based on the information in the Bulletin article, FAS and NRDC have created a virtual satellite image tour of the 18 nuclear weapons storage facilities in the United States and Europe. To take the tour you need to have GoogleEarth installed on your computer. (GoogleEarth is available for free here.) Once you’re set up, click here or on the link below the Google map below to begin. When GoogleEarth has finished loading, check the “Where the Bombs are, 2006” box in the “Places” window to the left to activate the placemarks, click once on a placemark to get an overview of the nuclear weapons stored at the base, and click twice to zoom in on the facility.
The U.S. government refuses to disclose where it stores nuclear weapons, but the researchers emphasize that all the locations have been known for years to house nuclear weapons. Safety of nuclear weapons is determined not by knowledge of their location but by the military’s physical protection of the facilities and that the weapons cannot be detonated by unauthorized personnel.
Background: Where the Bombs are, 2006 | Status of World Nuclear Forces