Russian Nuclear Missile Submarine Patrols Decrease Again

By Hans M. Kristensen
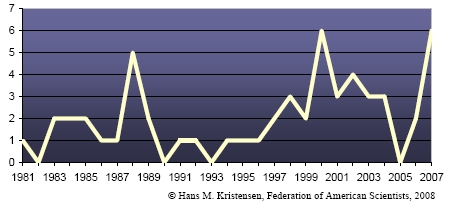
The number of deterrence patrols conducted by Russia’s 11 nuclear-powered ballistic missiles submarines (SSBNs) decreased to only three in 2007 from five in 2006, according to our latest Nuclear Notebook published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
In comparison, U.S. SSBNs conducted 54 patrols in 2007, more than three times as many as all the other nuclear weapon states combined.
The low Russian patrol number continues the sharp decline from the Cold War; no patrols at all were conducted in 2002 (see Figure 1). The new practice indicates that Russia no longer maintains a continuous SSBN patrol posture like that of the United States, Britain, and France, but instead has shifted to a new posture where it occasionally deploys an SSBN for training purposes.
An Occasional Sea-Based Deterrent
The shift to an occasional sea-based deterrent became apparent in 2007, when then Defense Minister Sergei Ivanov declared on September 11 that five SSBNs were on patrol at that time. Four months later, I received information from U.S. Naval Intelligence showing that those five patrols were all Russian SSBNs did that year. Combined, the two sources indicated a cluster of patrols at approximately the same time rather than distributed throughout the year.
|
Figure 1: |
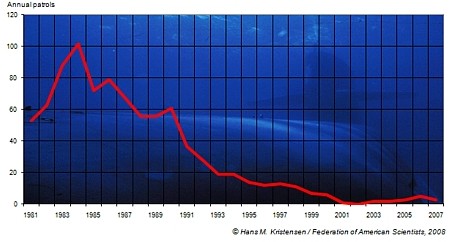 |
| Russian SSBNs conducted only three deterrent patrols in 2007, a decline from five in 2006. |
.
The reason for the shift is unclear. Perhaps the Russian navy is still not over the financial and technical constraints that hit it after the collapse of the Soviet Union. SSBNs can launch their missile from pier side if necessary, although such a posture essentially converts each SSBN into a very soft and vulnerable target. Russia might simply have decided that it’s no longer necessary to maintain a continuous nuclear retaliatory force at sea, and that a few training patrols are all that’s needed to be able to deploy the SSBNs in a hypothetical crisis if necessary.
SSBN Patrol Areas
Little is known in public about where Russian SSBNs conduct their deterrent patrols. However, in 2000, U.S. Naval Intelligence released a series of rough patrol maps for Soviet/Russian SSBNs that showed the locations of the patrol areas used by Delta IV and Typhoon class SSBNs in the late-1980s and 1990s (see Figure 2). The few SSBNs that occasionally sail on patrol today probably use roughly the same areas.
|
Figure 2: |
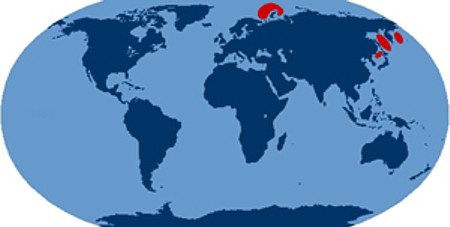 |
| Russian SSBN patrol areas today are probably similar to those used in the 1990s. |
.
In Perspective
The decline in SSBN patrols is in stark contrast to Russian bomber and surface fleet operations in 2006-2007, which are said to have increased in scope and reach. For now, at least, SSBN patrols are not used to “signal” Russian status.
Approximately 20 percent of Russia’s strategic warheads are sea-based. But with the upcoming replacement of old Delta III SSBNs and their three-warhead missiles with the new Borey SSBNs (the first of which is scheduled to enter service later this year) with six-warhead missiles, the SSBNs’ share of the posture might increase to approximately 30 percent by 2015.
Overall, the Nuclear Notebook estimates that Russia currently has approximately 5,200 nuclear warheads in its operational stockpile, including some 3,110 strategic and 2,090 non-strategic warheads. Another 8,800 warheads are thought to be in reserve or awaiting dismantlement.
Additional information: Russian Nuclear Forces 2007, Nuclear Notebook, Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists
New Chinese SSBN Deploys to Hainan Island
By Hans M. Kristensen
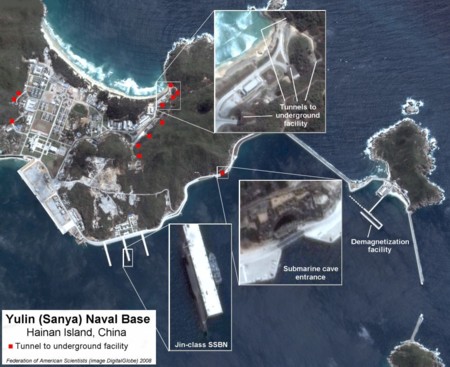
The Chinese navy has deployed a Jin-class (Type 094) ballistic missile submarine to a new base near Yulin on Hainan Island on the South China Sea, according to a satellite image obtained by FAS. The image shows the submarine moored at a pier close to a large sea-entrance to an underground facility.
Also visible is a unique newly constructed pier that appears to be a demagnetization facility for submarines.
A dozen tunnels to underground facilities are visible throughout the base compound.
The satellite image, which has also been described in Jane’s Defense Weekly, was taken by the QuickBird satellite on February 27, 2008, and purchased by FAS from DigitalGlobe.
The Arrival of the Jin-Class Submarine
The dimensions of the submarine in the satellite image are similar to the Jin-class SSBN I spotted at Xiaopingdao Submarine Base in July 2007 and the two Jin-class SSBNs I detected at the Bohai shipyard in October 2007.
China is believed to have launched two Jin-class SSBNs with a third possibly under construction. The U.S. Intelligence community estimates that China might possibly build five SSBNs if it wants to have a near-continuous deterrent at sea. Of course, it is not known whether China plans to operate its SSBNs that way. See Figure 1 for the location of the submarine.
.
Missile loadout of the SSBN will probably take place at pierside at the main pier to the left of the narrow triple-pier where the submarine is seen, unless the underground facility is large enough to permit such operations out of satellite view. Not yet visible at the base is a dry dock large enough to accommodate an SSBN; the Northern Fleet submarine base at Jianggezhuang has a dry dock.
New Demagnetization Facility
One of the most interesting new additions to the base is what appears to be a submarine demagnetization facility (see Figure 2). Located in the southern part of the base and connected by pier to a facility on a small island, the demagnetization facility closely resembles such facilities at U.S. SSBN bases. Demagnetization is conducted before deployment to remove residual magnetic fields in the metal of the submarine to make it harder to detect by other submarines and surface ships. There is no demagnetization facility at the Jianggezhuang base, so this appears to be a new capability for China.
|
Figure 2: |
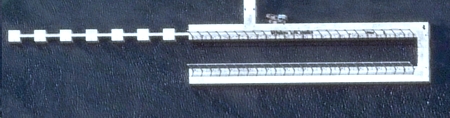 |
| Since 2005, what appears to be a submarine demagnetization facility has been added to the base. Click on image for larger photo. |
.
Underground Facilities
The base has extensive underground facilities. The most obvious is a large portal over a sea-entrance to what is probably an underground facility. The entrance appears to be approximately 3 meters (15 feet) wider than a similar entrance at the Northern Fleet Jianggezhuang Naval Base (see Figure 3 for comparison).
|
Figure 3: |
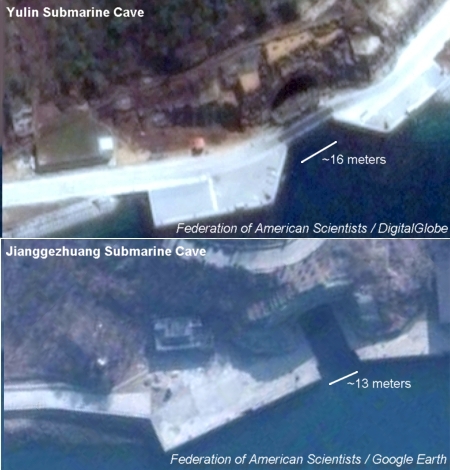 |
| The submarine cave entrance at Yulin Naval Base (top) is approximately 3 meters wider than the one at Jianggezhuang Naval Base. Click on image for larger photo of the Yulin entrance. Description of the Jianggezhuang facility is available here. |
.
Although the interior of the facility is not known, it probably includes a canal at least the length of one submarine as well as halls for handling or possibly storing equipment as well as rooms for personnel. Directly on the other side of the mountain are several land-entrances that might connect to the central facility as well, although none of this is known for sure. Two of those entrances appear from their shadows to be very tall structures (see Figure 4).
.
Some Implications
The SSBN base on Hainan Island will probably be seen as a reaffirmation of China’s ambitions to develop a sea-based deterrent. To what extent the Chinese navy will be capable of operating the SSBNs in a way that matters strategically is another question. China’s first SSBN, the Xia, was no success and never sailed on a deterrent mission. As a consequence, the Chinese navy has virtually no tactical experience in operating SSBNs at sea. Yet the Jin-class and the demagnetization facility on Hainan Island show they’re trying.
The location of the base is important because the Indian government already has pointed to a future threat from Chinese missile submarines operating in the South China Sea or Indian Ocean. The arrival of the Jin-class in Hainan will probably help sustain India’s own SSBN program. For China to sail an SSBN into the India Ocean and operate it there in a meaningful way, however, will be very difficult and dangerous in a crisis. Chinese SSBNs are more likely to stay close to home.
The base on Hainan Island is near deep water and some analysts suggest this will support submarine patrols better that operations from the Northern Fleet base at Jianggezhuang. Of course, if the water is so shallow the submarine can’t submerge fully it will limit operations, but deep water is – contrary to popular perception – not necessarily an advantage. Military submarines generally are not designed to dive deeper than 400-600 meters, so great ocean depth may be of little value. The U.S. navy has several decades of experience in trailing Soviet SSBNs in the open oceans; shallow waters are much more challenging. And the South China Sea is a busy area for U.S. attack submarines, which have unconstrained access to the waters off Hainan Island. And I’d be surprised if there were not a U.S. “shadow” following the Jin-class SSBN when it arrived at Hainan Island.
Additional information: Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning | Chinese Submarine Patrols Rebound in 2007, but Remain Limited | A Closer Look at China’s New SSBNs
Finally, Some Sense About Uranium and Dirty Bombs
The Columbian military recently raided FARC camps just across their borders. The Columbians confiscated lap top computers containing emails between the FARC and dealers offering to sell them explosives, which the emails suggested included uranium that the dealer was willing to sell for about one million dollars a pound. The press has several times bit on these types stories, sensationalizing them and getting the science all wrong.
There seems to be a widespread idea that uranium can be used for nuclear weapons. Well, it can. That is, one isotope of uranium can be, but natural uranium is less than 1% of that isotope and enriching it is a daunting technical challenge. (Many chemical elements have more than one isotope, atoms that have identical chemical properties but slightly different weights.) Since uranium can power nuclear weapons and nuclear bombs, it must be highly radioactive and could at least be used as a dirty bomb, right? Wrong, but you would never know by reading most such stories in the newspapers. So it is refreshing to read a story that gets it right and is properly skeptical. Kelly Hearn of The Washington Times has written that piece. (more…)
Old Anti-nuclear Movie from FAS
The Federation of American Scientists was formed just a couple of months after the dawning of the nuclear age by scientists as who had worked on the Manhattan Project to develop the world’s first nuclear weapons. In the fall of 1945, there was tremendous interest in the new atomic bomb: what it was, how it worked, and its effects–and not just direct effects but the effect this invention would have on the military balance and politics of the world. FAS organized a group of its members, which it called the National Committee on Atomic Information, to talk to the public, the press, and political leaders, and to produce media materials for distribution. (Sixty two years later and we still seem to be at it…)
Jeff Aron here at FAS recently came across this amazing little film on YouTube called One World or None. It was produced by FAS and the National Committee. I have to admit, no one currently at FAS knew about it, it predates anyone’s memory here, and we are ourselves doing some research on its origins and asking our long-term members what they know. (If any of our blog readers can provide any information, please let us know.) Presumably, it was released in conjunction with the release of the first publication of the Federation, also called One World or None, a collection of essays by great scientists of the day, including Albert Einstein, that was first published in 1946. One World has recently been reprinted by the New Press in New York and is available through bookstores, Amazon, and the FAS website.
The film is clearly a bit dramatic, but the dangers of nuclear weapons are dramatic. By today’s standards, the graphics are Stone Age but the message is as important today as it ever was and doesn’t depend on fancy graphics. I can’t say you should enjoy this little film–not much to enjoy when discussing nuclear dangers–but I hope you take it to heart. The Federation is still working to reduce the global threat of nuclear weapons.
Chinese Nuclear Arsenal Increased by 25 Percent Since 2006, Pentagon Report Indicates
 |
| China’s nuclear weapons arsenal has increased by 25 percent since 2006, Pentagon reports indicate, due to deployment of new ballistic and cruise missiles. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
| Updated April 8, 2008 |
The Pentagon’s 2008 annual report to Congress on China’s military power indicates, when compared with previous versions, that China has increased its nuclear arsenal by 25 percent since 2006. The increase has happened due to deployment of new long-range solid fueled ballistic missiles and cruise missiles.
Part of the increase can be expected to be offset by retirement of older liquid fueled missiles over the next several years, but the trend is toward a slightly larger arsenal in the future.
As a reminder of the tendency to estimate too much too soon, however, the 2008 report lowers the range estimates for all three types of China’s new long-range ballistic missiles, one of them by as much as 10 percent.
DF-31 and DF-31A Being Deployed
A decade after the Department of Defense (DOD) first projected the DF-31 would be deployed, the 2008 report finally concludes that the missile is “now being deployed to units within the Second Artillery Corps.” The report lists less than 10 (“<10”) DF-31 missiles deployed on as many launchers. Last year’s report listed the DF-31 as having achieved “initial threat availability in 2006” and possible “operational status” by May 2007.
| Figure 1: DF-31 Deployment Said to be Underway |
 |
| The DOD reports says the DF-31 (shown here) and its longer-range DF-31A version are now being deployed to Second Artillery Corps units. |
–
More surprising is that the DF-31A is now said to be deploying. The missile, which is a longer-range version of the DF-31, has not previously been reported flight tested or with “initial threat availability,” but less than 10 missiles are now said to be deploying to Second Artillery Corps units. Like the DF-5, which has been operational since 1981, the DF-31A can target the Continental United States, and much of the intelligence community’s 2001 prediction of “about 75 to 100 warheads deployed primarily against the United States” by 2015 hinges upon whether China deploys 40-55 DF-31As over the next eight years (see pp. 39-41 in Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning, FAS/NRDC, November 2006).
The range estimates for both missiles are lowered. The range for the DF-31 is lowered by 50 km from 7,250+ to 7,200 km (4,505+ to 4,474 miles), after it was thought only a few year ago that the range was 8,000+ km (4,971+). The DF-31 cannot be used to target the Continental United States, and will only be able to reach Hawaii from the most North-Eastern districts of China.
The DF-31A range estimate is lowered from 11,270+ to 11,200 (7,003+ to 6,959+ miles), or to a range 14 percent less than that of the DF-5A.
The Mysterious Growth of the DF-21 Force
A significant portion of the arsenal increase comes from additional DF-21 (CSS-5) that the Pentagon says have been deployed since 2006. The 2008 report estimates that 60-80 DF-21s are now deployed with 60 launchers, significantly more than the 40-50 missiles estimated to be deployed with 34-38 launchers in 2007, and the 19-50 missiles stated in the 2006 report.
Previous versions of the DOD report listed two versions of the DF-21 – Mod 1 and Mod 2 – but the 2008 report only lists one nuclear version with no Mod-number.
It is possible, although not clear from the DOD report, that the 60-80 DF-21s include the “conventionally-armed ASBMs [Anti-Ship Ballistic Missiles] based on the SS-5 (DF-21) airframe,” that the report also describe. Since the “Nuclear Force Structure” section of the report only describes “upwards of 50 CSS-5 road mobile, solid fueled SRBMs (for regional deterrence missions),” it is possible that the remaining 20, or so, DF-21s refer to the conventional ASBMs. Consequently, I have only counted 60 nuclear DF-21s in this estimate.
In July 2007, I described changes to the missile launch sites at Delingha, which indicated deployment of DF-21 missiles at the sites (see Figure 2). The DF-21 has been replacing DF-3As since the early 1990s at a slow rate.
| Figure 2: Possible DF-21 Deployment at Delingha |
 |
| An increase in deployed DF-21 medium-range ballistic missiles is reported by the Pentagon. Commercial satellite images in 2007 indicated possible DF-21 deployment at Delingha in the northern parts of Central China. |
–
DF-25, What DF-25?
The DOD report is quiet on the new missile launcher that appeared on images (see Figure 3) circulating on the Internet in 2007. The images led many to speculate that the earlier DF-25, widely believed to have been canceled, had been revived and deployed with as many as three nuclear warheads.
I doubted that assessment – China is not known to have deployed multiple warheads on any of its ballistic missiles – and asked Air Force Intelligence officials on several occasions last year to comment on the images. They told me that they had seen the photo but were not ready to officially comment yet. Nor is apparently the Office of the Secretary of Defense, and the silence of the 2008 report on this development indicates that the “DF-25” instead may be the “conventionally-armed [Anti-Ship Ballistic Missile] based on the CSS-5 (DF-21) airframe.”
| Figure 3: Possible Modified DF-21 Launcher |
 |
| Images circulated on the Internet in 2007 showed what many concluded was a DF-25 launcher. The DOD report does not confirm or comment on the existence of a DF-25, but lists one nuclear and one conventional DF-21. |
–
DH-10 Cruise Missile Deployed
The DOD report also states that China has now deployed the DH-10 cruise missile; an unspecific 50-250 missiles on 20-30 launchers. The DH-10, which appears to be a Chinese version of the U.S. Tomahawk cruise missile, can carry either a conventional or nuclear warhead and has a range or more than 2,000 km (1,243+ miles). Both air- and ground-launched versions are said to exist, and the H-6 bomber appears to be undergoing an upgrade to carry up to six DH-10s (see Figure 4).
| Figure 4: DH-10 Cruise Missile Deployed |
 |
| The DOD report says China has deployed 50-250 DH-10 land-attack cruise missiles. The H-6 bomber is being upgraded to carry perhaps up to six missiles (see above), which can also be fired from ground-based launchers. sinodefenceforum.com |
–
The DOD report does not give an estimate for how many nuclear variants of the DH-10 are deployed with ground forces or H-6 wings, and the vague 50-250 total estimate leaves much uncertainty. A medium range estimate (150) might be a reasonable total estimate, of which perhaps only a dozen or so may be nuclear at this stage.
Submarine Force Modernizing But Stable
Curiously, only one Jin-class SSBN is mentioned, although commercial satellite images clearly show that at least two are under construction. In contrast to the 2007 report, however, the 2008 version gives a somewhat halfhearted endorsement the projection made by the Office of Naval Intelligence in 2007, by saying that China “will likely” build “up to five JIN-class SSBNs.” This is a less certain prediction than the one made by ONI, which said a fleet of “probably five TYPE 094 class SSBNs will be built….” On the other hand, while ONI avoided setting a year, the DOD report predicts that it will likely be 2010. But that seems a highly unrealistic projection, given that none of the Jin-class SSBNs are yet operational and that only two hulls have been launched so far.
As for sea-launched ballistic missiles, the DOD report no longer lists the JL-1, indicating that the weapon system is not considered fully operational. It has probably never been, but this is the first time the missile chart in the DOD report reflects that reality.
The new JL-2 is also not operational, but included in the missile chart. Initial Operational Capability might be achieved in 2009-2010, DOD predicts. The estimate for the JL-2’s range, however, is lowered by 10 percent from 8,000+ to 7,200+ km (4,971+ to 4,474 miles). The 8,000+ km estimate has long been questionable, and the new estimate is the same as for the DF-31 from which the JL-2 is derived. The JL-2 cannot target the Continental United States from Chinese waters, and will have to sail into the Sea of Japan or past the Japan-Okinawa island chain to target Hawaii.
Mysteriously, the DOD report continues the practice from last year of assigning 10-14 missiles to each Chinese SSBNs, a curious estimate given that images of the boats clearly show 12 launch tubes.
As for the SSBN mission, the DOD report echoes my conclusion that despite construction of new SSBNs, the lack of deterrent patrols means that China essentially has no experience in operating a sea-based deterrent in a way that would matter strategically. According to the DOD report, “the PLA has only a limited capacity to communicate with submarines at sea and the PLA Navy has no experience in managing an SSBN fleet that performs strategic patrols.”
Overall, despite recent media reports about “rapid expansion” of the Chinese submarine fleet, the DOD report shows an attack submarine fleet that is relatively stable around 54 diesel submarines and 4-5 nuclear-powered attack submarines. Although new diesel submarines are being commissioned, older types are being retired at the same time. Only 4 of the old Han-class SSNs are left, and the report leaves some confusion about the status of the new Shang-class SSN by including it in the naval forces table but stating elsewhere that it is not expected to be operational until 2010.
Nuclear (Military) Talks Underway
Finally, what the report doesn’t describe, but which the Pentagon announced earlier this week, is that China and the United States have now “agreed to move forward on our dialogue on nuclear strategy and policy.” A process is “in place now,” DOD says, that over the next couple of months will begin with “a discussion between Chinese military officers and Chinese military academics and counterparts here in the U.S.” An invitation was extended in November 2006 to General Jing Zhiyuan, head of Second Artillery Corps, to meet directly with his counterpart at U.S. Strategic Command.
Read more: Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
Nuclear Safety and the Saga About the Missing Bent Spear

By Hans M. Kristensen
The recent Senate Armed Services Committee hearing on Air Force nuclear weapons safety was a welcome but long-overdue event. Internal reports about deteriorating nuclear weapon safety and surety in the Air Force have been accumulating since the early 1990s, but six nuclear weapons had to “disappear” for a day from Minot Air Force Base last August to get the Pentagon and Congress to finally pay attention. Had it not been for reporter Michael Hoffman at Military Times, the incident likely would have been filed away in secret cabinets as well.
Two internal investigations have identified numerous deficiencies in the handling and management of nuclear weapons within the military and have recommended substantial changes. Some of the obvious recommendations – such as not storing nuclear and conventional weapons in the same bunker and that personnel must follow the rules – have now been implemented. Others will require more effort.
Yet the investigations have revealed an inherent problem in post-Cold War nuclear planning: self-management and lack of independent oversight. Indeed, the investigations themselves appear to have been hampered by the same shortcomings. The result is an inherent conflict between scrutinizing and promoting the nuclear mission and a reluctance to change things too much.
As a consequence, the reviews recommend revitalizing the nuclear mission and returning the bombers to a heightened nuclear alert posture to improve safety, while missing the most obvious and effective fix: removing nuclear weapons from bomber bases and ending the operational nuclear bomber mission.
Chinese Submarine Patrols Rebound in 2007, but Remain Limited

By Hans M. Kristensen
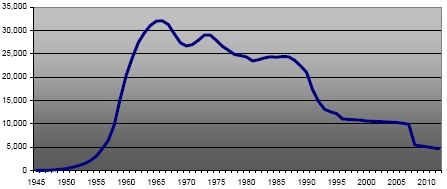
China’s entire fleet of approximately 55 general-purpose submarines conducted a total of six patrols during 2007, slightly better than the two patrols conducted in 2006 and zero in 2005.
The 2007 performance matches China’s all-time high of six patrols conducted in 2000, the only two years since 1981 that Chinese submarines conducted more than five patrols in a single year.
The new information, obtained by Federation of American Scientists from the U.S. Navy under the Freedom of Information Act, also shows that none of China’s ballistic missile submarines have ever conducted a deterrent patrol.
In Perspective
Just what constitutes a Chinese “patrol” is secret, according to the U.S. Navy, but it probably refers to an extended voyage away from the homeport area (see here for further definitions). The seven Chinese patrols conducted in 2007 is but a fraction of the number of patrols conducted by the U.S. submarine force, which musters well over 100 patrols per year. But a comparison of U.S. and Chinese submarine patrol levels is not possible because the two navies have very different missions. China has no overseas military commitments and uses its submarine fleet almost exclusively as a coastal defense force, whereas the U.S. submarine force is constantly engaged in forward operations alone or with allies.
The Chinese patrol rate compares better with that of the Russian Navy, which has largely ceased forward submarine operations compared with those of the Soviet Union during the Cold War. Russian general purpose submarines conducted seven patrols in 2007.
|
Chinese Submarine Patrols 1981-2007 |
 |
|
The entire Chinese submarine fleet conducted six patrols during 2007, matching the previous all-time high from 2000. The performance indicates that China operates its submarine fleet almost entirely as a coastal defense force. |
–
In historic perspective, the six Chinese submarine patrols conducted in 2007 continues a trend that China in this decade has sent slightly more submarines on patrol than during the 1990s. Whereas Chinese submarines in the 1990s conducted an average of 1.2 patrols each year, the average has been 3.4 patrols since 2000.
About Those Boomers
Twenty-five years after it launched its first ballistic missiles submarine, Xia (Type 092), China has yet to conduct its first deterrent patrol. The new information confirms that neither the Xia, nor the two new Jin-class (Type 094) ballistic missile submarines – the first of which was launched in 2004 – have ever conducted a deterrent patrol.
The single-warhead Julang-1 sea-launched ballistic missile developed for the Xia has been test launched twice, but is not thought to be fully operational and has been referred to by the U.S. intelligence community for years as the CSS-NX-3 (X for experimental). Each Jin-class submarine has 12 launch tubes for the new Julang-2 sea-launched ballistic missile, which the U.S. intelligence community estimates will carry a single warhead.
|
China’s New Nuclear Submarines |
 |
|
China’s new Chang-class (Type-093) nuclear-powered attack submarine (top) and Jin-class (Type-094) nuclear-powered sea-launched ballistic missile submarine (bottom) were photographed at the Xiaopingdao submarine base near Dalian by the Quickbird satellite on May 3, 2007, and October 17, 2006, respectively. A comparison of the two images shows the different size of the two submarines: roughly 100 meters versus 135 meters. |
–
The future mission of the missile submarines appears to be regional because the range of the missiles and operational constraints facing the submarines limit the targets that can be held at risk. The range of the Julang-2 is estimated by the US intelligence community at more than 8,000 km (4,970+ miles), which brings Hawaii and Alaska (but not the continental United States) within reach from Chinese territorial waters. Assuming they made it out of port past lurking U.S. attack submarines, the Chinese missile submarines would have to sail through the narrow straight between South Korea and Japan into the Sea of Japan for its Julang-2 missiles to be able to strike the Seattle area.
The Bo Hai Bay has been suggested as a possible deployment area for China’s missile submarines because it would offer more protection against hostile attack submarines. From the shallow bay, the Julang-2 missiles could be used to target Guam and Alaska, India, Russia, and – at the limit of its range – Hawaii.
There are also rumors – one apparently even with a photo – that China may plan to homeport some of its ballistic missile submarines at the new submarine base under construction at Hainan Island in the South China Sea. The infrastructure includes what appears to be a waterway entrance to an underground facility similar to the underground facility at Jianggezhuang submarine base near Qingdao where the Xia is based. Hainan Island has access to deeper waters than Jianggezhuang, but is also less protected. From Hainan Island the Julang-2 would be within range of Guam, India and most of Russia, but not Hawaii.
The U.S. Navy has assessed that China might build as many as five Jin-class submarines “in order to provide more redundancy and capacity for a near-continuous at-sea SSBN presence,” but is yet unclear whether China plans to develop a near-continuous sea-based deterrent or just a surge capability for deployment in a crisis. If all current ballistic missile boats became fully operational, China could deploy a maximum of 36 warheads at sea, although at least one of the boats would probably be in overhaul at any given time. Whatever the future mission, absent any deterrent patrols so far, the Chinese military will first have to learn how to operate the missile submarines in a way that would matter.
Implications
Despite the rebound in general purpose submarine patrols, dramatic reports from recent years about Chinese submarines operating inside Japanese territorial waters or surfacing close to U.S. aircraft carriers have been largely absent in 2007. The meaning of the patrol rebound is yet unclear. After all, it follows a complete absence of submarine patrols in 2005, the fourth year since 1981 that China’s submarine fleet did not conduct any patrols despite introduction of several new classes of more advanced submarines for greater reach. That modernization has (not yet) manifested itself in the form of a clear increase in submarine patrols.
The patrol number does not say anything about what the submarines did during the six patrols. They might have been basic attempts to sail far from shore to test navigational equipment or communication with the homebase, or they might have included more advanced tactical operations. They might have been conducted by six different submarines, or only a couple.
Yet for the Chinese submarine force overall, six patrols do not provide very much operational experience for more than 50 submarines and their crews. If China did plan a more extended reach for its submarine force, one might expect the patrol rate to continue to increase in the next couple of years. Only the future will tell. But the operational experience from the 55 patrols conducted by the entire submarine force between 1981 and the end of 2007 suggests that China’s submarine force – at least for now – remains a coastal defense force.
More information: browse previous blogs about China | Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
White House Announces (Secret) Nuclear Weapons Cuts
 |
|
The W62 is the only nuclear warhead that has been publicly identified for elimination under the Bush administration’s secret nuclear stockpile reduction plan. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
The While House announced earlier today that the President had “approved a significant reduction in the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile to take effect by the end of 2007.” The decision reaffirmed an earlier decision from June 2004 to cut the stockpile “nearly 50 percent,” but moved the timeline up five years from 2012 to 2007.
Not included in the White House statement, but added by other government officials, is an additional decision to cut the remaining stockpile by another 15% percent, although not until 2012.
The announcement of these important initiatives unfortunately was hampered by Cold War secrecy which meant that government officials were not allowed to reveal how many nuclear weapons will be cut or what the size of the stockpile is. As a result, news media accounts were full of errors, and one can only imagine the misperceptions this misplaced secrecy creates in other nuclear weapon states.
Estimates of the Secret Cuts
Before the latest announcements, I and my colleague Robert Norris estimated that the stockpile consisted of approximately 9,900 warheads of which roughly 4,600 were operational. With the new announcements, we predict the following development:
The White House announcement reaffirms the 2004 decision to reduce the size of the Defense Department’s nuclear weapons stockpile “by nearly 50 percent from the 2001 level.” This objective was reaffirmed by the National Nuclear Security Administration in a press release earlier today. The DOD stockpile included roughly 10,500 warheads in 2001, which means that the 2004 stockpile plan probably envisioned a stockpile of some 5,400 warheads by 2012. It is this cut that the White House reaffirmed today, but implemented by the end of 2007 instead of 2012.
The additional 15 percent reduction announced today and confirmed by the White House would cut approximately 800 warheads more from the 5,400, resulting in an estimated stockpile of roughly 4,600 warheads by 2012.
At that time the SORT agreement signed with Russian in 2002 is scheduled to enter into effect, setting an upper limit of no more than 2,200 operationally deployed strategic warheads. The remaining 2,400 warheads will likely include 2,000 reserve warheads to “hedge” against unforseen political developments and 400 non-strategic bombs.
|
|
 |
|
The Bush administration’s planned reduction of the nuclear stockpile is significant but modest compared to the cuts in the 1990s, and will leave a stockpile that is four times larger than the combined arsenals of all other nuclear weapon states (excluding Russia). |
What Doesn’t Change
The White House’s announcement to implement the 2004 stockpile plan in 2007 does not mean that the “cut” warheads will have been dismantled by then – far from it. In fact, the decision to reduce the stockpile does not in itself result in the destruction of a single warhead. “Reducing” the stockpile by nearly half is a form of nuclear book keeping that means that ownership of the “cut” warheads will shift from DOD to DOE.
But DOE doesn’t have storage capacity for all of these weapons at its facility at Pantex. That factory is busy rebuilding the warheads slated to remain in the “enduring stockpile” beyond 2012. As a result, dismantlement of the backlog of warheads from the current reductions is not scheduled to be completed until 2023, more than a decade-and-a-half after today’s White House announcement to speed things up. Indeed, the current administration has demonstrated the lowest warhead dismantlement rate of any U.S. government since the Eisenhower administration.
So for now, most of the “cut” warheads will likely remain at the bases where they are and only gradually be moved to the central warhead storage locations such as Kirtland Air Force Base in New Mexico. The only known timeline for this move is 2012, by which time no more than 2,200 strategic warheads can remain at bases for operational delivery platforms according to the SORT agreement.
Observations
The While House statement highlights that “the U.S. nuclear stockpile will be less than one-quarter its size at the end of the Cold War” [1991, ed.]. But the stockpile the administration plans for 2012 is large by post-Cold War standards:
* Four times the combined number of nuclear weapons of all the world’s nuclear weapons states, excluding Russia.
* Almost half of the stockpile – a maximum of 2,200 warheads – will be operational, and a third of those (more than 850) will be on alert.
* More than 10 times bigger than in 1950, when the United States decided to contain the Soviet Union.
Although the White House says the planned reductions seek to “reduce U.S. reliance on nuclear weapons,” the statement not only reaffirms that “a credible deterrent remains an essential part of U.S. national security,” but also declares that “nuclear forces remain key to meeting emerging security challenges.”
In the weeks ahead, we will fine-tune this estimate further.
More background: Estimates of the U.S. Nuclear Stockpile Today and Tomorrow | Estimates of the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Stockpile, 2007 and 2012
Congress Zeroes Out Money for the Reliable Replacement Warhead. Part Funding for Global Nuclear Energy Partnership.
The spending bill just agreed by Congress over the weekend explicitly specifies zero funding for the Reliable Replacement Warhead, or RRW, and support for the Global Nuclear Energy Partnership, but below the administration’s request.
The RRW is a new nuclear weapon that the administration claims is essential to maintaining the integrity of the nuclear arsenal. Most outside experts believe that existing nuclear weapons are more than adequately reliable. Moreover, as I have commented previously in this blog, the Reliable Replacement warhead will almost certainly not be more reliable than current warheads and absolutely certainly will not be meaningfully more reliable. Moreover, it will not replace existing warheads but be deployed alongside them for decades, and it is not even the reliable replacement warhead, because a minimum of four new types were planned.
(more…)
Oh, No! Not another “Uranium Dirty Bomb” Story!
According to a recent report from AP, Slovak police arrested people trying to sell highly enriched uranium to undercover agents. According to the police, the material, said to be about a kilogram of uranium, could be used for a dirty bomb. This is a replay of the Padilla case, the so-called “Dirty Bomber,” who was allegedly going to use uranium to make a radiological, or “dirty,” bomb. (The government later dropped reference to the dirty bomb but convicted Padilla on other charges.) I don’t think what the Slovaks have is actually uranium (see below) but, even if it is, dirty bombs are not the problem.
(more…)
A Rebuttal to Brown and Deutch Op-Ed in the Wall Street Journal
Arguments justifying the continuing existence of the world’s nuclear arsenals are like the tired joke about the joke convention. Many of these arguments have been with us for decades. Some made sense decades ago but do no longer, now that the Cold War is history. Others never made sense even during the Cold War but have, through sheer longevity, taken on a wholly undeserved intellectual authority. And some statements are not really logical arguments at all but merely catch-phrases that have been with us so long we no longer question their truth; indeed, we don’t even reflect on what, if anything, they actually mean. So one can, like at the joke convention, just shout out “Number 37!” and, instead of laughing, the wise ones of the nuclear establishment nod in sage agreement.
(more…)
White House Guidance Led to New Nuclear Strike Plans Against Proliferators, Document Shows
By Hans M. Kristensen
The 2001 Nuclear Posture Review (NPR) and White House guidance issued in response to the terrorist attacks against the United States in September 2001 led to the creation of new nuclear strike options against regional states seeking to acquire weapons of mass destruction, according to a military planning document obtained by the Federation of American Scientists.
Rumors about such options have existed for years, but the document is the first authoritative evidence that fear of weapons of mass destruction attacks from outside Russia and China caused the Bush administration to broaden U.S. nuclear targeting policy by ordering the military to prepare a series of new options for nuclear strikes against regional proliferators.
Responding to nuclear weapons planning guidance issued by the White House shortly after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001, U.S. Strategic Command created a series of scenario driven nuclear strike options against regional states. Illustrations in the document identify the states as North Korea and Libya as well as SCUD-equipped countries that appear to include Iran, Iraq (at the time), and Syria – the very countries mentioned in the NPR. The new strike options were incorporated into the strategic nuclear war plan that entered into effect on March 1, 2003.
The creation of the new strike options contradict statements by government officials who have insisted that the NPR did not change U.S. nuclear policy but decreased the role of nuclear weapons.
Non-Denial Denials and a Few Hints
When portions of the 2001 Nuclear Posture Review (NPR) were leaked in the Los Angeles Times in March 2002, government officials responded by playing down the importance of the document and its effect on nuclear planning. And officials have since continue to credit the NPR with reducing the reliance on nuclear weapons.
The NPR is “not a plan, it’s not an operational plan,” then Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Richard B. Myers insisted on CNN the day after the NPR was leaked. “It’s a policy document. And it simply states our deterrence posture, of which nuclear weapons are a part….And it’s been the policy of this country for a long time, as long as I’ve been a senior officer, that the president would always reserve the right up to and including the use of nuclear weapons if that was appropriate. So that continues to be the policy.”
A formal statement published by the Department of Defense added that the NPR “does not provide operational guidance on nuclear targeting or planning,” but that the military simply “continues to plan for a broad range of contingencies and unforeseen threats to the United States and its allies.”
Most recently, on October 9, 2007, Christina Rocca, the U.S. permanent representative to the Conference on Disarmament, told the First Committee of the U.N. General Assembly that the United States has been “reducing the…degree of reliance on [nuclear] weapons in national security strategies….It was precisely the new thinking embodied in the NPR that allowed for the historic reductions we are continuing today.”
Yet a few officials hinted in 2002 that the same guidance expanded nuclear planning. “There are nations out there developing weapons of mass destruction,” then Secretary of State Colin Powell said on CBS’ Face the Nation. “Prudent planners have to give some consideration as to the range of options the president should have available to him to deal with these kinds of threat,” he said.
The declassified U.S. Strategic Command (STRATCOM) document shows that one of the first results of “the new thinking” of the NPR was the creation of a series of new nuclear strike options against regional states.
A Series of Regional Options
The 26-page declassified document, an excerpt from a 123-page STRATCOM briefing on the production of the 2003 strategic nuclear war plan known as OPLAN 8044 Revision 03, includes two slides that describe the planning against “regional states.” The first of these slides lists a “series of [deleted] options” directed against regional countries with weapons of mass destruction programs. The planning is “scenario driven,” according to the document. The majority of the document deals with targeting of Russia and China, but virtually all of those sections were withheld by the declassification officer.
The names of the “regional states” were also withheld, but three images used to illustrate the planning were released, and they leave little doubt who the regional states are: One of the images is the North Korean Taepo Dong 1 missile; another image shows the Libyan underground facility at Tarhuna; and the third image shows a SCUD B short-range ballistic missile. The SCUD B image is not country-specific, but the Air Force National Air and Space Intelligence Center report Ballistic and Cruise Missile Threat from 2003 listed 12 countries with SCUD B missiles: Belarus, Bulgaria, Egypt, Iran, Kazakhstan, Libya, North Korea, Syria, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Vietnam and Yemen. Five of these were listed in the NPR as examples of countries that were “immediate, potential, or unexpected contingencies…setting requirements for nuclear strike capabilities”: Iran, Iraq, Libya, North Korea and Syria.
 |
|
Images included in the declassified STRATCOM document identify several regional states as targets for new nuclear strike plans. |
The inclusion of regional nuclear counterproliferaiton strike options into the national (strategic) war plan is a new development because such scenarios have normally been thought to reside at a lower level than the national strategic plan, which has traditionally been focused on targeting of Russia and China. During the 1990s, STRATCOM developed adaptive planning capabilities that enabled quick production of strikes against “rogue” states if necessary, but “there were no immediate plans on the shelf for target packages to give to bombers or missile crews,” a former senior Pentagon official told Washington Post in 2002. OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 changed that by producing executable strike options to the nuclear forces.
The “target base” for the regional states is outlined in the STRATCOM document, but everything except the title has been withheld. But the target base probably included weapons of mass destruction, deep, hardened bunkers containing chemical or biological weapons, or the command and control infrastructure required for the states to execute a WMD attack against the United States or its friends and allies. The U.S. Nuclear Weapons Employment Policy (NUWEP) that entered into effect one year after OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 stated in part: “U.S. nuclear forces must be capable of, and be seen to be capable of, destroying those critical war-making and war-supporting assets and capabilities that a potential enemy leadership values most and that it would rely on to achieve its own objectives in a post-war world.”
The creation of a “target base” indicates that the planning went further than simple retaliatory punishment with one or a few weapons, but envisioned actual nuclear warfighting intended to annihilate a wide range of facilities in order to deprive the states the ability to launch and fight with WMD. The new plan formally broadened strategic nuclear targeting from two adversaries (Russia and China) to a total of seven.
Iraq presumably disappeared from the war plan again after U.S. forces invaded the country in March 2003 – only three weeks after OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 went into effect – and discovered that Iraq did not have weapons of mass destruction. Libya presumably disappeared after December 2003, when President Muammar Gaddafi declared that he was giving up efforts to develop weapons of mass destruction.
The nuclear strike plans against Iran, North Korea and Syria, however, presumably were carried forward into the next OPLAN 8044 Revision 05 from October 2004, a plan that was still in effect as recently as July 2007.
|
Nuclear Guidance |
|
|
|
|
| “The 2001 Nuclear Posture Review (top) and White House guidance led to an expansion of U.S. nuclear targeting plans. |
New Guidance for the Regions
The STRATCOM document indicates that National Security Presidential Directive (NSPD)-14 signed by President Bush on June 28, 2002, was the key While House guidance that resulted in the incorporation into the strategic nuclear war plan of strike options against regional proliferators.
Very little has been disclosed about NSPD-14, except that it laid out Presidential nuclear weapons planning guidance and provided broad overarching directions to the agencies and commands for nuclear weapon planning. As such, NSPD-14 might have been replacing Presidential Decision Directive (PDD)-60 signed by President Clinton in November 1997 as the primary White House guidance for nuclear weapons planning. PDD-60 reportedly also required planning against proliferators, but the new strike options incorporated into Revision 03 were “notable changes” compared with the previous plan, according to the STRATCOM document.
Flowing from NSPD-14 were several other important guidance documents that deepened the commitment to targeting regional proliferators. The first was the JSCP Transitional Guidance in June 2002, which directed changes to the Joint Strategic Capabilities Plan (JSCP). JSCP includes a nuclear annex or supplement, known as JSCP-N, that give detailed nuclear planning guidance to the unified and regional commanders. The new JSCP-N was published on October 1, 2002. Another document was the NUWEP (Nuclear Weapons Employment Policy) Transitional Guidance signed on August 29, 2002, which led to the publication of NUWEP-04 in April 2004.
Three months after NSPD-14, on September 14, 2002, President Bush also signed NSPD-17 (National Strategy to Combat Weapons of Mass Destruction), a directive that articulated a comprehensive strategy to counter nuclear and other weapons of mass destruction. NSPD-17 reaffirmed that, if necessary, the United States will use nuclear weapons against anyone using weapons of mass destruction against the United States, its forces abroad, and friends and allies, according to Washington Times. But a top-secret appendix to NSPD 17 specifically named Iran, Syria, North Korea and Libya as being among the countries that are the central focus of the new strategy, and that options included nuclear weapons. Those options were in place with OPLAN 8044 Revision 03. The motivation for the new strategy, one participant in the interagency process that drafted it told Washington Post, was the conclusion that “traditional nonproliferation has failed, and now we’re going into active interdiction.” NSPD-17 is sometimes also called the preemption doctrine.
The regional strike plans also found their way into the draft Doctrine for Joint Nuclear Operations (Joint Publication 3-12), which was under preparation within the military at the time Revision 03 was created. Yet the doctrine showed that planning went beyond retaliation and included preemptive strikes. The second draft from March 2005 listed five scenarios where use of nuclear weapons might be requested:
• To counter an adversary intending to use weapons of mass destruction against U.S., multinational, or allies forces or civilian populations;
• To counter an imminent attack from an adversary’s biological weapons that only effects from nuclear weapons can safely destroy;
• To attack on adversary installations including weapons of mass destruction, deep, hardened bunkers containing chemical or biological weapons, or the command and control infrastructure required for the adversary to execute a WMD attack against the United States or its friends and allies; [this was probably the “target base” in OPLAN 8044 Revision 03]
• To counter potentially overwhelming adversary conventional forces;
• To demonstrate U.S. intent and capability to use nuclear weapons to deter adversary WMD use.
After I disclosed this development in an article in Arms Control Today in September 2005 and the Washington Post followed up with a front-page story, sixteen members of Congress – including the current chair of the House Armed Services Committee – reacted by writing to the president to object to what they considered to be a “drastic shift in U.S. nuclear policy.”
Embarrassed by the exposure, the Pentagon canceled not only the draft doctrine (and four other related doctrine documents) but also the existing Doctrine for Joint Nuclear Operations document that had been publicly available on the Joint Chiefs of Staff web site for a decade. A Joint Staff official explained that the documents would not be published, revised or classified, explaining that that they had been found not to be real doctrine documents but “pseudo doctrine” documents discussing nuclear policy issues. The public “visibility led a lot of people to question why we have them,” he said.
|
|
 |
|
During the tenure of Admiral Ellis (right), STRATCOM prepared, and CJCS Richard Myers (left) approved, an expansion of the SIOP to “a family of plans applicable in a wider range of scenarios.” |
From SIOP to OPLAN 8044: A “Family of Plans”
There is no indication that cancelation of the Doctrine for Joint Nuclear Operations documents changed nuclear policy. The declassified STRATCOM document describes OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 as “a transitional step toward the new TRIAD and future war plans.” That transition began long before the “New Triad” phrase was coined by the 2001 NPR, and has gradually transformed the top-heavy self-standing Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP) to a broader set of strike options applicable in a wider range of scenarios against more adversaries. When preparation of Revision 03 began in March 2002, the combat employment portion of the strategic nuclear war plan was still known as the SIOP, but the name had to be changed to reflect the emerging multitude of strike options.
As the Joint Staff started to review the new war plan, STRATCOM commander Admiral James Ellis wrote to General Myers that the name SIOP did not properly describe the new plan. “STRATCOM is changing the nation’s nuclear war plan from a single, large, integrated plan to a family of plans applicable in a wider range of scenarios,” Ellis explained with a reference to Revision 03. The first STRATCOM commander, General George Lee Butler, had tried to change the name in 1992, but with no luck. Butler wanted to change the name to National Strategic Response Plans. Eleven years later, Admiral Ellis tried again. The SIOP name, he said, was a Cold War legacy.
This time, the JCS chairman was more receptive. On February 8, 2003, only one month before Revision 03 went into effect, General Myers authorized STRATCOM to formally change the name to reflect the creation the “new family of plans.” Yet Myers was concerned that confusion might arise “between the basic USSTRATCOM OPLAN 8044 and the combat employment portion of that OPLAN, currently known as the SIOP.” The solution, he decided, was to continue to call the basic plan OPLAN 8044, but incorporate the term OPLAN 8044 Revision (FY) to describe that portion of the plan currently known as the SIOP. The Revision number (FY) would correspond to the fiscal year the combat employment plan was put into effect. OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 of March 1, 2003, was the first plan to carry the new name.
The new strike options apparently were carried forward into OPLAN 8044 Revision 05, the next strategic war plan that entered into effect on October 1, 2004. This plan was described as a “major revamping” of the U.S. strategic war plan, which, according to General Myers, “provides more flexible options to assure allies, and dissuade, deter, and if necessary, defeat adversaries in a wider range of contingencies.” OPLAN 8044 Revision 05 was still in effect as of July 2007 (for a chronology of U.S. nuclear guidance and war plans under the Bush administration, go here).
Claims About Reducing Reliance On Nuclear Weapons
Officials frequently credit the NPR with having significantly reduced the reliance on nuclear weapons in U.S. nuclear policy. The basis for this claim is that non-nuclear capabilities also should play a role in deterring potential adversaries, an goal exemplified by the incorporation of conventional strike options into OPLAN 8044 Revision 05, the war plan than followed OPLAN 8044 Revision 03, and the removal of Russia as an “immediate contingency.”
“The United States has set in motion an entirely new way of looking at the role of nuclear weapons in our defense strategy,” Jackie W. Sanders, U.S. Ambassador and Special Representative of the President for the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons, told the 2005 Nonproliferation Treaty Review Conference. “I speak, Mr. Chairman, of the U.S. Nuclear Posture Review, or NPR, of 2001. The United States has undertaken reviews of this sort in the past, but the 2001 NPR is unique, and fully consistent with Article VI. The 2001 NPR established a New Triad of strategic capabilities, one that places far less reliance on nuclear weapons to meet U.S. defense policy goals…. Let me emphasize, Mr. Chairman, that the New Triad concept resulting from the NPR, in principle and in practice, will reduce reliance on nuclear weapons in U.S. national security strategy. It reflects a totally new vision of the future, and is fully consistent with our indisputable resolve to implement Article VI.”
But while some conventional weapons are being incorporated into the national war plan and planning against Russia is not done in the same way it was during the Cold War, the NPR (building on the 1997 PDD-60) and White House guidance also resulted in an increased nuclear targeting of China and, as the declassified STRATCOM document illustrates, an geographic expansion of national-level nuclear targeting to regional proliferators. Prudent or not, this is not a development that is highlighted by U.S. diplomats at NPT conferences.
Description of Document
The declassified document is heavily redacted and consists of 26 of a total of 123 slides from the Revision 03 Periodic Update of the U.S. strategic war plan that went into effect on March 1, 2003. The plan was the first strategic war plan to carry the new name Operations Plan (OPLAN) 8044 Revision 03, which replaced the Single Operational Strategic Plan (SIOP) name used since 1960. OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 replaced SIOP-03 from October 1, 2002.
The document describes six parts of the new plan preparation: Revision 03 production status, planning guidance, target base, committed forces, options, and conclusions.
The document is not dated, but appears to be from October 2002, shortly before the Secretary of Defense was briefed. Targeting intelligence and selection had been completed, warheads allocated to the strike plans, and strike (sortie) planning for Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs), Sea-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs), and long-range bombers nearly completed. After a Joint Staff review and production of the final Revision Report 03 in January 2003, final Defense Secretary review and approval by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff were scheduled for late January 2003 before OPLAN 8044 Revision 03 went into effect on March 1, 2003.
Declassification of the document took four years. It was released in response to a FOIA request submitted in October 2003 for documents pursuant to remarks made by then Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Richard Myers during a Senate Foreign Relations Committee Hearing in July 2002. When asked if there had been a review of the SIOP since the mid-1990s, Myers replied: “Yes, there absolutely has. In fact, the secretary and I spent considerable time revising the SIOP. I think we started that last year and have gotten another major review ongoing.” The declassified document was released on October 10, 2007.
Resources: U.S. Nuclear Weapons Guidance | The Matrix of Deterrence | The Post Cold War SIOP and Nuclear Warfare Planning: A Glossary, Abbreviations, and Acronyms
Acknowledgements: This research has been made possible by support from the Ford Foundation, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, and the Ploughshares Fund.