After Trump Secrecy, Biden Administration Restores US Nuclear Weapons Transparency
[Updated] The Biden administration yesterday afternoon declassified the number of nuclear weapons the United States possesses. The act reverses the secrecy of the Trump administration, which denied release of the number for three years, and restores the nuclear transparency of the Obama administration.
FAS’ Steve Aftergood asked for this information in March 2021. We have still not received an official response.
Although a victory for nuclear transparency, the data shows only very limited nuclear weapons reductions in recent years – a stark reminder of the international nuclear climate, domestic policies, and that a lot more work is needed to reduce nuclear dangers.
Stockpile Numbers
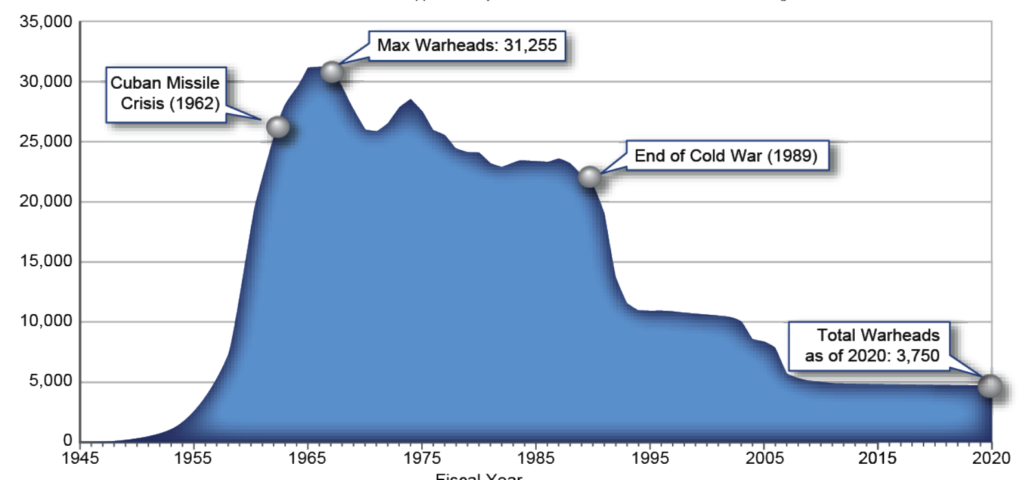
According to the new data, the United States possessed a total of 3,750 nuclear warheads in the Department of Defense nuclear weapons stockpile as of September 2020. That number is only 50 warheads less than our estimate of 3,800 warheads from early this year.
The 3,750-warhead number is only 72 warheads fewer than in September 2017, the last number made available before the Trump administration closed the books.
That reduction is by any measure mediocre. In its announcement about the new stockpile numbers, the US Department of State highlights that the current stockpile of 3,750 warheads “represents an approximate 88 percent reduction in the stockpile from its maximum (31,255) at the end of fiscal year 1967, and an approximate 83 percent reduction from its level (22,217) when the Berlin Wall fell in late 1989.” While that is true and an amazing accomplishment, the fact remains that the vast majority of that reduction happened in two phases during the H.W. Bush and W. Bush administrations. Since 2008 the reduction has been slow and limited. The trend is that the reduction is decreasing and leveling out.
A peculiar revelation in the new data is that it shows that the stockpile increased by 20 warheads between September 2018 and September 2019 when Trump was in office. The increase is not explained but one possibility is that it reflects the production of the new W76-2 low-yield warhead that the Trump administration rushed into production in response to what it said was Russia’s plans for first-use of tactical nuclear weapons. The first W76-2 was produced in February 2019, NNSA was scheduled to deliver all the warheads by end of Fiscal Year 2019, but the W76-2 wasn’t completed until June 2020. Arkin and Kristensen reported in January 2020 that the first W76-2s had been deployed, which was later confirmed by the Pentagon.
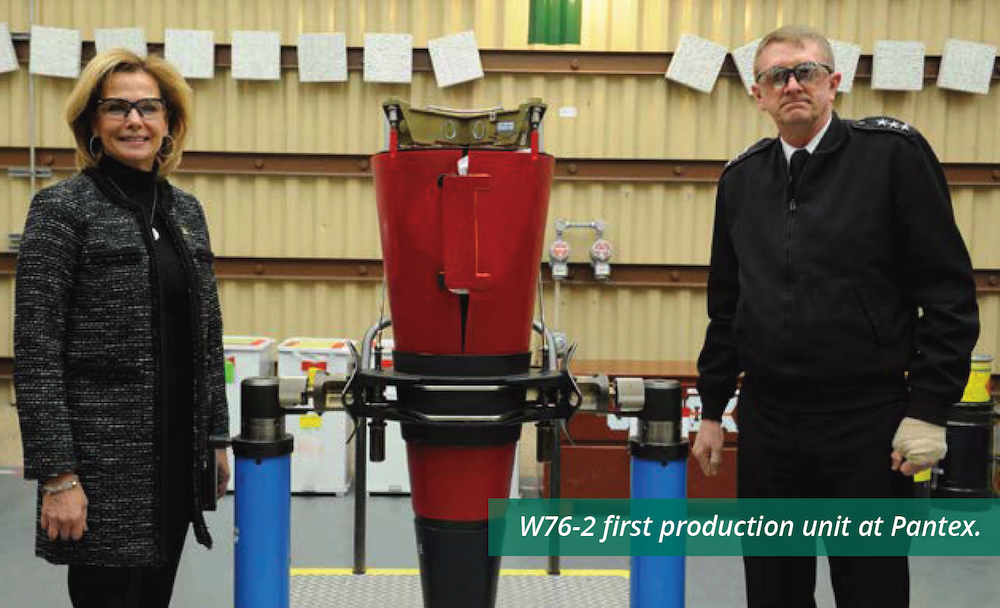

It is possible (but unconfirmed) that the 20-warhead stockpile increase between 2018 and 2019 was caused by production of the Trump administration’s W76-2 low-yield Trident warhead. Image: NNSA.
The Trump administration’s brief increase of the stockpile is only the second time the United States has increased its number of nuclear warheads since the Cold War. The first time was in 1995-1996 when the Clinton administration increased the stockpile by 107 warheads. Since the W76-2 production continued after September 2019, the increase of 20 warheads should not be misinterpreted as being the final number of W76-2 warheads. After the 2018-2019 increase, the stockpile number dropped again by 55 warheads.
Update: Another possibility for the brief stockpile increase is that a small number of retired warheads were returned to the stockpile. This could potentially be B83-1 bombs that the Trump administration decided to retain instead of retiring with the fielding of the B61-12. It could potentially also be retired warheads brought in as feedstock for new weapon systems such as the planned nuclear sea-launched cruise missile. We just don’t know at this point.
Apparently, the nuclear modernization program supported by both Republicans and most Democrats, will result in significant additional reductions of the stockpile. In 2016, the former head of the Navy’s Strategic Systems Program, Vice Admiral Terry Benedict, said that once the W76-1 warhead production was completed by the end of FY2019, the W76-0 warheads that had not been converted to W76-1 would be retired and the total number of W76 warheads in the stockpile decrease by nearly 50%.
At the same time, the Pentagon’s Principal Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Nuclear, Chemical, and Biological Defense Programs, Arthur T. Hopkins, told Congress that production and fielding of the B61-12 bomb would “result in a nearly 50 percent reduction in the number of nuclear gravity bombs in the stockpile” and “facilitate the removal from the stockpile of the last megaton-class weapon––the B83-1.”
Production of the W76-1 has now been completed but the promised reduction is not yet visible in the stockpile data – unless the excess warheads were gradually removed during the production years. The B61-12 has not been fielded yet so the gravity bomb reduction presumably will not happen until the mid-2020s.
Whatever the number of the additional stockpile reduction is, it is not planned to be nice to Kremlin and Beijing but because the US military doesn’t need the excess warheads anymore. Whether Russia and China’s nuclear increases will cause the Biden administration to change the plan outlined by Benedict and Hopkins will be decided by the Nuclear Posture Review.
Dismantlement Numbers
The data also shows that the United States as of September 2020 had about 2,000 retired warheads in storage awaiting dismantlement. Retired warheads are owned by the Department of Energy and not part of the DOD stockpile.
That number matches the available data. Former Secretary of State John Kerry said in 2015 that there were about 2,500 retired weapons left (as of September 2014). Since then, 1,432 warheads have been dismantled and an additional 967 weapons retired, which would leave just over 2,000 warheads in the dismantlement queue.
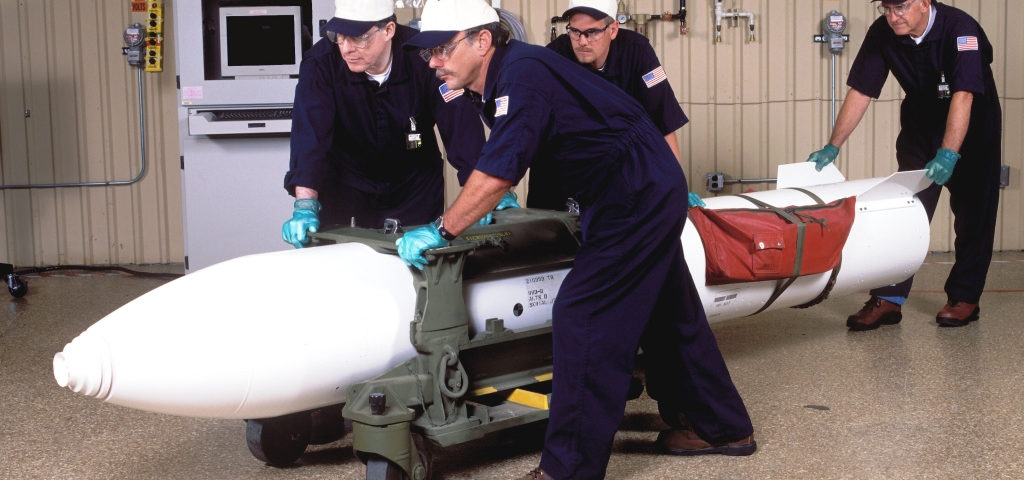

Approximately 2,000 retired warheads away dismantlement, including the B83 megaton gravity bomb. More are expected to follow during the next decade. Image: NNSA.
In our estimate from early this year, we thought the dismantlement queue had dropped to 1,750 warheads because we assumed the annual dismantlement rate had remained around 300. But as the data shows, both the Trump and Biden administrations reduced the number of warheads being dismantled per year.
In 2016, NNSA stated that it “will increase weapons dismantlement by 20 percent starting in FY 2018” and that the “accelerated rate will allow NNSA to complete the dismantlement commitment a year early, before the end of FY 2021.” NNSA reaffirmed in 2018, that all warheads retired prior to 2009 would be dismantled by end-FY 2022.
This pledge appears to have faded from recent documents after the 2018 Nuclear Posture Review was published. Instead, the annual number of warheads dismantled has decreased since FY 2018. Is it still the goal? Some of the warheads that should have been dismantled but are still with us reportedly include the W84 warheads from the ground-launched cruise missiles that were eliminated by the 1987 INF treaty and retired well before 2009.
Many of the warheads in the current dismantlement queue were retired after 2009. At the current rate of 184 warheads dismantled per year, it will take more than a decade to dismantle the current backlog. Once the excess W76s and old gravity bombs enter the queue, it will take even longer.
In Context
We commend the Biden administration for reversing the Trump administration’s shortsighted and counterproductive nuclear secrecy and restore transparency to the US nuclear weapons stockpile. This decision is a heavy lifting at a time when so-called Great Power Competition is overtaking defense and arms control analysis. The Federation of American Scientists has for years advocated for increased transparency of nuclear arsenals and have worked to provide that through our estimates of nuclear weapons arsenals.
Although the recent reductions shown in stockpile and dismantlement data are modest, to put it mildly, we believe declassification is the right decision because making the record public will help US diplomats make the case that the United States is continuing its efforts to reduce nuclear arsenals and increase nuclear transparency. This is especially important in the context of the upcoming January 2022 Review Conference for the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons. Dissatisfaction with the lackluster disarmament progress – and a belief that the nuclear-armed states are walking back decades of arms control progress with their excessive nuclear modernization programs and dangerous changes to operations and strategy – have fueled support for the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW).
The decision to disclose the stockpile and dismantlement data will also enhance the US credibility when urging other nuclear-armed states to be more transparent about their arsenals. We have no illusions that Russia or China will follow the example in the short term, but keeping the US numbers secret will certainly not help. And over time, the disclosure can help shape discussions and norms about nuclear transparency to shape future decisions. This is also important because the Trump secrecy recently provided cover for the United Kingdom to reduce information about its nuclear forces.
Hardliners will no doubt criticize the Biden administration’s decision to disclose the stockpile and dismantlement data. They will argue that past nuclear transparency has not given the United States any leverage, that nuclear-armed states previously have not followed the example, and it that makes the United States look naive – even irresponsible – in view of Russia and China’s nuclear secrecy and build-up.
On the contrary: without transparency the United States has no case. Past transparency has given the United States leverage to defend its record and promote its policies in international fora, dismiss rumors and exaggerations about its nuclear arsenal, and publicly and privately challenge other nuclear-armed states’ secrecy and promote nuclear transparency. And since the disclosure does not reveal any critical national security information, there is no reason to classify the stockpile and dismantlement data.
Hardliners obviously will have to acknowledge that the data shows that there has been no unilateral US disarmament but only a very modest reduction in recent years. And although there appear to be additional unilateral reductions built into the modernization programs, those are actually programs that have been supported and defended by the hardliners.
Now it is up to the Biden administration’s Nuclear Posture Review to articulate how and to what extent those plans support and strengthen US national security and nonproliferation objectives. Arms control obviously will have to be part of that assessment. The declassified stockpile and dismantlement data will help make the case that additional reductions are both needed and possible.
Background Information:
- US Department of State, Transparency in the U.S. Nuclear Weapons Stockpile, Fact Sheet, October 5, 2021
- “United States Nuclear Forces, 2021,” FAS Nuclear Notebook, Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, March/April 2021
- “Pentagon Slams Door On Nuclear Weapons Stockpile Transparency,” FAS Strategic Security Blog, April 17, 2019
- Status of World Nuclear Forces, Federation of American Scientists global arsenal page
This article was made possible by generous support from the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the New Land Foundation, the Prospect Hill Foundation, and the Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the authors.
75 Years Ago: The Trinity Nuclear Test
On this day 75 years ago, the world entered the nuclear age. The first ever nuclear detonation – known as the Trinity test – took place in New Mexico on July 16th, 1945. Since then, ten countries built more than 134,000 nuclear weapons. More than 13,400 remain today.
In the decades that followed, nuclear testing contaminated lands, oceans, and people, and triggered a nuclear arms race that continues to this day. The Federation of American Scientists is honored to join our colleagues at the Union of Concerned Scientists and Tularosa Basin Downwinders Consortium in a joint statement with five other U.S. organizations on the humanitarian consequences of nuclear testing, endured by victims in the United States and its Pacific territories, from French nuclear testing in French Polynesia and Algeria, Russian nuclear testing in Kazakhstan, British nuclear testing in Australia, and others.
In addition to these harms, the Trinity test marked the beginning of the global nuclear arms race with its endless cycles of nuclear modernization and competition, which continue to this day. Unlike any other invention, nuclear weapons have the capability to destroy human civilization and much or life on Planet Earth.
The Federation of American Scientists has tracked the rise and fall of global nuclear arsenals for many years. Despite reductions since the Cold War, there are still more than 13,000 nuclear weapons in the world. And we are disappointed to note the emergence of five disturbing trends regarding the current and future state of nuclear weapons:
- Every nuclear-armed country is currently in the midst of modernizing their nuclear arsenals. Some countries are actually increasing their stockpiles, while others are swapping out their older weapons with newer, more effective ones that will endure almost until the end of the 21st century.
- Not only are nuclear arsenals either increasing or improving, but it appears that many states are reinvigorating or even expanding the role of nuclear weapons – specifically tactical nuclear weapons – in their military doctrines. State representatives have often claimed that these deployments are actually intended to prevent conflict; however, regardless of how much stake one puts into that sort of statement, it is a fact that many states are now increasingly posturing themselves for nuclear warfighting. This development will make it more difficult to reduce the role of nuclear weapons and pursue significant reductions – and certainly disarmament – in the future.
- In recent years, we have also seen the decline – and general disinterest – in arms control writ large. Today, bilateral and multilateral arms control agreements have fallen away or are under severe stress, multilateral efforts to engage in good faith arms reductions appear to have completely stagnated, and states often seem more interested in blaming and shaming their prospective arms control partners than actually pursuing measures that would offer a modicum of transparency and predictability in an otherwise unpredictable world.
- Rather than pursue arms control, it seems that states are more content with pursuing arms competition and even arms races. This is a result of renewed military competition and is fueled by the tremendous influence that weapons contractors and lobbyists have on government decisions; indeed, sometimes nuclear decisions seem to be driven as much – if not more – by corporate interests than by national security concerns.
- Nuclear-armed states largely do not appear to consider nuclear disarmament to be an urgent global security, humanitarian, or environmental imperative. Instead, most states seem to consider disarmament as a type of chore mandated by the Non-Proliferation Treaty – and not one that they are seriously interested in completing in the foreseeable future. It is increasingly rare to hear any officials from nuclear weapon states express a coherent rationale for pursuing disarmament other than as a result of the obligation to do so under the Non-Proliferation Treaty. Moreover, they seem increasingly focused on shifting the disarmament responsibility onto the non-nuclear states by arguing they first must create the security conditions that will make nuclear disarmament possible.
Although the Trinity test took place 75 years ago, its destructive legacy continues to this day. And despite these harms, some politicians are even trying to return to an era of live nuclear testing. Resuming nuclear explosive testing would be taking a monumental step backward and would open the floodgates for worldwide resumption of nuclear testing and development of new nuclear weapons. Instead, on this 75th anniversary, we must look forward, try our best to reverse these worrying trends, responsibly reduce the arsenals and the role that nuclear weapons serve, and work towards a world eventually free from nuclear weapons.
The Federation of American Scientists is honored to provide the world with the best non-classified estimates of the nuclear weapons arsenals. We are grateful for the financial support from the New Land Foundation, MacArthur Foundation, Ploughshares Fund, and the Prospect Hill Foundation to do this work. To explore this vast data, developed over many decades, start here: https://fas.org/issues/nuclear-weapons/status-world-nuclear-forces/
Russia Upgrades Western Nuclear Weapons Storage Sites
Amidst a deepening rift between the United States and Russia about the role of non-strategic nuclear weapons, Russia has begun to upgrade an Air Force nuclear weapons storage site near Tver, some 90 miles (145 kilometers) northeast of Moscow.
Satellite photos show clearing of trees within the site as well as the construction of a new security fence and guard post. The upgrade, which started late-2017 and was completed late last year, was followed by the arrival of what appears to be weapons transport and service trucks earlier this year (see image below).
The Tver site includes two nuclear weapons bunkers as well as service and security buildings. The new security fence and gate added within the site separates the bunker area from the service area. The site is near the Migalovo Air Base, which is not thought to be housing nuclear strike aircraft but might serve a nuclear weapons transport function. If so, it could potentially be responsible for the distribution of nuclear warheads to tactical air bases in north-western Russia in a crisis.
It is impossible to determine from the satellite images if the Tver site stores nuclear weapons at this time, but it is clearly active with considerable personnel and activities indicating weapons might be present. Alternatively, Tver could serve as an Air Force storage site in a crisis. Tver is one of several dozen nuclear weapons storage sites operated by the Russian ministry of defense and military services (see here and here.
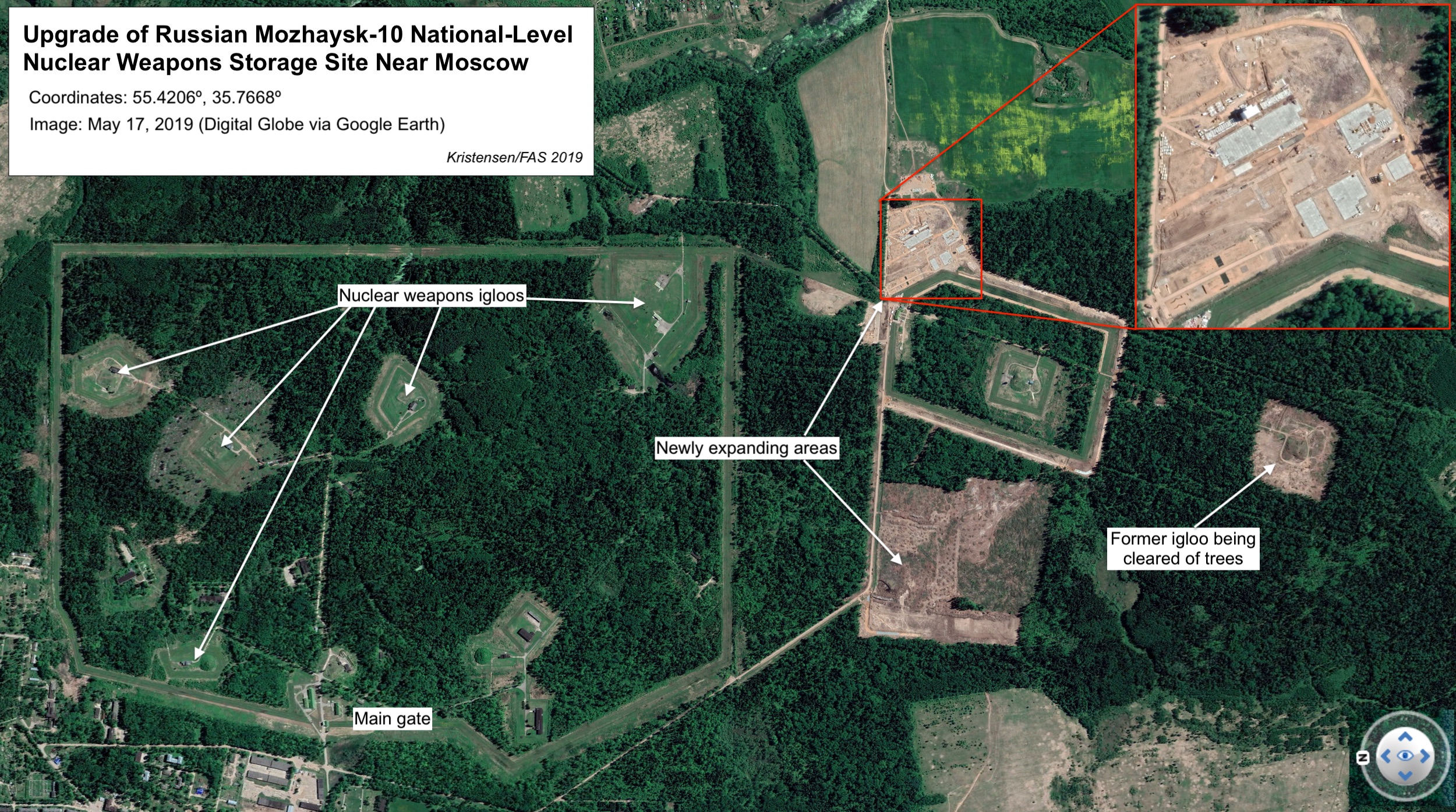
There are also important upgrades underway at the Mozhaysk-10 storage site about 70 miles (114 kilometers) west of Moscow, including addition of new support facilities as well clearing of a previously tree-covered weapons storage igloo. Mozhaysk-10 is one of a dozen national-level nuclear weapons storage site and includes six underground igloos and appears to be expanding (see below). Mozhaysk-10 might be used to store both strategic and tactical nuclear weapons.
The upgrades at the Tver and Mozhaysk-10 sites follow an ongoing upgrade to a nuclear weapons storage site in Kaliningrad that began in 2016 and appears intended to support nuclear-capable forces in the isolated enclave.
Russia is estimated to possess approximately 6,500 nuclear warheads, of which an estimated 4,330 are thought to be available for use by the military. We estimate that Russia has about 1,830 nuclear warheads assigned to non-strategic forces; the Pentagon says the number is “up to 2,000” warheads. The US Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) recently said it expects to see “a significant projected increase in the number of Russia’s non-strategic nuclear weapons” over the next decade, although some past DIA growth projections have turned out to exaggerated.
In response, the United States has begun to increase the upgrade of its non-strategic nuclear weapons beyond the already-planned B61-12 guided gravity bomb for stealthy F-35 fighter-bombers. New weapons with “tactical” missions include the W76-2 low-yield warhead on the Trident II D5LE SLBM and a new nuclear sea-launched cruise missile. And NATO has been upgrading US nuclear weapons storage sites in Europe.
Russia and the United States refuse to disclose how many tactical nuclear weapons they have or where they are stored, and none of these weapons are limited by arms control agreements.
We will further describe these developments, and much more, in our upcoming Nuclear Notebook on tactical nuclear weapons scheduled for publication in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists in September 2019.
Additional information:
This publication was made possible by generous contributions from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the New Land Foundation, the Ploughshares Fund, and the Prospect Hill Foundation. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Pentagon Slams Door On Nuclear Weapons Stockpile Transparency
The Pentagon has decided not to disclose the current number of nuclear weapons in the Defense Department’s nuclear weapons stockpile. The decision, which came as a denial of a request from FAS’s Steven Aftergood for declassification of the 2018 nuclear weapons stockpile number, reverses the U.S. practice from the past nine years and represents an unnecessary and counterproductive reversal of nuclear policy.
The United States in 2010 for the first time declassified the entire history of its nuclear weapons stockpile size, a decision that has since been used by officials to support U.S. non-proliferation policy by demonstrating U.S. adherence to the nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), providing transparency about U.S. nuclear weapons policy, counter false rumors about secretly building up its nuclear arsenal, and to encourage other nuclear-armed states to be more transparent about their arsenals.
Importantly, the U.S. also disclosed the number of warheads dismantled each year back to 1994. This disclosure helped document that the United States was not hiding retired weapons but actually dismantling them. In 2014, the United States even declassified the total inventory of retired warheads still awaiting dismantlement at that time: 2,500.
The 2010 release built on previous disclosures, most importantly the Department of Energy’s declassification decisions in 1996, which included – among other issues – a table of nuclear weapons stockpile data with information about stockpile numbers, megatonnage, builds, retirements, and disassemblies between 1945 and 1994. Unfortunately, the web site is poorly maintained and the original page headlined “Declassification of Certain Characteristics of the United States Nuclear Weapon Stockpile” no longer has tables, another page is corrupted, but the raw data is still available here. Clearly, DOE should fix the site.
The decision in 2010 to disclose the size of the stockpile and the dismantlement numbers did not mean the numbers would necessarily be updated each subsequent year. Each year was a separate declassification decision that was announced on the DOD Open Government web site. The most recent decision from 2018 in response to a request from FAS showed the stockpile number as of September 2017: 3,822 stockpiled warheads and 354 dismantled warheads.
The 2017 number was extra good news because it showed the Trump administration, despite bombastic rhetoric from the president, had continued to reduce the size of the stockpile (see my analysis from 2018).
Since 2010, Britain and France have both followed the U.S. example by providing additional information about the size of their arsenals, although they have yet to disclose the entire history of their warhead inventories. Russia, China, India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea have not yet provided information about the size or history of their arsenals.
FAS’ Role In Providing Nuclear Transparency
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) has been tracking nuclear arsenals for many years, previously in collaboration with the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC). The 5,113-warhead stockpile number declassified by the Obama administration in 2010 was only 13 warheads off the FAS/NRDC estimate at the time.
We provide these estimates on our web site, on our Strategic Security Blog, and in publications such as the bi-monthly Nuclear Notebook published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists and the annual nuclear forces chapter in the SIPRI Yearbook. The work is used extensively by journalists, NGOs, scholars, parliamentarians, and government officials.
With the Pentagon decision to close the books on the stockpile, and the rampant nuclear modernization underway worldwide, the role of FAS and others in documenting the status of nuclear forces will be even more important.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The Pentagon’s decision not to disclose the 2018 nuclear weapons stockpiled and dismantled warhead numbers is unnecessary and counterproductive.
The United States or its allies are not suffering or at a disadvantage because the nuclear stockpile numbers are in the public. Indeed, there seems to be no rational national security factor that justifies the decision to reinstate nuclear stockpile secrecy.
The decision walks back nearly a decade of U.S. nuclear weapons transparency policy – in fact, longer if including stockpile transparency initiatives in the late-1990s – and places the United States is the same box as over-secretive nuclear-armed states, several of which are U.S. adversaries.
The decision also puts the United States in an even more disadvantageous position for next year’s nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) review conference where the administration will be unable to report progress on meeting its Article VI obligations. Instead, this decision, as well as decisions to withdraw from the INF treaty, start producing new nuclear weapons, and the absence of nuclear arms control negotiations, needlessly open up the United States to criticism from other Parties to the NPT – a treaty the United States needs to protect and strengthen to curtail nuclear proliferation.
The decision also puts U.S. allies like Britain and France in the awkward position of having to reconsider their nuclear transparency policies as well or be seen to be out of sync with their largest military ally at a time of increased East-West hostilities.
With this decision, the Trump administration surrenders any pressure on other nuclear-armed states to be more transparent about the size of their nuclear weapon stockpiles. This is curious since the Trump administration had repeatedly complained about secrecy in the Russian and Chinese arsenals. Instead, it now appears to endorse their secrecy.
The decision will undoubtedly fuel suspicion and worst-case mindsets in adversarial countries. Russia will now likely argue that not only has the United States obscured conversion of nuclear launchers under the New START treaty, it has now decided also to keep secret the number of nuclear warheads it has available for them.
Finally, the decision also makes it harder to envision achieving new arms control agreements with Russia and China to curtail their nuclear arsenals. After all, if the United States is not willing to maintain transparency of its warhead inventory, why should they disclose theirs?
It is yet unclear why the decision not to disclose the 2018 stockpile number was made. There are several possibilities:
- Is it because the chaos and incompetence in the Trump administration have enabled hardliners and secrecy zealots to reverse a policy they disagreed with anyway?
- Is it a result of the Nuclear Posture Review’s embrace of Great Power Competition with Cold War-like instincts to increase reliance on nuclear weapons, kill arms control treaties, increase secrecy, and scuttle policies that some say appease adversaries?
- Is it because of a Trump administration mindset opposing anything created by president Obama?
- Or is it because the United States has secretly begun to increase the size of its nuclear stockpile? (I don’t think so; the stockpile appears to have continued to decrease to now at or just below 3,800 warheads.)
The answer may be as simple as “because it can” with no opposition from the White House. Whatever the reason, the decision to reinstate stockpile secrecy caps a startling and rapid transformation of U.S. nuclear policy. Within just a little over two years, the United States under the chaotic and disastrous policies of the Trump administration has gone from promoting nuclear transparency, arms control, and nuclear constraint to increasing nuclear secrecy, abandoning arms control agreements, producing new nuclear weapons, and increasing reliance on such weapons in the name of Great Power Competition.
This is a historic policy reversal by any standard and one that demands the utmost effort on the part of Congress and the 2020 presidential election candidates to prevent the United States from essentially going nuclear rogue but return it to a more constructive nuclear weapons policy.
This publication was made possible by generous contributions from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the New Land Foundation, the Ploughshares Fund, and the Prospect Hill Foundation. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the authors.
FAS Nuclear Notebook Published: US Nuclear Forces, 2016

By Hans M. Kristensen and Robert S. Norris
Our latest FAS Nuclear Notebook has been published in the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. This issue provides a new overview of the status and plans for US nuclear forces and updates our estimate of the number of nuclear weapons in the stockpile and deployed force.
The next issue scheduled for May will be on Russian nuclear forces.
For an update on worldwide nuclear weapons inventories, see our World Nuclear Forces web page.
The research for this publication was made possible by a grant from the New Land Foundation, and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the authors.
New Nuclear Notebook: Russian Nuclear Forces 2015
By Hans M. Kristensen
Russian nuclear weapons have received a lot of attention lately. Russian officials casually throw around direct or thinly veiled nuclear threats (here, here and here). And U.S. defense hawks rail (here and here) about a Russian nuclear buildup.
In reality, rather than building up, Russia is building down but appears to be working to level off the force within the next decade to prevent further unilateral reduction of its strategic nuclear force in the future. For details, see the latest FAS Nuclear Notebook on the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists web site.
This trend makes it more important for the United States and Russia to reach additional nuclear arms control agreements to reduce strategic nuclear forces. Hard to imagine in the current climate, but remember: even at the height of the Cold War the two sides reached important arms limitation agreements because it was seen then (as it is now) to be in their national security interest.
Trends: Launchers and Warheads
There are many uncertainties about the future development of Russian nuclear forces. Other than three aggregate numbers released under the New START Treaty, neither Russia nor the United States publish data on the numbers of Russian nuclear forces.
Russian officials occasionally make statements about the status of individual nuclear launchers and modernization programs, and Russian news articles provide additional background. Moreover, commercial satellite photos make it possible to monitor (to some extent) the status of strategic nuclear forces.
As a result, there is considerable – and growing – uncertainty about the status and trend of Russian nuclear forces. The available information indicates that Russia is continuing to reduce its strategic nuclear launchers well below the limit set by the New START Treaty. Over the next decade, all Soviet-era ICBMs (SS-18, SS-19, and SS-25) will be retired, the navy’s Delta III SSBN and its SS-N-18 missiles will be retired, and some of the Delta IV SSBNs will probably be retired as well.
To replace the Soviet-era launchers, Russia is deploying and developing several versions of the SS-27 ICBM and developing a new “heavy” ICBM. The navy is deploying the Borey-class SSBN with a new missile, the SS-N-32 (Bulava). This transition has been underway since 1997.
Depending on the extent of modernization plans over the next decade and how many missiles Russia can actually produce and deploy, the overall strategic force appears to be leveling off just below 500 launchers (see below), well below the New START Treaty limits of 700 deployed strategic launchers and 800 deployed and non-deployed strategic launchers.
The warhead loading on the strategic launchers is also decreasing mainly because of the retirement of warhead-heavy SS-18 and SS-19 ICBMs. But because single-warhead SS-25s are being replaced with MIRVed SS-27s, and because the navy’s new SS-N-32 (Bulava) missile carries more warheads than the SS-N-18 and SS-N-23 missiles it is replacing, the overall warhead loading appears to be leveling off as well (see below).

Not all of these warheads are deployed on launchers at any given time. Weapons are not loaded on bombers under normal circumstances and some SSBNs and ICBMs are down for maintenance or repair. The latest New START Treaty warhead count was 1,582 warheads, which means approximately 1,525 warheads were on SSBNs and ICBMs (excluding the roughly 55 counted bombers that are artificially attributed one weapon each).
Non-strategic nuclear weapons are also described in the Notebook. Their status is even more uncertain than the strategic forces. We estimate there are roughly 2,000 warheads assigned to fighter-bombers, short-range ballistic missiles, naval cruise missiles and anti-submarine weapons, and land-based defense and missile-defense forces. Some of the non-strategic nuclear forces are also being modernized and the United States has accused Russia of developing a new ground-launched cruise missile in violation of the INF Treaty, but overall the size of the non-strategic nuclear forces will likely decreased over the next decade.
Russian Nuclear Strategy: What’s Real?
Underpinning these nuclear forces is Russia’s nuclear strategy, which reportedly is causing concern in NATO. A new study was discussed at the NATO ministerial meeting in February. “What worries us most in this strategy is the modernization of the Russian nuclear forces, the increase in the level of training of those forces and the possible combination between conventional actions and the use of nuclear forces, including possibly in the framework of a hybrid war,” one unnamed NATO official told Reuters.
That sounds like a summary of events over the past decade merged with fear that Putin’s currently military escapades could escalate into something more. The nuclear modernizations have been underway for a long time and the increased training is widely reported but its implications less clear. For all its concern about Russian nuclear strategy, NATO hasn’t said much in public about specific new developments.
A senior NATO official recently said Russia’s Zapad exercise in 2013 was “supposed to be a counter-terrorism exercise but it involved the (simulated) use of nuclear weapons.” In contrast, an earlier private analysis of Zapad-13 said the exercise included “virtually the entire range of conceivable military operations except for nuclear strikes…”
Russian nuclear strategy has been relatively consistent over the past decade. The most recent version, approved by Putin in December 2014, states that Russia “shall reserve for itself the right to employ nuclear weapons in response to the use against it and/or its allies of nuclear and other kinds of weapons of mass destruction, as well as in the case of aggression against the Russian Federation with use of conventional weapons when the state’s very existence has been threatened.”
This formulation is almost identical to the mission described in the 2010 version of the doctrine, which stated that Russia “reserves the right to utilize nuclear weapons in response to the utilization of nuclear and other types of weapons of mass destruction against it and (or) its allies, and also in the event of aggression against the Russian Federation involving the use of conventional weapons when the very existence of the state is under threat.”
Despite many rumors in both 2010 and 2014 that the strategy would incorporate preemptive nuclear strikes, neither document discusses such options (it is unknown what is in the secret versions). On the contrary, the nuclear portion of the strategy doesn’t seem that different from what NATO and the United States say about the role of their nuclear weapons: responding to use of weapons of mass destruction and even significant conventional attacks. The Russian strategy appears to limit the nuclear use in response to conventional attacks to when the “very existence” of Russia is threatened.
Given this defensive and somewhat restrictive nuclear strategy, why do we hear Russian officials throwing around nuclear threats against all sorts of scenarios that do not involve WMD attacks against Russia or threaten the very existence of the country?
For example, why does the Russian Ambassador to Denmark threaten nuclear strikes against Danish warships if they were equipped with radars that form part of the U.S. missile defense system when they would not constitute a WMD attack or threaten the existence of Russia?
Or why does President Putin say he would have considered placing nuclear weapons on alert if NATO had intervened to prevent annexation of the Crimean Peninsula if it were not an WMD attack or threaten the existence of Russia? (Note: Russia already has nuclear weapons on alert, although not in Crimea).
Or why did Russian officials tell U.S. officials that Russia would consider using nuclear weapons if NATO tries to force return of Crimea to Ukrainian control or deploys sizable forces to the Baltic States, if these acts do not involve WMD attacks or threaten the existence of Russia? (Kremlin denied its officials said that).
When officials from a nuclear-armed country make nuclear threats one obviously has to pay attention – especially if made by the president. But these nuclear threats so deviate from Russia’s public nuclear strategy that they are either blustering, or Russia has a very different nuclear strategy than its official documents portray.
Ironically, the more Russian officials throw around nuclear threats, the weaker Russia appears. Whereas NATO and the United States have been reluctant to refer to the role of nuclear weapons in the current crisis (despite what you might hear, the justification for U.S. non-strategic nuclear weapons in Europe is weaker today than it was before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine) and instead emphasized conventional forces and operations, Russia’s nuclear threats reveal that Russian officials do not believe their conventional forces are capable of defending Russia – even against conventional attack.
That makes it even stranger that Putin is wasting enormous sums of money on maintaining a large nuclear arsenal instead of focusing on modernizing Russia’s conventional forces, as well as using arms control to try to reduce NATO’s nuclear and conventional forces. That would actually improved Russia’s security.