A Research, Learning, and Opportunity Agenda for Rebuilding Trust in Government
American trust in government institutions is at historic lows. You’ve heard that so many times – we get it! Our series on trust in government functions has given you all the context you might ever desire on why that matters. What we haven’t done yet (and what too few do) is talk about what may be needed to rebuild trust in government institutions, broadly, but also specifically.
At a recent workshop hosted by the Federal of American Scientists, we explored the nature of trust in specific government functions, the risk and implications of breaking trust in those systems, and how we’d known we were getting close to specific trust breaking points. The scenarios we developed were not only meant as cautionary tales, but to serve as reference foundations to plan against for any future reform efforts, should trust continue to decline generally or specifically. But we also started to explore the question of what actions may be needed to rebuild trust from a total breakdown – or, absent that, what we need to know to make that rebuilding possible.
What follows is an opportunity agenda for those invested in rebuilding trust in government functions. Instead of admiring the problem with another dozen think pieces on how dire the situation has been for decades, there’s homework we can do now to build our our trust toolkit. This includes:
- Research Opportunities: questions we don’t know the answer to
- Learning Opportunities: Areas where pilots, experiments, explorations or iteration can test what works
- Design Opportunities: Spaces where we already know enough to start building solutions, but need creativity, co-design, champions, and implementation pathways.
This is just the start, reflecting the dozens of suggestions by workshop participants in our too-short session. You undoubtedly have more (let us know!). What we hope it offers is a list of possibilities for policymakers, academics, funders, and practitioners to deepen understanding and test reforms.
Workforce: Trust as a System-Level Challenge
Research Questions
- How does American’s trust vary between career civil servants, short-term experts, and political appointees?
- What is the relationship between negative news coverage about an agency (e.g., performance or layoffs) and different measures of public engagement with that agency (e.g., application rates to that agency?)
- What incentives might make a national service requirement acceptable to Americans?
- What are current views by college age and early career Americans on public service? How has public service motivation changed?
- What are public and key stakeholder views on “merit,” and do expectations of merit drive trust?
- Are there examples of senior leaders who highlight the work of public servants in the United States, and are trust measures in those locations notably different?
- What approaches may better communicate the compliance and oversight barriers civil servants face (both as a means showing anti-corruption/anti-waste and potentially incentivizing support for barrier reduction)?
- How might Americans better understand the “risk management” or “preventative” role that public servants play?
Learning Opportunities
- Pilot programs: test and learn (or document prior learning from) initiatives like civilian mid-career recruitment (e.g., AI leaders in civilian roles, building on military parallels), national and targeted hiring fairs that generate long-term interests.
- Experiment with models of “frictionless” federal applications and one-stop hiring actions.
- Explore early-career exposure to inspiring public servants as a way to seed pride and long-term interest.
- Explore what would be required to restart proven pathways like PMF and broaden service corps models beyond college grads.
- In states with fewer public sector workforce protections, explore what hiring incentives are most in use/most effective
Design Challenges
- Campaigns to highlight federal workers at local/state/national levels, including “famous names” doing stints in public service.
- Meet mission on a specific, high-salience task (ex. Philly I-95) and connect with a “join us” campaign.
- Expand representation of communicators about federal work and workers beyond spokespeople, encouraging all federal workers to take responsibility of public engagement.
- Instill recruitment and overall workforce health as an SES competency.
Procurement: Trust Through Smarter Buying and Clearer Accountability
Research Needs
- What does a sophisticated sourcing strategy look like (market shaping, competition), and what capacities are missing?
- How might AI reshape procurement—and how might it affect perceptions of fairness and accountability?
- Where should procurement risk and responsibility lie to encourage creative but accountable strategies?
- Consider differentiation between “hard”procurement and “bad”procurement and how to productively learn from each.
Learning Opportunities
- Transparently evaluate agile and creative sourcing pilots.
- Develop, refine, and use vendor and bidder experience surveys as part of trust-building.
- Study the impacts of various kinds of procurement transparency on public confidence (e.g.,taking different approaches around contracts, bids, subcontractors, progress, cost overruns, and past performance)
Design Challenges
- Elevate acquisitions professionals as strategic leaders and outcomes builders, not compliance gatekeepers.
- Begin to build in capacity in priority agencies better oversee modern digital contracts.
- Invest in capacity in key areas for strategic insourcing.
Customer Experience: Trust as an Exercise in Proactive Service and Listening
Research Needs
- How does diminished service quality affect public trust, and how hard is it to earn back?
- Can community trust be influenced by CX improvements? How?
- What role does casework play in shaping congressional perspectives on service delivery?
- Where do Americans think priority public services come from?
Learning Opportunities
- Pilot outcome-driven legislation toolkits to help Congress set goals that agencies are trusted to deliver.
- Pilot agency field-office expansion or deployment opportunities to better meet people where they are for service needs and benefit questions
- Expand testing of approaches to embed resources like user experience, equity impact assessments and trauma-informed practices into service design.
- Pilot casework supports (e.g., staff details) and casework connectivity to federal service communities to better connect Congressional casework and federal services.
- Support communities of practice among CX experts.
Design Challenges
- Educate congressional staffs on appointee CX responsibilities to improve oversight.
- Reduce administrative burdens: plain language, translation, integration across agencies.
- Embed use of authentic co-design and public engagement (including with AI tools) to close feedback loops.
- Expand civic education and change management campaigns to reframe government as a source of pride.
- Link CX and public outcomes transparently through KPIs tied to delivery.
Data: Trust in Evidence, Transparency, Reliability, and Capacity
Research Needs
- How might government (and champions of good government) communicate the importance of federal data to the public in ways that build trust and legitimacy?
- Which datasets are of highest public value (beyond economic value), and what is their role? What are upstream and downstream impacts of changes those data sets?
- How do we evaluate and communicate the staffing and technical capacity needed for robust statistical functions (as a point of comparison, like military readiness)?
- How might we forecast or scenario plan around disappearance of data sets, and how might we plan for future potential reintegration of such datasets? With what sort of governance models?
Learning Opportunities
- Test public AI tools with strong user interfaces to make data more accessible and usable – both increasing utility and also public awareness and investment.
- Pilot, learn from, and grow robust public engagement opportunities around public sector data governance.
- Explore public participation pilots in data collection and governance, particularly among underrepresented groups. Assess what works, what generates impact, what captures imagination.
- As external groups take on data collection, governance, and analytic roles previously held by government, explore and test different models for public governance, ownership, oversight and potential transition plans.
Design Challenges
- Develop public-facing data maps (e.g., Sankey charts of data flows and uses) to visualize and communicate government’s role.
- Strengthen public data governance, potentially through new institutions (e.g., equivalent of the National Assessment Governing Board for education).
- Invest in public sector career development pathways where data skills are rewarded.
Cross-Cutting Directions
Research Needs
- Communicating accountability: What are different successful and unsuccessful models of communicating accountability measures and actions in public sector functions?
- Participatory accountability, oversight, and performance measures: What are more participatory or community based efforts to engage citizens in public oversight, accountability and performance measurement?
- Absence of trust: What are the compliance-based costs of absence of trust in government?
Conclusion
The actions surfaced by participants reflect more than tactical fixes—they point to a research and design agenda for the field. Trust is not just the hoped-for outcome of reform, but the principle that should shape how reforms are tested and evaluated. By pursuing these questions, piloting these ideas, and designing around trust, the government capacity community can help rebuild institutions that are not only effective but also respected, legitimate, and deeply connected to the people they serve.
In Remembrance of Dearly Departed Federal Datasets
On this All Hallow’s Eve, let us recognize the losses of datasets that served the American people
There’s been lots of talk – and some numbers (often in the thousands) – about disappearing federal datasets, especially after many went dark last January when agencies rushed to scrub the perceived spectre of data on gender, DEI, and climate from the public record. Most of those datasets have returned from the dead, some permanently changed by the experience.
Though it’s premature to breathe a sigh of relief – the future of federal data remains in jeopardy – we thought Halloween was an opportune time to ask, which federal datasets have left this mortal realm?
Here’s what we found.
The good news
For the most part, the vast majority of the hundreds of thousands of datasets produced by the federal government are still alive, and have so far escaped mutilation1 or termination. By our rough counts, the datasets that have been truly axed number perhaps in the dozens (not hundreds or thousands).
The bad news
All federal datasets are currently at risk of death by a thousand cuts, weakened by the loss of staff and expertise, contracts, and scientific advisory committees. Just because a given dataset hasn’t been explicitly killed off, doesn’t mean that an agency still has the capacity to collect, protect, process, and publish that data. Also, datasets and variables that do not align with Administration priorities, or might reflect poorly on Administration policy impacts, seem to be especially in the cross-hairs.
The details
We’ve identified three types of data decedents. Examples are below, but visit the Dearly Departed Dataset Graveyard at EssentialData.US for a more complete tally and relevant links.
- Terminated datasets. These are data that used to be collected and published on a regular basis (for example, every year) and will no longer be collected. When an agency terminates a collection, historical data are usually still available on federal websites. This includes the well-publicized terminations of USDA’s Current Population Survey Food Security Supplement, and EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program, as well as the less-publicized demise of SAMHSA’s Drug Abuse Warning Network (DAWN). Meanwhile, the Community Resilience Estimates Equity Supplement that identified neighborhoods most socially vulnerable to disasters has both been terminated and pulled from the Census Bureau’s website.
- Removed variables. With some datasets, agencies have taken out specific data columns, generally to remove variables not aligned with Administration priorities. That includes Race/Ethnicity (OPM’s Fedscope data on the federal workforce) and Gender Identity (DOJ’s National Crime Victimization Survey, the Bureau of Prison’s Inmate Statistics, and many more datasets across agencies).
- Discontinued tools. Digital tools can help a broader audience of Americans make use of federal datasets. Departed tools include EPA’s Environmental Justice Screening and Mapping tool – known to friends as “EJ Screen” – which shined a light on communities overburdened by environmental harms, and also Homeland Infrastructure Foundation-Level Data (HIFLD) Open, a digital go-bag of ~300 critical infrastructure datasets from across federal agencies relied on by emergency managers around the country.
Forever in our hearts, and in some cases, given a second life
Another pattern we saw is that some tools have been reincarnated in civil society. Climate Central breathed life back into the U.S. Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters database, Public Environmental Data Partners did the same for EJScreen, and Fulton Ring brought back FEMA’s Future Risk Index. All of these tools still depend on the federal data underlying them. Beware, without fresh data to feed on, these tools will turn into the walking dead.
Lurking in the shadows
While our focus now is on deceased federal datasets, other threats loom heavy on the horizon. For example, there are a growing number of examples where the primary federal data remain, but the Administration’s interpretation of that data has veered away from science and toward politics (cases in point: Department of Energy’s July report on the impacts of greenhouse gas emissions on the climate or the CDC’s September guidance on COVID vaccines for children). The data systems aren’t dead, but the implications certainly are scary.
We invite you to take a moment to click through the graveyard of the federal datasets, variables, and tools mentioned above, and more, at the Dearly Departed Dataset Graveyard at EssentialData.US. And if we missed a dataset, please let us know.
Happy Halloween 🎃
Huge thanks to colleagues in the Federation of American Scientists and EssentialData.US, The Impact Project, and Public Environmental Data Partners for the collaboration on this project, and for all who submitted obituaries of their dearly departed datasets.
This analysis includes data, variables, and tools that have been terminated or removed before their time. It represents an attempt to capture substantive data losses and changes above baseline. For example, most data collections for evaluation purposes are not intended to go on indefinitely, and their termination is not included. Additionally, administrations often stand up websites and interactive tools to advance specific policies. We are not cataloging the breadth of such tools that disappeared.
CORRECTION: An earlier version of this post described the “System Name” column in the Federal AI Use Case Inventory as missing. In fact, the dataset had been restructured, but still retained that column. We’ll scratch that one off our list of datasets to light a candle for 
Innovation Ecosystem Job Board Launches to Connect Federal Talent to Opportunities
In a previous post, we announced an initiative to connect scientists, engineers, technologists, and skilled federal workers and contractors who have recently departed government service with the emerging innovation ecosystems across America that could use their expertise. With the support of FAS, we are now excited to share the launch of the Innovation Ecosystem Job Board. This unique job board contains opportunities from across the nation with the explicit goal of matching in-demand science and technology talent with open positions across the nation’s innovation ecosystems, in roles ranging from lab researchers and data scientists to workforce development practitioners and science communicators.
These innovation ecosystems – namely Tech Hubs and NSF Engines – are advancing critical technologies spanning from advanced manufacturing to quantum computing to biotech, all vital for our national and economic security. To accomplish this work, they operate as multi-stakeholder coalitions that bring together universities, industry, nonprofits, and other partners, all searching for talent to help them fulfill their missions.
These coalitions face growing talent needs, particularly for mission-driven roles that can help drive progress across critical technology areas. Meanwhile, we’re witnessing an exodus of thousands of experienced federal talent from agencies like the National Science Foundation, National Institutes for Health, and the Department of Energy whose knowledge gained from years of managing and working in multimillion-dollar technical programs could be lost entirely if not effectively redeployed.
This initiative directly addresses both challenges by collaborating with innovation ecosystems to identify their immediate talent needs while simultaneously engaging displaced federal workers through job fairs and targeted outreach to understand their backgrounds and geographic preferences. It’s a purposeful approach that ensures mission-driven federal talent can continue contributing to America’s technological leadership. By connecting talent to need, we help strategically imperative innovation ecosystems access the experienced professionals necessary for success.
We will be updating this job board regularly with opportunities from additional Tech Hubs, NSF Engines, and other innovation ecosystems. While our outreach is specifically to former federal workers and contractors, this job board is open to all, and we encourage others on the job hunt to take a look.
As economic policy wonks, we understand that there are often frictions that hinder matching between individuals with the right skills and geographic preferences and the jobs that exist. We are taking this seriously and will engage in what we’re calling “light-touch matching”. Please feel free to fill out this interest form (whether you have applied to a listing on the job board or not), and we will flag profiles that generally align with relevant innovation ecosystems and their needs.
Our process:
We spent the last several months talking to and learning from other talent connectors, innovation ecosystem builders, and the talent themselves. Through facilitated federal roundtables with former federal workers, we understood more deeply their diverse skill sets, their unwavering commitment to mission-driven work, and the unique challenges they face in their current job transition. Work for America’s research on federal workers also validated our hypotheses: these are experienced professionals (59% of survey respondents have a decade or more of experience), are geographically distributed (53% already live outside the DC-Virginia-Maryland area), and are mobile (54% are open to relocating). Job fairs additionally provided us an opportunity to meet individuals leaving the federal government and hear about their backgrounds and interests.
Simultaneously, we reached out to several innovation ecosystems to explore if they had immediate talent needs. Some ecosystems shared their most critical postings among their partners; others had recently conducted surveys of their coalitions to assess available positions and passed that information on to us; still others are actively developing comprehensive approaches to capture all the talent needs across their expansive coalitions. We reviewed and aggregated these opportunities into the job board which is now available and will be regularly updated. We are grateful for all these ecosystems that have engaged in this initiative and we look forward to continuing the conversation with more ecosystems and skilled former federal professionals alike.
Like anything new, this is an experiment. Does this effort in the end successfully match candidates and employers based on skills and geography? If you use this tool, please let us know how it goes!
Maryam Janani-Flores (mjananiflores@fas.org) is a Senior Fellow at FAS and former Chief of Staff at the U.S. Economic Development Administration. Meron Yohannes (myohannes@fas.org) is a Digital Services Alumni Fellow at FAS and most recently served as Senior Policy Advisor for the U.S. Secretary of Commerce.
Breaking Down the New Memos on Federal Hiring
On May 29, the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) published two memoranda that could substantially reshape federal hiring. The first–“Merit Hiring Plan”–issued with the White House Domestic Policy Council—implements Executive Order 14170. The second provides guidance on “Hiring and Talent Development for the Senior Executive Service”. Spanning 53 pages, the documents are written in dense HR jargon that can overwhelm even seasoned practitioners. To clarify their meaning and impact, the Niskanen Center and the Federation of American Scientists have teamed up to translate both memos for journalists, researchers, and the general public.
The Memos Generally: Lots To Like, Dangerous Partisanship, & A Long Road Ahead
The memos, at their core, attempt to address well-documented and long-existing challenges: federal hiring is too sluggish, procedural, and opaque. Both of our organizations have long argued for the need to move faster, hire better, and hold poor performing employees accountable while still adhering to the merit system principles. A high-performing, agile, and engaged federal workforce is essential if Americans are to trust if Americans are to trust that laws passed by Congress will be executed quickly, competently and efficiently.
These memos are the latest in a long line of efforts by Presidents of both parties to bring common sense to federal hiring and performance – speed up the hiring process, focus on the skills to do the job, evaluate those skills objectively, and share resources across agencies to economize on effort and investment. These memos push that agenda further than earlier efforts, delivering several long‑sought wins such as streamlined applications and résumés more in line with private‑sector norms.
They also venture further than any recent initiative in politicizing the civil service. Mandatory training and essay questions tied to the current Administration’s executive orders—and explicit political sign‑off on certain hiring actions—risk blurring the firewall between career professionals and partisan appointees. We have discussed the dangers associated with this type of partisan drift in other places, including in response to the recent OPM rulemaking on “Schedule Policy/Career”.
Implementing even the non-controversial portions will be daunting. Reforming the federal government–the largest employer in the country–requires sustained, years-long effort from OPM and OMB.
The memos themselves are only the starting gun. Notably absent is a realistic plan to resource this work: for example, OPM has fired or lost nearly all of its enterprise data analytics team, limiting its ability to supply the metrics needed for oversight and accountability. Additionally, the inclusion of extremely ideological and partisan goals politicizes the entire agenda and risks overshadowing the rest of the positive reform agenda, threatening its ability to succeed anywhere.
In evaluating these documents, we have to weigh each part of the Administration’s strategy separately and objectively – there is a lot to like in these documents, there are things that are deeply troubling, and there are things that desperately need leadership attention in implementation.
What We Like: Skills-Based Hiring, Resume Reform, Assessments, Sharing Across Agencies
The bulk of both memos represents a bold next step in long‑running federal hiring reforms—initiatives that agencies have piloted for years but often struggled to scale. We commend OPM for learning from past efforts and, in several critical areas, pushing further than any of its predecessors by:
- Recognizing the role of recruiting and sourcing talent – The plan highlights the importance of active recruiting in the hiring process.Agencies have long relied on USAJobs alone as a crutch, hoping the right kinds of talent will be scouring the job board every day and happen upon job postings – this works okay for some roles that are highly-specialized to government, but particularly as agencies have need for emerging talent it they cannot assume critical talent pools are even aware that the federal government wants to hire them.
- Focusing on skills and evaluating for those skills – The memo limits the use of self-assessments to minimum qualifications only and requires agencies to use some form of technical or alternative assessment for all postings, implementing 2024’s bipartisan Chance to Compete Act. This is a critical move forward from the reliance on applicant’s self-assessment,a status quo that disadvantages honesty and self-awareness.
- Implementing ‘Rule of Many’ ranking procedures – OPM will finalize its proposed ‘Rule of Many’ regulation from the last Administration, which empowers agencies to choose the various ways to “cut off” applicants after they are assessed. Finalizing ‘Rule of Many’ will enable agencies to set clear, objective criteria for which applicants it will consider based on test scores (e.g., considering the top 10% of scorers), a numerical approach (e.g., considering the top 50 applicants), and other mechanisms (e.g., clear pass/fail standards) that give hiring managers and HR specialists the flexibility they need to tailor hiring procedures to specific needs.
- Sharing resources and certifications of eligibles across agencies – This expands requirements for agencies to share candidates, position descriptions, and talent pools across agencies, including conducting pooled hiring actions where one candidate can apply once to many similar jobs across government. It builds on recent tremendous success agencies have with recruiting high-quality applicants across government through shared hiring actions, which enables agencies to surge talent in a specific field and advertise as one enterprise to potential applicants.
- Reducing size of referral resumes to two pages – OPM is finally attempting to move away from a “federal resume” format that needlessly burdens members of the public with overly-specific requirements. Previously, applicants that didn’t know to include things like the “average number of hours worked per week” or their complete salary history were unknowingly disqualifying themselves from federal employment and even those that knew better had to maintain two separate resumes, making it harder to jump between sectors.
- Simplifying Senior Executive applications – Applicants for Senior Executive Service roles will no longer be required to write multiple pages of essays describing their experience – a process so unique it has spawned a cottage industry of professional writers – and will be evaluated via resumes and structured interviews like their peers across the economy. This builds on a long history of successful pilots of new selection procedures focusing on resumes and structured interviews rather than the traditional essays.
- Removing unnecessary degree requirements – While efforts have been underway since the first Trump Administration to remove unnecessary degree requirements. The new memos solidify that trajectory, embracing a skills‑first hiring model that prizes demonstrated ability over paper credentials—a trend mirrored in state governments and the private sector. Yet dropping degree rules is only half the battle. To truly broaden the talent pool, agencies must replace résumé shortcuts (like “years of experience”) with rigorous, job‑relevant assessments that let candidates prove what they can actually do.
- Focusing on speed and responsiveness – The memo doesn’t ignore the aspect of the applicant experience that differs most from the private sector: speed and responsiveness, setting a government-wide target of 80 days for hiring actions and requiring timely updates to applicants on their status. This builds on years of work to wrestle down timelines for security clearances and recognizes that one of the biggest reasons the federal government loses amazing applicants is the length of the process, not the pay.
Finally, the memos contain a compendium of useful resources in Appendices that agencies that can use to improve their approach to hiring.
Potential Red Flags: Politicization, Red Tape, & Extra, Unfunded Mandates
While OPM is advancing important nonpartisan reforms, we are concerned that several explicitly ideological provisions could erode the civil service’s neutrality and jeopardize the very hiring‑efficiency agenda OPM seeks to champion:
- Requiring essay questions on political views–Despite reducing applicant burden in other areas, OPM also introduces a requirement for all applicants for jobs above GS-05 (98%+ of jobs) to draft responses to free-response essay questions that describe their views on the present administration, including identifying which of the current president’s Executive Orders are “significant” to them. At best, this is an additional requirement that will be irrelevant for most jobs – there shouldn’t be any impact of EOs on a seasonal wildland firefighter’s strategy for fighting fires, for instance. More realistically, this constitutes a partisan loyalty test for federal employees to evaluate their views on the current President. Federal employees swear their allegiance to the Constitution, not the current President and there are legitimate open questions about the constitutionality of many Executive Orders.
- Introducing extra layers of political approval in the hiring process–While the memo emphasizes time to hire, it also emphasizes that “agency leadership” must either personally approve or designate an official to approve all positions before they are posted and all selections prior to extension of an offer. It also requires that they do an “executive interview” with candidates and opens the door to obvious partisan abuse of the merit hiring process when paired with the free response essay questions. Even without that risk, however, this requirement adds tremendous amounts of friction into a process that is already too full of approvals and pulls the decision-making authority in the wrong direction: to leadership instead of to the line management that knows the needs of a given program best. We are already seeing the problems with this approach play out with a similar requirement for agency leadership to personally approve payments or contracts, leading to extreme slowdowns. Additionally, just as with OPM’s recent rulemaking on Schedule Policy/Career, the opportunity for abuse is extremely obvious: highly partisan agency leaders may see it as their right to disapprove of candidates for purely political reasons–like, for example, donations to opposing candidates.
- Prioritizes political training for the SES corps–While the Administration has closed down training programs like the Federal Executive Institute that were designed to train new generations of federal leaders, it is also adding ideological training to the SES that lacks a clear purpose or evidence that it will improve governing outcomes. Requiring Senior Executives to watch an “80-hour video-based program that provides training regarding President Trump’s Executive Orders” is both offensive to the principle of a nonpartisan civil service and a waste of time for the busiest, most senior leaders across the entire enterprise. While America’s most productive tech companies are trying to reduce the meeting load to free staff to get things done, torching 4% of our senior executives’ working years for ideological training is the opposite of efficient.
- No mention of resources to carry out these changes – As with past legislation, EOs, and memos requiring skills-based talent practices, no apparent financial or other resources come with these memos. This has hampered adoption for more than a decade. The Talent Teams at OPM and the agencies, the communications and education support, the changes to OPM and agency systems all need people, money, and IT support. The lack of committed resources will delay, and perhaps scuttle, implementation. We know this because it has happened before. In the Clinton Administration, for example, a major push to de-proceduralize federal hiring fell down because they underresourced agency HR offices to stick the landing. This will happen again on skills-based hiring without commensurate investment, a problem discussed at length in a recent paper from the Niskanen Center.
What’s Missing: A Scalable Implementation Strategy
Executing these reforms will be no small feat, and the toughest tasks are also the most crucial: getting good technical assessments in the hands of managers, conducting strategic workforce planning, changing the culture around hiring to empower managers and not HR, and letting line managers be managers. OPM’s memos are light on details about how they intend to resource and manage implementation, an omission that they have plenty of time to correct but one that needs some serious consideration if they are going to be successful:
- Changing entrenched oversight, HR, and hiring manager policies, practices, and culture – OPM and the agencies will need to focus on how to move decades-learned compliance and risk aversion behaviors embedded in the current hiring and performance management practices into a skills-based future. The change management and consistent leadership required here is a substantial undertaking. Because OPM has conditioned the federal HR profession to be incredibly risk-averse, it won’t immediately embrace these new mandates without coaching, training, and professional development. To facilitate this, OPM should re-submit its uncontroversial legislative proposal from last year to help professionalize and develop the federal HR workforce, and Congress should expeditiously pass it.
- Hiring is just one piece of the effective federal employee puzzle – Though the SES Memo addresses some aspects of performance management, the focus on hiring diminishes other parts of the management system that impact effectiveness and performance. Onboarding, the early job experience, consistent feedback, professional development, challenging assignments, and career paths all help to ensure employees are helping meet agency missions. Implementation needs to take the whole system into account if OPM and the agencies are going to impact effectiveness and accountability.
- An all-of-the-above approach for getting assessments into the hands of agencies – The memo focuses on USAHire but, as we’ve discussed, there are many third-party assessment vendors that offer validated assessments and tools to help lower the unit and marginal cost of using objective assessments. Emerging companies offer things like AI-proctored video interviews that could quickly surface the most promising candidates and are already in use by the private sector for high-volume roles. At the federal level, parts of the Department of Homeland Security and other agencies have already experimented with some of these platforms. We want to see OPM think bigger about how to quickly bring assessments online and recognize that the private sector can play a role in accelerating this transformation.
- Focus on the candidate experience – Job candidates – users of the federal hiring system – complain that the experience of applying for a federal job is neither easy nor seamless, as it can be in the private sector. While the memos make some progress in reducing the burden on candidates (e.g., reducing resume and SES application requirements), the system is still rife with bureaucratic bloat. High-performing candidates have many options; they will go elsewhere if we do not reduce the friction.
- Public accountability & data – According to the hiring plan memo, agencies need to develop a data-driven plan for implementation and report frequently to OPM and OMB on their progress. With the practical dissolution of OPM’s human capital data team and a years-long problem with lagging human capital data releases via Fedscope, OPM should commit to releasing data publicly on their progress: how many people are hired, where they are hired, how many apply, how many pass technical assessments, etc. that will hold agencies accountable for getting this work done, give Congress the insight it needs to trust OPM, and provide the public with a window into progress.
- A plan to staff for success – In the best of times, OPM struggles with capacity for human capital policy work, and it will need every federal human capital expert it can get to pull off implementation of these memos. However, at the same time, OMB’s FY2026 budget proposal outlines a significant reduction in total headcount for OPM that locks in a 25%+ reduction in headcount across all parts of the agency, from policy to direct support for agencies. Given the technical complexity involved in many of these efforts–delivering validated assessments, for example, will likely require bringing in new expertise from outside government–OPM will need a plan to staff itself for success that is missing in these memos today.
In urgent circumstances, agencies have experimented with some of these practices and policies (e.g., cybersecurity hiring and intelligence community hiring, infrastructure and energy development). However, action on skills-based talent practices is far from pervasive. Together with outside experts, we continue to map the obstacles that keep skills‑first hiring from taking root: limited resources, hesitant leadership, and a pervasive fear of downside risk. Many of the opportunities and chokepoints highlighted in the memos came from this work, and we will keep collaborating with all stakeholders to craft practical fixes.
Most of the reforms in these memoranda set federal hiring on a promising trajectory, but their impact will hinge on disciplined execution. Some of them are deeply troubling attacks on the basis of the merit system. We will track OPM’s progress closely—amplifying best practices and calling out any drift from merit‑based, nonpartisan norms. These challenges are not new, yet they have become increasingly existential to building a government that works; OPM must keep that urgency front and center as implementation moves forward.
Reforming the Federal Advisory Committee Landscape for Improved Evidence-based Decision Making and Increasing Public Trust
Federal Advisory Committees (FACs) are the single point of entry for the American public to provide consensus-based advice and recommendations to the federal government. These Advisory Committees are composed of experts from various fields who serve as Special Government Employees (SGEs), attending committee meetings, writing reports, and voting on potential government actions.
Advisory Committees are needed for the federal decision-making process because they provide additional expertise and in-depth knowledge for the Agency on complex topics, aid the government in gathering information from the public, and allow the public the opportunity to participate in meetings about the Agency’s activities. As currently organized, FACs are not equipped to provide the best evidence-based advice. This is because FACs do not meet transparency requirements set forth by GAO: making pertinent decisions during public meetings, reporting inaccurate cost data, providing official meeting documents publicly available online, and more. FACs have also experienced difficulty with recruiting and retaining top talent to assist with decision making. For these reasons, it is critical that FACs are reformed and equipped with the necessary tools to continue providing the government with the best evidence-based advice. Specifically, advice as it relates to issues such as 1) decreasing the burden of hiring special government employees 2) simplifying the financial disclosure process 3) increasing understanding of reporting requirements and conflict of interest processes 4) expanding training for Advisory Committee members 5) broadening the roles of Committee chairs and designated federal officials 6) increasing public awareness of Advisory Committee roles 7) engaging the public outside of official meetings 8) standardizing representation from Committee representatives 9) ensuring that Advisory Committees are meeting per their charters and 10) bolstering Agency budgets for critical Advisory Committee issues.
Challenge and Opportunity
Protecting the health and safety of the American public and ensuring that the public has the opportunity to participate in the federal decision-making process is crucial. We must evaluate the operations and activities of federal agencies that require the government to solicit evidence-based advice and feedback from various experts through the use of federal Advisory Committees (FACs). These Committees are instrumental in facilitating transparent and collaborative deliberation between the federal government, the advisory body, and the American public and cannot be done through the use of any other mechanism. Advisory Committee recommendations are integral to strengthening public trust and reinforcing the credibility of federal agencies. Nonetheless, public trust in government has been waning and efforts should be made to increase public trust. Public trust is known as the pillar of democracy and fosters trust between parties, particularly when one party is external to the federal government. Therefore, the use of Advisory Committees, when appropriately used, can assist with increasing public trust and ensuring compliance with the law.
There have also been many success stories demonstrating the benefits of Advisory Committees. When Advisory Committees are appropriately staffed based on their charge, they can decrease the workload of federal employees, assist with developing policies for some of our most challenging issues, involve the public in the decision-making process, and more. However, the state of Advisory Committees and the need for reform have been under question, and even more so as we transition to a new administration. Advisory Committees have contributed to the improvement in the quality of life for some Americans through scientific advice, as well as the monitoring of cybersecurity. For example, an FDA Advisory Committee reviewed data and saw promising results for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD) which has been a debilitating disease with limited treatment for years. The Committee voted in favor of gene therapy drugs Casgevy and Lyfgenia which were the first to be approved by the FDA for SCD.
Under the first Trump administration, Executive Order (EO) 13875 resulted in a significant decrease in the number of federal advisory meetings. This limited agencies’ ability to convene external advisors. Federal science advisory committees met less during this administration than any prior administration, met less than what was required from their charter, disbanded long standing Advisory Committees, and scientists receiving agency grants were barred from serving on Advisory Committees. Federal Advisory Committee membership also decreased by 14%, demonstrating the issue of recruiting and retaining top talent. The disbandment of Advisory Committees, exclusion of key scientific external experts from Advisory Committees, and burdensome procedures can potentially trigger severe consequences that affect the health and safety of Americans.
Going into a second Trump administration, it is imperative that Advisory Committees have the opportunity to assist federal agencies with the evidence-based advice needed to make critical decisions that affect the American public. The suggested reforms that follow can work to improve the overall operations of Advisory Committees while still providing the government with necessary evidence-based advice. With successful implementation of the following recommendations, the federal government will be able to reduce administrative burden on staff through the recruitment, onboarding, and conflict of interest processes.
The U.S. Open Government Initiative encourages the promotion and participation of public and community engagement in governmental affairs. However, individual Agencies can and should do more to engage the public. This policy memo identifies several areas of potential reform for Advisory Committees and aims to provide recommendations for improving the overall process without compromising Agency or Advisory Committee membership integrity.
Plan of Action
The proposed plan of action identifies several policy recommendations to reform the federal Advisory Committee (Advisory Committee) process, improving both operations and efficiency. Successful implementation of these policies will 1) improve the Advisory Committee member experience, 2) increase transparency in federal government decision-making, and 3) bolster trust between the federal government, its Advisory Committees, and the public.
Streamline Joining Advisory Committees
Recommendation 1. Decrease the burden of hiring special government employees in an effort to (1) reduce the administrative burden for the Agency and (2) encourage Advisory Committee members, who are also known as special government employees (SGEs), to continue providing the best evidence-based advice to the federal government through reduced onerous procedures
The Ethics in Government Act of 1978 and Executive Order 12674 lists OGE-450 reporting as the required public financial disclosure for all executive branch and special government employees. This Act provides the Office of Government Ethics (OGE) the authority to implement and regulate a financial disclosure system for executive branch and special government employees whose duties have “heightened risk of potential or actual conflicts of interest”. Nonetheless, the reporting process becomes onerous when Advisory Committee members have to complete the OGE-450 before every meeting even if their information remains unchanged. This presents a challenge for Advisory Committee members who wish to continue serving, but are burdened by time constraints. The process also burdens federal staff who manage the financial disclosure system.
Policy Pathway 1. Increase funding for enhanced federal staffing capacity to undertake excessive administrative duties for financial reporting.
Policy Pathway 2. All federal agencies that deploy Advisory Committees can conduct a review of the current OGC-450 process, budget support for this process, and work to develop an electronic process that will eliminate the use of forms and allow participants to select dropdown options indicating if their financial interests have changed.
Recommendation 2. Create and use public platforms such as OpenPayments by CMS to (1) aid in simplifying the financial disclosure reporting process and (2) increase transparency for disclosure procedures
Federal agencies should create a financial disclosure platform that streamlines the process and allows Advisory Committee members to submit their disclosures and easily make updates. This system should also be created to monitor and compare financial conflicts. In addition, agencies that utilize the expertise of Advisory Committees for drugs and devices should identify additional ways in which they can promote financial transparency. These agencies can use Open Payments, a system operated by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), to “promote a more financially transparent and accountable healthcare system”. The Open Payments system makes payments from medical and drug device companies to individuals, healthcare providers, and teaching hospitals accessible to the public. If for any reason financial disclosure forms are called into question, the Open Payments platform can act as a check and balance in identifying any potential financial interests of Advisory Committee members. Further steps that can be taken to simplify the financial disclosure process would be to utilize conflict of interest software such as Ethico which is a comprehensive tool that allows for customizable disclosure forms, disclosure analytics for comparisons, and process automation.
Policy Pathway. The Office of Government Ethics should require all federal agencies that operate Advisory Committees to develop their own financial disclosure system and include a second step in the financial disclosure reporting process as due diligence, which includes reviewing the Open Payments by CMS system for potential financial conflicts or deploying conflict of interest monitoring software to streamline the process.
Streamline Participation in an Advisory Committee
Recommendation 3. Increase understanding of annual reporting requirements for conflict of interest (COI)
Agencies should develop guidance that explicitly states the roles of Ethics Officers, also known as Designated Agency Ethics Officials (DAEO), within the federal government. Understanding the roles and responsibilities of Advisory Committee members and the public will help reduce the spread of misinformation regarding the purpose of Advisory Committees. In addition, agencies should be encouraged by the Office of Government Ethics to develop guidance that indicates the criteria for inclusion or exclusion of participation in Committee meetings. Currently, there is no public guidance that states what types of conflicts of interests are granted waivers for participation. Full disclosure of selection and approval criteria will improve transparency with the public and draw clear delineations between how Agencies determine who is eligible to participate.
Policy Pathway. Develop conflict of interest (COI) and financial disclosure guidance specifically for SGEs that states under what circumstances SGEs are allowed to receive waivers for participation in Advisory Committee meetings.
Recommendation 4. Expand training for Advisory Committee members to include (1) ethics and (2) criteria for making good recommendations to policymakers
Training should be expanded for all federal Advisory Committee members to include ethics training which details the role of Designated Agency Ethics Officials, rules and regulations for financial interest disclosures, and criteria for making evidence-based recommendations to policymakers. Training for incoming Advisory Committee members ensures that all members have the same knowledge base and can effectively contribute to the evidence-based recommendations process.
Policy Pathway. Agencies should collaborate with the OGE and Agency Heads to develop comprehensive training programs for all incoming Advisory Committee members to ensure an understanding of ethics as contributing members, best practices for providing evidence-based recommendations, and other pertinent areas that are deemed essential to the Advisory Committee process.
Leverage Advisory Committee Membership
Recommendation 5. Uplifting roles of the Committee Chairs and Designated Federal Officials
Expanding the roles of Committee Chairs and Designated Federal Officers (DFOs) may assist federal Agencies with recruiting and retaining top talent and maximizing the Committee’s ability to stay abreast of critical public concerns. Considering the fact that the General Services Administration has to be consulted for the formation of new Committees, renewal, or alteration of Committees, they can be instrumental in this change.
Policy Pathway. The General Services Administration (GSA) should encourage federal Agencies to collaborate with Committee Chairs and DFOs to recruit permanent and ad hoc Committee members who may have broad network reach and community ties that will bolster trust amongst Committees and the public.
Recommendation 6. Clarify intended roles for Advisory Committee members and the public
There are misconceptions among the public and Advisory Committee members about Advisory Committee roles and responsibilities. There is also ambiguity regarding the types of Advisory Committee roles such as ad hoc members, consulting, providing feedback for policies, or making recommendations.
Policy Pathway. GSA should encourage federal Agencies to develop guidance that delineates the differences between permanent and temporary Advisory Committee members, as well as their roles and responsibilities depending on if they’re providing feedback for policies or providing recommendations for policy decision-making.
Recommendation 7. Utilize and engage expertise and the public outside of public meetings
In an effort to continue receiving the best evidence-based advice, federal Agencies should develop alternate ways to receive advice outside of public Committee meetings. Allowing additional opportunities for engagement and feedback from Committee experts or the public will allow Agencies to expand their knowledge base and gather information from communities who their decisions will affect.
Policy Pathway. The General Services Administration should encourage federal Agencies to create opportunities outside of scheduled Advisory Committee meetings to engage Committee members and the public on areas of concern and interest as one form of engagement.
Recommendation 8. Standardize representation from Committee representatives (i.e., industry), as well as representation limits
The Federal Advisory Committee Act (FACA) does not specify the types of expertise that should be represented on all federal Advisory Committees, but allows for many types of expertise. Incorporating various sets of expertise that are representative of the American public will ensure the government is receiving the most accurate, innovative, and evidence-based recommendations for issues and products that affect Americans.
Policy Pathway. Congress should include standardized language in the FACA that states all federal Advisory Committees should include various sets of expertise depending on their charge. This change should then be enforced by the GSA.
Support a Vibrant and Functioning Advisory Committee System
Recommendation 9. Decrease the burden to creating an Advisory Committee and make sure Advisory Committees are meeting per their charters
The process to establish an Advisory Committee should be simplified in an effort to curtail the amount of onerous processes that lead to a delay in the government receiving evidence based advice.
Advisory Committee charters state the purpose of Advisory Committees, their duties, and all aspirational aspects. These charters are developed by agency staff or DFOs with consultation from their agency Committee Management Office. Charters are needed to forge the path for all FACs.
Policy Pathway. Designated Federal Officers (DFOs) within federal agencies should work with their Agency head to review and modify steps to establishing FACs. Eliminate the requirement for FACs to require consultation and/or approval from GSA for the formation, renewal, or alteration of Advisory Committees.
Recommendation 10. Bolster agency budgets to support FACs on critical issues where regular engagement and trust building with the public is essential for good policy
Federal Advisory Committees are an essential component to receive evidence-based recommendations that will help guide decisions at all stages of the policy process. These Advisory Committees are oftentimes the single entry point external experts and the public have to comment and participate in the decision-making process. However, FACs take considerable resources to operate depending on the frequency of meetings, the number of Advisory Committee members, and supporting FDA staff. Without proper appropriations, they have a diminished ability to recruit and retain top talent for Advisory Committees. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) reported that in 2019, approximately $373 million dollars was spent to operate a total of 960 federal Advisory Committees. Some Agencies have experienced a decrease in the number of Advisory Committee convenings. Individual Agency heads should conduct a budget review of average operating and projected costs and develop proposals for increased funding to submit to the Appropriations Committee.
Policy Pathway. Congress should consider increasing appropriations to support FACs so they can continue to enhance federal decision-making, improve public policy, boost public credibility, and Agency morale.
Conclusion
Advisory Committees are necessary to the federal evidence-based decision-making ecosystem. Enlisting the advice and recommendations of experts, while also including input from the American public, allows the government to continue making decisions that will truly benefit its constituents. Nonetheless, there are areas of FACs that can be improved to ensure it continues to be a participatory, evidence-based process. Additional funding is needed to compensate the appropriate Agency staff for Committee support, provide potential incentives for experts who are volunteering their time, and finance other expenditures.
With reform of Advisory Committees, the process for receiving evidence-based advice will be streamlined, allowing the government to receive this advice in a faster and less burdensome manner. Reform will be implemented by reducing the administrative burden for federal employees through the streamlining of recruitment, financial disclosure, and reporting processes.
Solutions for an Efficient and Effective Federal Permitting Workforce
The United States faces urgent challenges related to aging infrastructure, vulnerable energy systems, and economic competitiveness. Improving American competitiveness, security, and prosperity depends on private and public stakeholders’ ability to responsibly site, build, and deploy critical energy and infrastructure. Unfortunately, these projects face one common bottleneck: permitting.
Permits and authorizations are required for the use of land and other resources under a series of laws, such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), the Endangered Species Act (ESA), and National Historic Preservation Act of 1966. However, recent court rulings and the Trump Administration’s executive actions have brought uncertainty and promise major disruption to the status quo. The Executive Order (EO) on Unleashing American Energy mandates guidance to agencies on permitting processes be expedited and simplified within 30 days, requires agencies prioritize efficiency and certainty over any other objectives, and revokes the Council of Environmental Quality’s (CEQ) authority to issue binding NEPA regulations. While these changes aim to advance the speed, efficiency, and certainty of permitting, the impact will ultimately depend on implementation by the permitting workforce.
Unfortunately, the permitting workforce is unprepared to swiftly implement changes following shifts in environmental policy and regulations. Teams responsible for permitting have historically been understaffed, overworked, and unable to complete their project backlogs, while demands for permits have increased significantly in recent years. Building workforce capacity is critical for efficient and effective federal permitting.
Project Overview
Our team at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS) has spent 18 months studying and working to build government capacity for permitting talent. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) provided resources to expand the federal permitting workforce, and we partnered with the Permitting Council, which serves as a central body to improve the transparency, predictability, and accountability of the federal environmental review and authorization process, to gain a cross-agency understanding of the hiring challenges experienced in permitting agencies and prioritize key challenges to address. Through two co-hosted webinars for hiring managers, HR specialists, HR leaders, and program leaders within permitting agencies, we shared tactical solutions to improve the hiring process.
We complemented this understanding with voices from agencies (i.e., hiring managers, HR specialists, HR teams, and leaders) by conducting interviews to identify new issues, best practices, and successful strategies for building talent capacity. With this understanding, we developed long-term solutions to build a sustainable, federal permitting workforce for the future. While many of our recommendations are focused on permitting talent specifically, our work naturally uncovered challenges within the broader federal talent ecosystem. As such, we’ve included recommendations to advance federal talent systems and improve federal hiring.
Problem
Building permitting talent capacity across the federal government is not an easy endeavor. There are many stakeholders involved across different agencies with varying levels of influence who need to play a role: the Permitting Council staff, the Permitting Council members-represented by Deputy Secretaries (Deputy Secretaries) of permitting agencies, the Chief Environmental Review and Permitting Officers (CERPOs) in each agency, the Office of Personnel and Management (OPM), the Chief Human Capital Officer (CHCO) in each permitting agency, agency HR teams, agency permitting teams, hiring managers, and HR specialists. Permitting teams and roles are widely dispersed across agencies, regions, states, and programs. The role each agency plays in permitting varies based on their mission and responsibilities, and there are many silos within the broader ecosystem. Few have a holistic view of permitting activities and the permitting workforce across the federal government.
With this complex network of actors, one challenge that arises is a lack of standardization and consistency in both roles and teams across agencies. If agencies are looking to fill specialized roles unique to one permitting need, it means that there will be less opportunity for collaboration and for building efficiencies across the ecosystem. The federal hiring process is challenging, and there are many known bottlenecks that cause delays. If agencies don’t leverage opportunities to work together, these bottlenecks will multiply, impacting staff who need to hire and especially permitting and/or HR teams who are understaffed, which is not uncommon. Additionally, building applicant pools to have access to highly qualified candidates is time consuming and not scalable without more consistency.
Tracking workforce metrics and hiring progress is critical to informing these talent decisions. Yet, the tools available today are insufficient for understanding and identifying gaps in the federal permitting workforce. The uncertainty of long-term, sustainable funding for permitting talent only adds more complexity into these talent decisions. While there are many challenges, we have identified solutions that stakeholders within this ecosystem can take to build the permitting workforce for the future.
There are six key recommendations for addressing permitting workforce capacity outlined in the table below. Each is described in detail with corresponding actions in the Solutions section that follows. Our recommendations are for the Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, CERPOs, OPM, CHCOs, OMB, and Congress.
Solutions
The six solutions described below include an explanation of the problem and key actions our signal stakeholders (Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, CERPOs, OPM, CHCOs, OMB, and Congress) can take to build permitting workforce capacity. The table in the appendix specifies the stakeholders responsible for each recommendation.
Enhance the Permitting Council’s Authority to Improve Permitting Processes and Workforce Collaboration
Permitting process, performance, and talent management cut across agencies and their bureaus—but their work is often disaggregated by agency and sub-agency, leading to inefficient and unnecessarily discrete practices. While the Permitting Council plays a critical coordinating role, it lacks the authority and accountability to direct and guide better permitting outcomes and staffing. There is no central authority for influencing and mandating permitting performance. Agency-level CERPOs vary widely in their authority, whereas the Permitting Council is uniquely positioned for this role. Choosing to overlook this entity will lead to another interagency workaround. Congress needs to give the Permitting Council staff greater authority to improve permitting processes and workforce collaboration.
- Enhance Permitting Council Authority for Improved Performance: Enhance provisions in FAST-41 and IRA by passing legislation that empowers the Permitting Council staff to create and enforce consistent performance criteria for permitting outcomes, permitting process metrics, permitting talent acquisition, talent management, and permitting teams KPIs.
- Enhance Permitting Council Authority for Interagency Coordination: Empower the Permitting Council staff to manage interagency coordination and collaboration for defining permitting best practices, establishing frameworks for permitting, and reinforcing those frameworks across agencies. Clarify the roles and responsibilities between Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, CERPOs, and the Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ).
- Assign Responsibility for Tracking Changes and Providing Guidance for Permitting Practices: Assign the Permitting Council staff in coordination with OMB responsibility for tracking changes and providing guidance on permitting practices in response to recent and ongoing court rulings that change how permitting outcomes are determined (e.g., Loper Bright/Chevron Deference, CEQ policies, etc.).
- Provide Permitting Council staff with Consistent Funding: Either renew components of IRA and/or IIJA funding that enables the Council to invest in agency technologies, hiring, and workforce development, or provide consistent appropriations for this.
- Enhance CERPO Authority and Position CERPOs for Agency-Wide and Cross-Agency Permitting Actions: Expand CERPO authority beyond the FAST-41 Act to include all permitting work within their agency. Through legislation, policy, and agency-level reporting relationships (e.g., CERPO roles assigned to the Secretary’s office), provide CERPOs with clear authority and accountability for permitting performance.
Build Efficient Permitting Teams and Standardize Roles
In our research, we interviewed one program manager who restructured their team to drive efficiency and support continuous improvement. However, this is not common. Rather, there is a lack of standardization in roles engaged in permitting teams within and across agencies, which hinders collaboration and prevents efficiencies. This is likely driven by the different roles played by agencies in permitting processes. These variances are in opposition to shared certifications and standardized job descriptions, complicate workforce planning, hinder staff training and development, and impact report consistency. The Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, CERPOs, OMB, and the CHCO Council should improve the performance and consistency of permitting processes by establishing standards in permitting team roles and configurations to support cross-agency collaboration and drive continuous improvements.
- Characterize Types of Permitting Processes: Permitting Council staff should work with Deputy Secretaries, CERPOs, and Permitting Program Team leaders to categorize types of permitting processes based on project “footprint”, complexity, regulatory reach (i.e., regulations activated), populations affected and other criteria. Identify the range of team configurations in use for the categories of processes.
- Map Agency Permitting Roles: Permitting Council staff should map and clarify the roles played by each agency in permitting processes (e.g., sponsoring agency, contributing agency) to provide a foundation for understanding the types of teams employed to execute permitting processes.
- Research and Analyze Agency Permitting Staffing: Permitting Council staff should collaborate with OMB to conduct or refine a data call on permitting staffing. Analyze the data to compare the roles and team structures that exist between and across agencies. Conduct focus groups with cross agency teams to identify consistent talent needs, team functions, and opportunities for standardization.
- Develop Permitting Team Case Studies: Permitting Council staff should conduct research to develop a series of case studies that highlight efficient and high performing permitting team structures and processes.
- Develop Permitting Team Models: In collaboration with Deputy Secretaries and CERPOs, Permitting Council staff should develop team models for different agency roles (i.e., sponsor, lead agency, coordinating agency) that focus on driving efficiencies through process improvements and technology, and develop guidelines for forming new permitting teams.
- Create Permitting Job Personas: In collaboration with Deputy Secretaries and CERPOs, Permitting Council staff should develop personas to showcase the roles needed on each type of permitting team and roles, recognizing that some variance will always remain, and the type of hiring authority that should be used to acquire those roles (e.g., IPA for highly specialized needs). This should also include new roles focused on process improvements; technology and data acquisition, use, and development; and product management for efficiency, improved customer experience, and effectiveness.
- Define Standardized Permitting Roles and Job Analyses: With the support of Deputy Secretaries and CERPOs, Permitting Council staff should identify roles that can be standardized across agencies based on the personas, and collaborate with permitting agencies to develop standard job descriptions and job analyses.
- Develop Permitting Practice Guide: In collaboration with Deputy Secretaries and CERPOs, Permitting Council staff should develop a primer on federal permitting practices that explains how to efficiently and effectively complete permitting activities.
- Place Organizational Strategy Fellows: Permitting Council staff should hire at least one fellow to their staff to lead this effort and coordinate/liaise between permitting teams at different agencies.
- Mandate Permitting Hiring Forecasts: Permitting Council staff should collaborate with the CHCO Council to mandate permitting hiring forecasts annually with quarterly updates.
- Revise Permitting Funding Requirements: Permitting Council staff should include requirements for the adoption of new team models and roles in the resources and coordination provided to permitting agencies to drive process efficiencies.
Improve Workforce Strategy, Planning, and Decisions through Quality Workforce Metrics
Agency permitting leaders and those working across agencies do not have the information to make informed workforce decisions on hiring, deployment, or workload sharing. Attempts to access accurate permitting workforce data highlighted inefficient methods for collecting, tracking, and reporting on workforce metrics across agencies. This results in a lack of transparency into the permitting workforce, data quality issues, and an opaque hiring progress. With these unknowns, it becomes difficult to prioritize agency needs and support. Permitting provided a purview into this challenge, but it is not unique to the permitting domain. OPM, OMB, the CHCO Council, and Permitting Council staff need to accurately gather and report on hiring metrics for talent surges and workforce metrics by domain.
- Establish Permitting Workforce Data Standards: OPM should create minimum data standards for hiring and expand existing data standards to include permitting roles in employee records, starting with the Request for Personnel Action that initiates hiring (SF52). Permitting Council staff should be consulted in defining standards for the permitting workforce.
- Mandate Agency Data Sharing: OPM and OMB should require agencies share personnel action data; this should be done automatically through APIs or a weekly data pull between existing HR systems. To enable this sharing, agencies must centralize and standardize their personnel action data from their components.
- Create Workforce Dashboards: OPM should create domain-specific workforce dashboards based on most recent agency data and make it accessible to the relevant agencies. This should be done for the permitting workforce.
- Mandate Permitting Hiring Forecasts: The CHCO Council should mandate permitting hiring forecasts annually with quarterly updates. This data should feed into existing agency talent management/acquisition systems to track workforce needs and support adaptive decision making.
Invest in Professional Development and Early Career Pathways
There are few early career pathways and development opportunities for personnel who engage in permitting activities. This limits agencies’ workforce capacity and extends learning curves for new staff. This results in limited applicant pools for hiring, understaffed permitting teams, and limited access to expertise. More recently, many of the roles permitting teams hired for were higher level GS positions. With a greater focus on early career pathways and development, future openings could be filled with more internal personnel. In our research, one hiring manager shared how they established an apprenticeship program for early career staff, which has led 12 interns to continue into permanent federal service positions. The Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, and CERPOs should create more development opportunities and early career pathways for civil servants.
- Invest in Training to Upskill and Reskill Staff: The Permitting Council staff should continue investing in training and development programs (i.e., Permitting University) to upskill and reskill federal employees in critical permitting skills and knowledge. Leveraging the knowledge gained through creating standard permitting team roles and collaborating with permitting leaders, the Permitting Council staff should define critical knowledge and skills needed for permitting and offer additional training to support existing staff in building their expertise and new employees in shortening their learning curve.
- Allocate Permitting Staff Across Offices and Regions: CERPOs and Deputy Secretaries should implement a flexible staffing model to reallocate staff to projects in different offices and regions to build their experience and skill set in key areas, where permitting work is anticipated to grow. This can also help alleviate capacity constraints on projects or in specific locations.
- Invest in Flexible Hiring Opportunities: CERPOs and Deputy Secretaries should invest in a range of flexible hiring options, including 10-year STEM term appointments and other temporary positions, to provide staffing flexibility depending on budget and program needs. Additionally, OPM needs to redefine STEM to include technology positions that do not require a degree (e.g., Environmental Protection Specialists).
- Establish a Permitting Apprenticeship: The Permitting Council staff should establish a 1-year apprenticeship program for early career professionals to gain on-the-job experience and learn about permitting activities. The apprenticeship should focus on common roles shared across agencies and place talent into agency positions. A rotational component could benefit participants in experiencing different types of work.
Improve and Invest in Pooled Hiring for Common Positions
Outdated and inaccurate job descriptions slow down and delay the hiring process. Further delays are often caused by the use of non-skills-based assessments, often self-assessments, which reduce the quality of the certificate list, or the list of eligible candidates given to the hiring manager. HR leaders confront barriers in the authority they have to share job announcements, position descriptions (PDs), classification determinations, and certificate lists of eligible candidates (Certs). Coupled with the above ideas on creating consistency in permitting teams and roles and better workforce data, OPM, CHCOs, OMB, Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, and CERPOs should improve and make joint announcements, shared position descriptions, assessments, and certificates of eligibles for common positions a standard practice.
- Provide CHCOs the Delegated Authority to Share Announcements, PDs, Assessments, and Certs: OPM and OMB should lower the barriers for agencies to share key hiring elements and jointly act on common permitting positions by delegating the authority for CHCOs to work together within and across their agencies, including with the Permitting Council staff.
- Revise Shared Certificate Policies: OPM and OMB should revise shared certificate policies to allow agencies to share certificates regardless of locations designated in the original announcement and the type of hire (temporary or permanent). They should require skills-based assessments in all pooled hiring. Additionally, OPM should streamline and clarify the process for sharing certificates across agencies. Agencies need to understand and agree to the process for selecting candidates off the certificate list.
- Create a Government-wide Platform for Permitting Hiring Collaboration: OPM should create a platform to gather and disseminate permitting job announcements, PDs, classification determinations, job/competency evaluations, and cert. lists to support the development of consistent permitting teams and roles.
- Pilot Sharing of Announcements, PDs, Assessments, and Certs for Common Permitting Positions: OPM and the CHCO Council should collaborate with the Permitting Council staff to select most common and consistent permitting team roles (e.g., Environmental Protection Specialist) to pilot sharing within and across agencies.
- Track Permitting Hiring and Workforce Performance through Data Sharing and Dashboards: Permitting Council staff, Deputy Secretaries, and CERPOs should leverage the metrics (see Improve Workforce Decisions Through Quality Workforce Metrics) and data actions above to track progress and make adjustments for sharing permitting hiring actions.
- Incorporate Shared Certificates into Performance: OPM and the CHCO Council should incorporate the use of shared certificates into the performance evaluations of HR teams within agencies.
Improve Human Resources Support for Hiring Managers
Hiring managers lack sufficient support in navigating the hiring and recruiting process due to capacity constraints. This causes delays in the hiring process, restricts the agency’s recruiting capabilities, limits the size of the applicant pools, produces low quality candidate assessments, and leads to offer declinations. The CHCO Council, OPM, CERPOs, and the Permitting Council staff need to test new HR resourcing models to implement hiring best practices and offer additional support to hiring managers.
- Develop HR Best Practice Case Studies: OPM should conduct research to develop a series of case studies that highlight HR best practices for recruitment, performance management, hiring, and training to share with CHCOs and provide guidance for implementation.
- Document Surge Hiring Capabilities: In collaboration, the Permitting Council staff and CERPOs should document successful surge hiring structures (e.g., strike teams), including how they are formed, how they operate, what funding is required, and where they sit within an organization, and plan to replicate them for future surge hiring.
- Create Hiring Manager Community of Practice: In collaboration, the Permitting Council staff and Permitting Agency HR Teams with support from the CHCO Council should convene a permitting hiring manager community of practice to share best practices, lessons learned, and opportunities for collaboration across agencies. Participants should include those who engage in hiring, specifically permitting hiring managers, HR specialists, and HR leaders.
- Develop Permitting Talent Training for HR: OPM should collaborate with CERPOs to create a centralized training for HR professionals to learn how to hire permitting staff. This training could be embedded in the Federal HR Institute.
- Contract HR Support for Permitting: The Permitting Council staff should create an omnibus contract for HR support across permitting agencies and coordinate with OPM to ensure the resources are allocated based on capacity needs.
- Establish HR Strike Teams: OPM should create a strike team of HR personnel that can be detailed to agencies to support surge hiring and provide supplemental support to hiring managers.
- Place a Permitting Council HR Fellow: The Permitting Council should place an HR professional fellow on their staff to assist permitting agencies in shared certifications and build out talent pipelines for the key roles needed in permitting teams.
- Establish Talent Centers of Excellence: The CHCO Council should mandate the formation of a Talent Center of Excellence in each agency, which is responsible for providing training, support, and tools to hiring managers across the agency. This could include training on hiring, hiring authorities, and hiring incentives; recruitment network development; career fair support; and the development of a system to track potential candidates.
Next Steps
These recommendations aim to address talent challenges within the federal permitting ecosystem. As you can see, these issues cannot be addressed by one stakeholder, or even one agency, rather it requires effort from stakeholders across government. Collaboration between these stakeholder groups will be key to realizing sustainable permitting workforce capacity.
Setting the Stage for a Positive Employee Experience
Federal hiring ebbs and flows with changes in administrations, legislative mandates, attrition, hiring freezes, and talent surges. The lessons and practices in this blog post series explore the earlier stages of the hiring process. Though anchored in our permitting talent research, the lessons are universal in their application, regardless of the hiring environment. They can be used to accelerate and improve hiring for a single or multiple open positions, and they can be kept in reserve during hiring downturns.
Assessing, Selecting, and Onboarding the Successful Candidate
Previously we described the end-to-end hiring process, the importance of getting hiring right from the start, and how sharing resources speeds hiring. This post focuses on the last two phases of the process: Assessment and Offer. While these phases include eight steps, we’ve narrowed down our discussion to five key steps:
- Close Job Opportunity Announcement and Evaluate Applicants
- Review Certificate of Eligibles, Conduct Interviews, and Make Selection
- Make Tentative Job Offer and Receive Acceptance
- Initiate Investigation at the Appropriate Level (Security Check)
- Make Official Offer and Enter on Duty (Onboard New Hire)
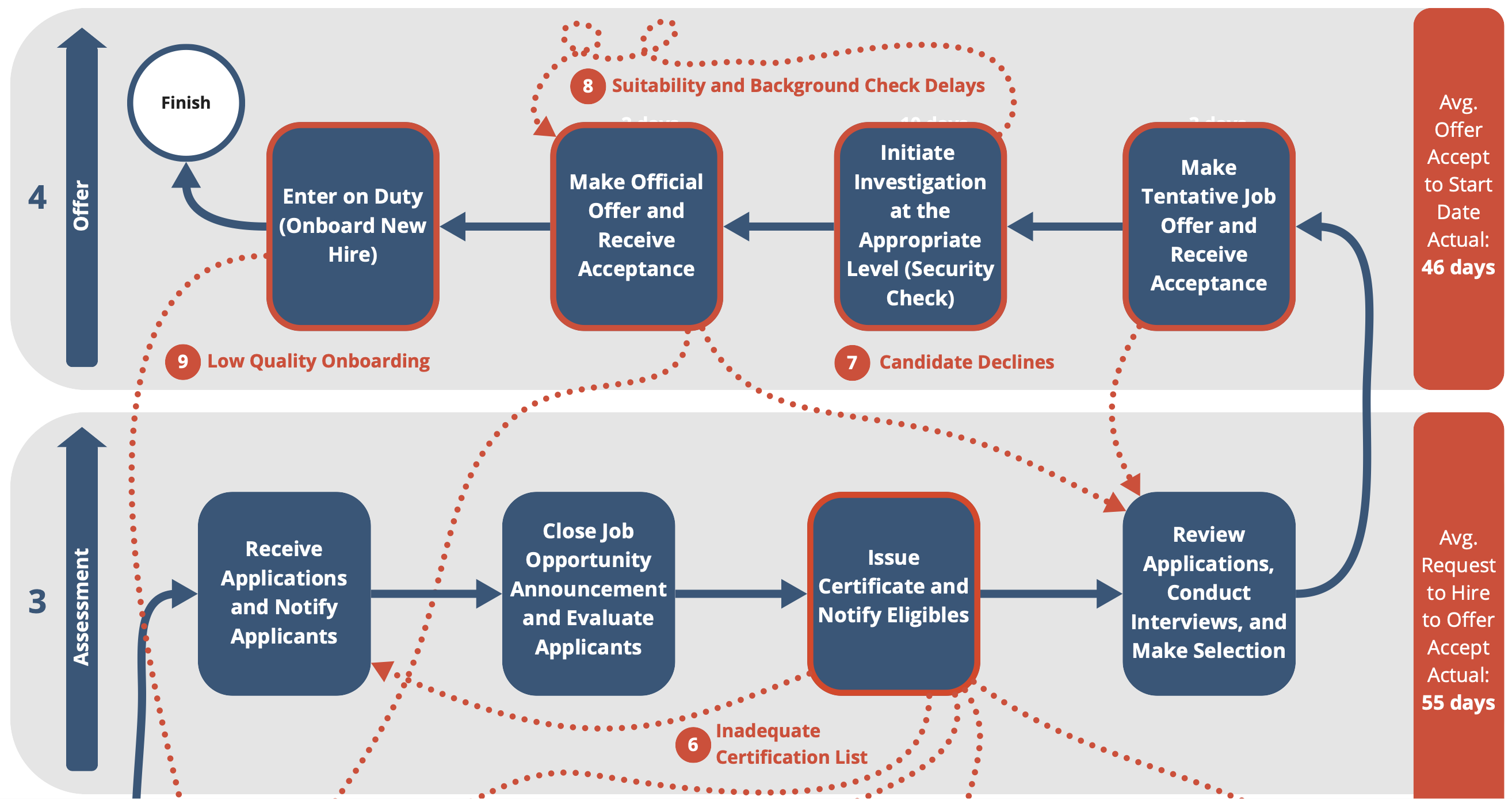
Our insights shared in this post are based on extensive interviews with hiring managers, program leaders, staffing specialists, workforce planners, and budget professionals as well as on-the-job experience. These recommendations for improvement focus on process and do not require policy or regulatory changes. They do require adoption of these practices more broadly throughout HR, program, and permitting managers, and staff. These recommendations are not unique to permitting; they apply broadly to federal government hiring. These insights should be considered both for streamlining efforts related to environmental permitting, as well as improving federal hiring.
Breaking Down the Steps
For each step, we provide a description, explain what can go wrong, share what can go right, and provide some examples from our research, where applicable.
Close Job Opportunity Announcement and Evaluate Applicants
Once the announcement period has ended, job announcements close, and HR begins reviewing the applications in the competitive hiring process. HR reviews the applications, materials provided by the applicants, and the completed assessments, which vary depending on the assessment strategy. This selection process is governed by policies in competitive examination and will be determined by whether the agency is following category rating, rule of many, or other acceptable evaluation methods.
If the agency is using a different hiring authority or flexibility, this step will change. For example, if the agency has Direct Hire Authority (DHA), they may not need to provide a rigorous assessment and may be able to proceed to selection after a review of resumes. Most agencies will still engage in some assessment process for these types of positions. After the applicants are evaluated, HR issues a Certificate of Eligibles (or “cert list”) with the ranking of the applicants from which the hiring manager can select, including the implementation of Veterans preference.
What Can Go Wrong
- Most applicant assessments rely on the resume review and candidate self-assessment. Applicants who understand the process rate themselves as highly qualified on all aspects of the job, resulting in a certificate list with unqualified applicants at the top. Agencies are now required by law to use skills-based assessments in the Chance to Compete Act and previous Executive Order guidance to prevent this, but the adoption process will be slow.
- HR staffing resources are frequently strained to immediately review applications and resumes causing delays. This causes applicant and hiring manager dissatisfaction and possibly a loss of attractive, qualified applicants. Within permitting, hiring managers have been struggling to find talent with the required expertise, especially specialized or niche expertise, and this loss is a critical setback.
- Frequently HR specialists do not consult with the program managers to gain a deep understanding of what they’re looking for in a resume or application and rely solely on their interpretation of the qualifications listed in the position description. This can result in poor quality applicants referred to the hiring manager.
What Can Go Right
- If the recruiters and hiring manager have engaged in effective recruiting, applicant quality is likely to be quite high. This eases the HR’s job of finding strong applicants.
- With a strong applicant pool, HR specialist can limit the number of applicants they consider and/or limit how long the job announcement is open. This will expedite the process, as the assessment will be faster. Rigorous assessments reduce the likelihood of unqualified applicants making it to the certificate list. A hiring manager who insists on a skills-based assessment will likely move forward with a successful hire. Using subject-matter experts in a Subject Matter Expert Qualifications Assessment (SME-QA) or similar assessment process can result in a strong list of applicants, and it has the added benefit of building familiarity by engaging the employee’s future peers in the process.
Review Certificate of Eligibles, Conduct Interviews, and Make Selection
HR sends a Certificate of Eligibles (certificate list) to the hiring manager that ranks the applicants who passed the assessment(s). Under competitive hiring rules (as opposed to some of the other hiring authorities), hiring managers are obligated to select from the top of the Certificate of Eligibles list, or those considered to be most qualified.
The Veterans preference rules also require that qualified Veterans move to the top of the list and must be considered first. Outside of competitive hiring and under other hiring authorities, the hiring manager may have more flexibility in the selection of candidates. For example, direct hire authority allows the hiring manager to make a selection decision based on their own review of resumes and applications.
If determined as part of the assessment process beforehand, the hiring manager may choose to conduct final interviews with the top candidates. In this case, the manager then informs HR of their selection decision.
What Can Go Wrong
- If the hiring manager cannot find an applicant they deem qualified on the certificate list, they inform HR, restart the hiring action, and/or re-post the position, further delaying the process. This happens frequently when the assessment tools default to a self-evaluation, or self-assessment. One Hiring Manager we met needed to request a second certificate list, and this extended the hiring process to nine months.
- Lack of resources in HR or the hiring manager’s program often results in evaluation and selection delays. Top applicants in high demand may take other jobs if the process takes longer than anticipated. This was a concern voiced by hiring managers during our interviews.
- In rare circumstances, agency funding could be uncertain and the budget function could rescind the approval to hire at this stage, frustrating hiring managers, applicants, and HR specialists.
What Can Go Right
- Strong recruiting early and throughout the process results in a strong certificate list with excellent candidates. One permitting agency, following best practice, kept a pipeline of potential candidates, including prior applicants to boost the quality of the applicant pool.
- An effective assessment process weeds out unqualified or unsuitable candidates and culls the list of applicants to only those who can do the job.
- A deep partnership between the HR staffing specialist and the hiring manager in which they discuss the skills and “fit” of the top candidates increases the hiring manager’s confidence in the selection.
Make Tentative Job Offer and Receive Acceptance
HR reaches out to the applicant to make a tentative job offer (i.e., tentative based on the applicant’s suitability determination, outlined below) and asks for a decision from the applicant within an acceptable time frame, which is normally a couple of days to a week. The HR staffing specialist will keep in close contact with the hiring manager and HR officials regarding the status of the candidate accepting the position.
What Can Go Wrong
- The applicant rejects the offer due to a misunderstanding of the job. This could be the location, remote work, or telework availability. In our interviews, we learned that some applicants declined offers because they believed the position was full time or a temporary position that could convert to a full time role, but that was not the case.
- The applicant rejects the offer due to a competing offer at a higher salary or as a result of other financial factors (e.g., relocation expenses). Some participants shared that financial factors had been the reason for some of their declinations.
- The applicant rejects the offer because of how they have been treated throughout the process or delays, which have led them to remain in their current role or accept another position.
What Can Go Right
- The HR specialist and others involved in the hiring process maintain regular communications with the candidate regarding their offer, listens to any concerns they may have about accepting their offer, and works with the hiring manager to correct any misperceptions about the job requirements.
- The HR specialist and the hiring manager understand the financial incentives they can use to negotiate salary, relocation expenses, signing bonuses, and other benefits to negotiate with the candidate. These options are usually agency-, function-, or job-specific.
Initiate Investigation at the Appropriate Level (Security Check)
Different federal occupations require different levels of suitability determinations or security clearances – from simple background checks to make sure the information an applicant provided on their application is accurate to a Top Secret clearance that enables the employee to access sensitive information. Each type of suitability determination has a different time frame needed for a security officer to evaluate the candidate. (Some positions require the security officer to not only interview the candidate, but also interview their friends, relatives, and neighbors.) This takes time during a part of the hiring process when both the candidate with the tentative offer and the hiring manager are anxious to move forward.
Once the candidate selection is made, the HR specialist works with the agency suitability professionals to initiate the background check and clearance process. Agency suitability experts work with the Defense Counterintelligence Security Agency (DCSA) to conduct the determination of the applicant.
What Can Go Wrong
- Applicants who have never applied for a federal job may be unfamiliar with their responsibilities during the suitability determination. If they do not fill out the forms properly, this causes delays, especially when the applicant is slow to respond.
- If the candidate does not know how long the suitability determination will take or what is involved in the process, the lack of transparency may create uncertainty and/or frustration among the applicant. Furthermore, if the candidate is not kept informed on where they are in the process or what to expect next, they may get discouraged and decline the tentative offer.
- Delays in scheduling fingerprinting appointments or access to fingerprinting facilities can also lengthen the time for the suitability determination.
What Can Go Right
- The hiring manager, HR specialist, and suitability experts work together to ensure the candidate knows where they are in the process and what is expected of them through frequent check-ins and progress tracking.
- Offering applicants a range of options for fingerprinting, including the opportunity to go to a third party vendor for prints. This can enable fast digital uploads within 24 hours (applicant may have to pay for third-party services).
- Hiring managers and HR specialists leverage the DCSA resources and tools, including the PDT Tool to determine the level of background check needed for their role.
- The Suitability manager uses a case management system to track and maintain all suitability requests. This will help ensure nothing is lost, and system notifications can help keep the process on track by requesting applicants, hiring managers, and HR specialists complete their tasks in a timely manner. One interview participant highlighted this as critical to the timeliness of the suitability process.
Make Official Offer and Enter on Duty (Onboard New Hire)
The last step in the hiring process is administering the final offer of employment, identifying and Entry on Duty date, and onboarding the new employee. HR staff usually shepherd the new employee through this step. The hiring manager, administrator, or a peer mentor frequently assists the new employee in making sure the employee understands what they need to do to begin contributing to the agency.
What Can Go Wrong
- The candidate declines the final offer of employment due to delays or dissatisfaction with their experience during the hiring process.
- Frequently, onboarding consists of filling out online forms, paperwork to register the new employee in the various agency systems, and required compliance training. Minimal attention is spent on their work and how it connects to the agency mission.
- All too often, the new employee does not receive their computer equipment, phone, or other resources necessary for them to do their jobs in a timely manner. These delays degrade the initial employee experience.
What Can Go Right
- HR and hiring manager program staff stay in constant connection with the candidate as they accept the job and start the onboarding process, ensuring that the early employee experience is positive. This includes not only the administrative activities but also introductions to the agency and the work they will be doing.
- Program managers and administrative staff can work with IT functions and other departments to make sure the new employee has the equipment and resources needed to start their job successfully.
- The hiring manager establishes their relationship with the new employee during onboarding, creating a positive atmosphere for the employee by clearly articulating expectations.
Conclusion
Hiring success depends heavily on the broader hiring ecosystem. There are many stakeholders (e.g., leadership, budget, program, HR, suitability, applicant) who play a crucial role; collaboration and communication is important for both a timely and successful hire. Adoption of best practices across the ecosystem will help to improve hiring outcomes, reduce process delays, and enhance the overall hiring experience for all parties involved. The best practices outlined in our blog post series provide a guide to better navigate the hiring process.
The overall intent of hiring is to improve the performance of the federal program or function. New employees expand the organization’s workforce capacity and bring capabilities needed to achieve the mission. A skilled, prepared, and engaged federal employee can have an outsized impact on a program’s success.
The National Security Council’s Decision-Making Process: When Consensus Becomes a Constraint
In the machinery of national security decision-making, innovation is the first casualty of consensus. At the heart of this process lies the National Security Council’s multi-layered committee structure to develop policy recommendations for the President. While this process ensures broad interagency coordination, it also means that agencies can effectively veto options that challenge their interests. The result is that the President often only sees consensus recommendations that preserve institutional status quo, rather than the full range of viable policy options that might better serve national interests. The new National Security Advisor, Congressman Mike Waltz, should reshape the NSC process to provide better foreign policy advice for the President.
The Current Process: Design vs. Reality
The NSC’s decision-making process follows a carefully structured path. At the working level, Interagency Policy Committees (IPCs) bring together Assistant Secretary-level officials and subject matter experts to develop initial policy options. These recommendations then move to the Deputies Committee, composed of deputy heads of relevant agencies, for refinement and further analysis. The Principals Committee, consisting of Cabinet-level officials, then reviews and shapes final recommendations before they reach the President through the National Security Advisor.
In theory, this layered approach should ensure thorough vetting while preserving diverse viewpoints. In practice, however, the system often produces the opposite effect. Each level of review tends to narrow options rather than expand them, as agencies work to protect their institutional interests and avoid conflict with other departments.
The Consensus Trap
The emphasis on interagency consensus, while well-intentioned, has become a structural impediment to bold or innovative policy options. Former National Security Advisor H.R. McMaster warned about this in his book Battlegrounds stating, “Presenting a single option designed to either tell the President what he or she wants to hear, or to present the consensus position of the cabinet is doing him or her a disservice.” He argued that it is “important to provide the President with multiple options.”
When every agency effectively holds veto power over proposals, the path of least resistance becomes maintaining existing approaches with minor modifications. This dynamic is particularly problematic in rapidly evolving security situations where status quo responses may be inadequate.
Consider, for example, how options that might gore the ox of the Defense Department’s budget are quietly culled, or how proposals that ruffle the diplomatic feathers of the State Department rarely survive the process. While both of the Department’s perspectives may have merit, the current system often leads to their mutual neutralization, rather than producing either a creative outcome or an advancement of an option with dissents.
The Cost of Lost Alternatives
The consequences of this consensus-driven approach are significant. The President is often presented with artificially limited choices, typically framed as minor variations on existing policy rather than genuinely distinct alternatives. This narrowing of options can be particularly problematic in crisis situations where innovative approaches might be most needed.
More concerning is what the President doesn’t see: options that challenge conventional wisdom, propose significant departures from existing policy, or require substantial institutional compromise or change. These alternatives, while potentially valuable, often don’t survive the gauntlet of interagency review.
Potential Reforms
During the Obama NSC we identified several reforms that could help address these structural limitations. Some of these ideas included:
- Mandate a presentation of competing options: Require that multiple, genuinely distinct policy alternatives reach the President’s desk, even if they don’t have unanimous agency support.
- Create independent analysis channels: Borrow the Intelligence Community’s Red Cell process and establish mechanisms for policy options to reach senior decision-makers without requiring consensus at every level.
- Strengthen the NSC staff’s role: Empower NSC staff to develop independent options that might challenge agency preferences.
- Reform the Deputies Committee process: Modify procedures to focus on developing multiple viable options rather than driving toward consensus.
The NSC’s current decision-making process, while sophisticated in design, often fails to provide the President with the full range of policy options needed for effective decision-making. The system’s emphasis on consensus, while valuable for implementation, has become an impediment to innovative policy development.
Reform is possible without dismantling the valuable coordination functions of the current system. By modifying procedures to ensure that diverse options reach senior decision-makers, the NSC can better fulfill its core mission: providing the President with the best possible range of choices for addressing national security challenges.
The goal isn’t to eliminate interagency coordination but to prevent it from unduly constraining presidential options. In an increasingly complex security environment, the President needs access to the fullest possible range of policy alternatives, not just those that survive the consensus-building process.
Jim Thompson is the Director of Government Capacity at the Federation of American Scientists. He served as a Director on both President Obama’s and President Biden’s National Security Councils.
Herding Unicorns: Sharing Resources Speeds Hiring
“There really are fewer unicorn positions out there than we all imagined” – Bob Leavitt, HHS CHCO on shared PDs and certificates for common positions
Creating a job announcement that attracts high quality applicants is critical to the hiring process. For hiring managers, finding a balance between identifying the unique details of the position and managing the time and resources required is a challenge. When defining a position, there are many potential “off-ramps.” While these diversions are sometimes necessary, they often result in significant time delays and demand scarce resources from both hiring managers and HR staff. Improvements over the past few years offer hiring managers opportunities to accelerate the process while improving applicant quality, primarily done through collaboration within and across agencies that requires a level of standardization.
In our previous blog posts, we outlined the hiring process and dove into the first phase – Getting Hiring Right from the Start. This post discusses the second phase of the process: planning for and announcing the job. This phase includes four steps:
- Review Position Description and Confirm Job Analysis
- Classify or Reclassify the Position
- Confirm Job Analysis and Assessment Strategy
- Create and Post the Job Opportunity Announcement (JOA)
Our insights shared in this post are based on extensive interviews with hiring managers, program leaders, staffing specialists, workforce planners, and budget professionals as well as on-the-job experience. These recommendations for improvement focus on process and do not require policy or regulatory changes. They do require adoption of these practices more broadly throughout HR, program, and permitting managers, and staff. Additionally, our insights here are not unique to permitting, rather they apply broadly to federal government hiring. These insights should be considered both for streamlining efforts related to environmental permitting, as well as improving federal hiring.
Breaking Down the Steps
For each step in this phase, we provide a description, explain what can go wrong, share what can go right, and provide some examples from our research, where applicable.
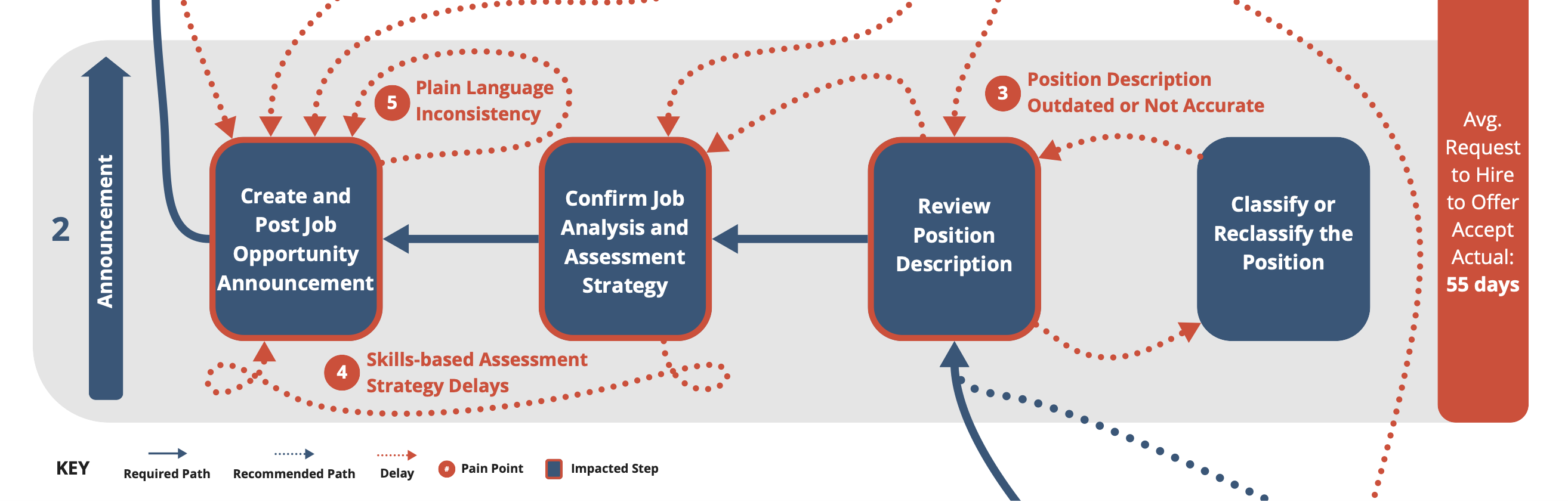
Review Position Description and Confirm Job Analysis
The Position Description (PD) is core to the hiring process. It describes the occupation, grade level, job duties, qualifications, and any special skills needed for the job and agency. In hiring, it is used to develop the job announcement, review the position’s classification, and establish a foundation for assessing candidates. Outside of hiring, it is used in performance management, position management, probation period evaluation, and serves as a reference for disciplinary action.
At this step, a hiring manager reviews the position description to make sure it is an accurate, current depiction of the job requirements, which may require a review of the past job analysis, or the evaluation of the knowledge, skills, abilities, behaviors, and experience needed for the positions (i.e., the competencies). The PD can be inaccurate due to dynamic changes in the job: core duties, technologies used, process changes, and supervisory responsibilities. These updates can range from simple wording changes to major changes that require additional work.
In our interviews, we heard from hiring managers and HR specialists that updating position descriptions had been a challenge and bottleneck in their hiring process. One hiring manager shared that they chose to not change their positions even if they wanted a different role because of the anticipated time delays. Other participants shared that they have begun moving towards standardized PDs within their agency to reduce redundancies and enable more collaboration.
What Can Go Wrong
- Based on hiring manager feedback to the HR specialist, a significantly out-of-date PD can result in major revisions that require a job analysis and/or reclassification of the position. This can delay the hiring process by weeks, or even months. If the grade level or other key aspects of the position need to be changed, the position requisition (SF-52 form) needs to be revised, adding even more time.
- Overzealous staffing specialists or classifiers may perceive major job changes where they do not exist in practice, causing delays for additional reviews and revisions.
- Too much specificity in job task descriptions will require additional job analyses, causing further delays. Whereas not enough specificity provides insufficient guidance for developing the assessment strategy, JOA, and other management actions dependent on the PD (e.g., performance management, development plans, or disciplinary action).
What Can Go Right
- With permission from their Chief Human Capital Office (CHCO) office, a hiring manager can use a current PD from elsewhere in the agency that accurately describes the job. A number of agencies have created PD libraries that bring together common PDs from across the organization. One HR Leader we interviewed described having a library of available positions that hiring managers are encouraged to look through when creating a new position. Hiring managers can even include specialized skills in an existing PD to augment the fundamental job duties, avoiding reclassification.
- Hiring managers can offer flexibility in location, where possible. Based on our interviews, agencies are seeing greater success attracting strong applicants with flexible locations, remote work, or telework options.
- The HR staffing specialist can search for and find a shared certificate of eligibles (i.e., a list of eligible candidates) for their PD already available through their own agency HR talent systems or through the USAJOBS Agency Talent Portals. As long as the job and grade match, the hiring manager can bypass much of the hiring process and move quickly to identifying applicants.
- Many agencies require managers to review and if needed, revise position description every year during the performance management process. This can make sure the PD is ready to go for the hiring process. In our interviews, we heard that this is required, but may not be regularly completed.
Classify/Reclassify the Position
Position classification is a structured process in every Cabinet agency in which an expert assesses the requirements of the job by evaluating factors such as knowledge, skills, abilities, complexity, and supervisory controls/responsibilities. The process is initiated when a PD is deemed inaccurate due to changes in the role. The HR staffing specialist will ask a classification expert to assess the role. This is done by reviewing the PD, existing job analyses, past classifications, and classification audits. They will also gather and review data from the hiring manager and others working in similar roles. Based on their assessment, the classifier can recommend changes to the grade level and/or the occupational series. These changes could be simple revisions or a more extensive reclassification. This process can take days or weeks to complete and can delay the hiring process significantly.
What Can Go Wrong
- HR staff and classifiers sometimes do not explain the need for classification and its benefits. This makes the process opaque and leaves the hiring manager wondering how long it will take to complete.
- HR staffing specialists and classifiers vary widely in how they apply the classification standards. Some seek greater specificity, and therefore insist on a full classification review when it may not be needed.
- Agency HR functions frequently lack workforce capacity for classification and job analyses. As a result, they have to prioritize requests, which can cause further delays.
What Can Go Right
- Collaboration and transparency between hiring managers, staffing specialists, and classifiers can lead to rapid approval of a PD and classification review. If there cannot be a quick approval, this close engagement leads to clearer expectations and realistic timelines.
- If the same position, at the same grade level, has recently completed a classification audit in a different part of the agency, the hiring team can use it. This can also be done across agencies with CHCO approval.
- Hiring managers who invest time to understand the position well and articulate the roles, duties, relationships, and complexity to the classifier can improve the outcomes and make the process more efficient.
- Agencies that lack classification resources frequently engage with outside contractors or retired annuitants to provide more capacity for the classification and job analysis work.
Develop Assessment Strategy
A critical, but sometimes overlooked step in hiring is developing the assessment strategy for the position. This determines how the HR staff and hiring manager will evaluate applicants and identify candidates for the certificate list, or the list of eligible applicants. The strategy needs to assess candidates based on the defined job duties and position criteria, and it plays a major role in determining the quality of candidates.The assessment strategy consists of three parts:
- How job applications and resumes are reviewed
- How the applicants demonstrate the required skills and abilities
- How the hiring manager makes the final selection
Recently, agencies have moved toward evaluating applicants by assessing their skills, spurred on by the Executive Order and guidance on skills-based assessments and now reinforced by the Chance to Compete Act. This shift aims to move away from relying on education and/or self-assessments. Skills-based assessments can include online tests, skills-based simulation exercises, simulated job tryouts, as well as the Subject Matter Expert Qualifications Assessment (SME-QA) process developed by OPM and USDS/OMB. This improves the quality of assessments and aims to ensure the candidates on the certificate list are qualified for the job.
What Can Go Wrong
- If a hiring manager and HR staffing specialist bypass this step, this frequently results in a certificate list with unqualified candidates. Without a strategy, many default to using a resume review and self-assessments. Unfortunately, our research indicated that many agencies are still using self-assessments.
- Most of the time, resume screening is left solely to the HR staff. Lack of alignment between HR specialists and hiring managers on essential qualifications results in an inaccurate screening, leading unqualified candidates to make the cut. Too often, HR staff will only screen applications for the exact phrases that appear in the job announcement. Applicants know this and revise their documents accordingly.
- When a skills-based assessment does not exist for the position and specific grade level, it needs to be created. This takes time and expert resources, thus delaying the hiring process.
- Inaccurate resume screenings and self-assessments frequently lead to a high number of unqualified Veterans making the top of the certificate list due to Veterans preference. Unfortunately, this leads to a negative perception of Veterans preference.
What Can Go Right
- Working with HR staffing specialists to find existing assessments can save time and improve candidate selection quality. In addition, USA Hire, Monster, and other HR talent acquisition platforms are offering compendiums of assessment strategies and tools that can be accessed, usually for free.
- Deep engagement between hiring managers, staffing specialists, and assessment professionals in developing an assessment strategy and selecting tools pays off. This can lead to enhanced resume and application screening, stronger alignment between candidate and position needs, and higher quality certificate lists of eligible candidates.
- Engagement with staffing specialists and assessment experts can also help the hiring manager understand and make tradeoff decisions related to the speed and ease of administration. For example, an online test may be easier to utilize, while embedding Subject Matter Experts into the selection process may increase the efficacy.
Create and Post Job Opportunity Announcement
Though creating and posting the JOA is relatively straightforward, lack of attention to this step can reduce the number of attractive candidates. The HR staffing specialist usually creates the JOA in consultation with the hiring manager to ensure that it not only accurately reflects the job duties, but also sells the job to potential applicants. The JOA is an opportunity to showcase the importance of the role and its contribution to the agency’s mission.
The JOA outlines applicant eligibility, job duties, job requirements (e.g., conditions of employment, qualifications, etc.), education (if needed), assessment strategy, and application requirements. It also lists the occupation, grade level, location, and other details. See USAJOBS for examples.
What Can Go Wrong
- Some hiring managers and staffing specialists are under the misapprehension that the JOA needs to contain the exact language from the PD in both the title and description. This can include jargon and terms that are unfamiliar to those not within the organization.
- Unintentionally, a hiring manager may lock the job location in a specific city or metropolitan area when the job could be remote or in multiple locations. To correct this, the JOA will need to be taken down and re-posted if no suitable applicants can be found.
What Can Go Right
- JOAs need to be tailored to the target applicants, and working with those currently in the job or in a related-discipline can help in crafting an attractive JOA.
- Using plain language in the job title and description instead of jargon will attract more candidates. OPM has published plain language guidance to help hiring managers and staffing specialists do this effectively.
- Earlier in the hiring process, successful hiring managers and staffing specialists define recruiting and sourcing strategies to attract candidates. This can include posting the job on alternative sites (e.g., agency websites, LinkedIn, Handshake, Indeed, etc.) in addition to USAJOBS to reach a broader audience. One agency’s HR team described leveraging multiple platforms for outreach and was able to successfully recruit many qualified candidates for their open roles. Strategies can also include asking hiring managers, peers, agency leaders, and recruiters to message highly qualified candidates to expand the applicant pool and bring in more qualified applicants.
Conclusion
Throughout this phase of work, there are many actions hiring managers and staffing specialists can take to streamline the process and improve the quality of eligible candidates. Most importantly, hiring managers and staffing specialists can collaborate within and across agencies to expedite and simplify the process. Using an existing PD from another part of the agency, finding an assessment tool for the job and grade level, pooling resources on a common job announcement with a peer, and using shared certificates to move straight to a job offer are all ways you can find a well-qualified hire faster. More tips and techniques to improve hiring can be found in OPM’s Workforce of the Future Playbook.
Changes that can be made to improve efficiency and promote collaboration. These center on moving to standardized PDs, where appropriate, leveraging shared certifications with those standardized PDs, and investing in skills-based assessments, which are now required by law in the Chance to Compete Act.
Making these actions common practice is one of the key challenges to improving hiring. The Executive Order on skills-based hiring states “in light of today’s booming labor market, the Federal government must position itself to compete with other sectors for top talent.” It is critical we take advantage of these collaboration tools that can improve the hiring experience for all those involved.
Unpacking Hiring: Toward a Regional Federal Talent Strategy
Government, like all institutions, runs on people. We need more people with the right skills and expertise for the many critical roles that public agencies are hiring for today. Yet hiring talent in the federal government is a longstanding challenge. The next Administration should unpack hiring strategy from headquarters and launch a series of large scale, cross-agency recruitment and hiring surges throughout the country, reflecting the reality that 85% of federal employees are outside the Beltway. With a collaborative, cross-agency lens and a commitment to engaging jobseekers where they live, the government can enhance its ability to attract talent while underscoring to Americans that the federal government is not a distant authority but rather a stakeholder in their communities that offers credible opportunities to serve.
Challenge and Opportunity
The Federal Government’s hiring needs—already severe across many mission-critical occupations—are likely to remain acute as federal retirements continue, the labor market remains tight, and mission needs continue to grow. Unfortunately, federal hiring is misaligned with how most people approach job seeking. Most Americans search for employment in a geographically bounded way, a trend which has accelerated following the labor market disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, federal agencies tend to engage with jobseekers in a manner siloed to a single agency and across a wide variety of professions.
The result is that the federal government tends to hire agency by agency while casting a wide geographic net, which limits its ability to build deep and direct relationships with talent providers, while also duplicating searches for similar roles across agencies. Instead, the next Administration should align with jobseekers’ expectations by recruiting across agencies within each geography.
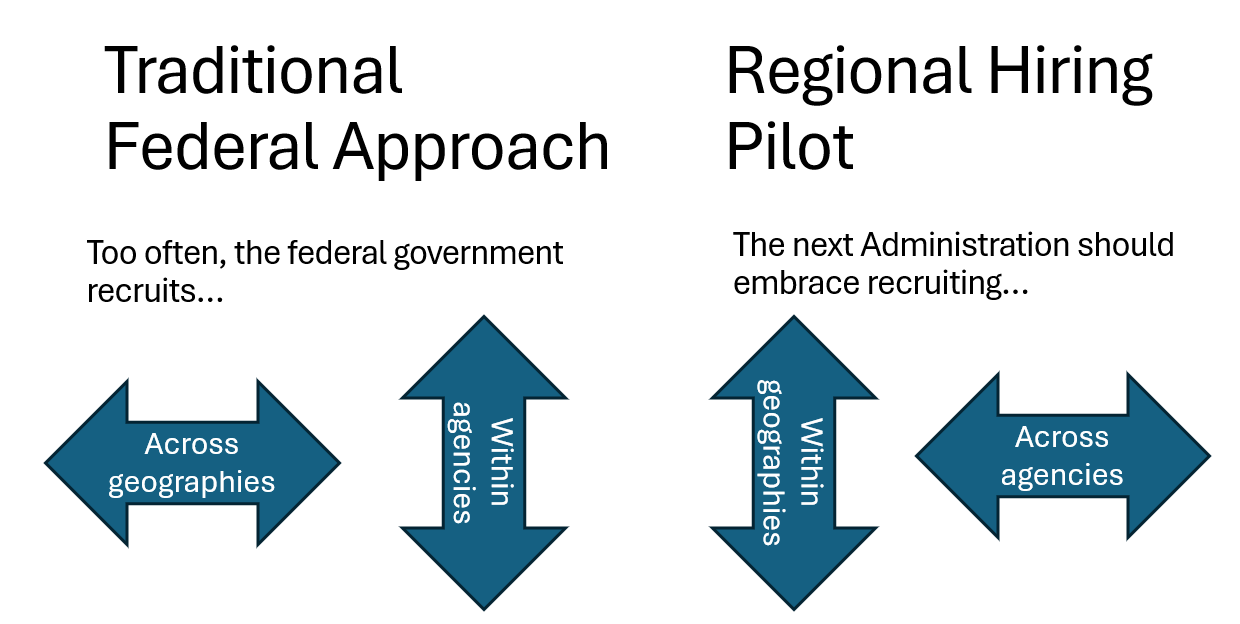
By embracing a new approach, the government can begin to develop a more coordinated cross-agency employer profile within regions with significant federal presence, while still leveraging its scale by aggregating hiring needs across agencies. This approach would build upon the important hiring reforms advanced under the Biden-Harris Administration, including cross-agency pooled hiring, renewed attention to hiring experience for jobseekers, and new investments to unlock the federal government’s regional presence through elevation of the Federal Executive Board (FEB) program. FEBs are cross-agency councils of senior appointees and civil servants in regions of significant federal presence across the country. They are empowered to identify areas for cross-agency cooperation and are singularly positioned to collaborate to pool talent needs and represent the federal government in communities across the country.
Plan of Action
The next Administration should embrace a cross-agency, regionally-focused recruitment strategy and bring federal career opportunities closer to Americans through a series of 2-3 large scale, cross-agency recruitment and hiring pilots in geographies outside of Washington, DC. To be effective, this effort will need both sponsorship from senior leaders at the center of government, as well as ownership from frontline leaders who can build relationships on the ground.
Recommendation 1. Provide Strategic Direction from the Center of Government
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) and the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) should launch a small team, composed of leaders in recruitment, personnel policy and workforce data, to identify promising localities for coordinated regional hiring surges. They should leverage centralized workforce data or data from Human Capital Operating Plan workforce plans to identify prospective hiring needs by government-wide and agency-specific mission-critical occupations (MCOs) by FEB region, while ensuring that agency and sub-agency workforce plans consistently specify where hiring will occur in the future. They might also consider seasonal or cyclical cross-agency hiring needs for inclusion in the pilot to facilitate year-to-year experimentation and analysis. With this information, they should engage the FEB Center of Operations and jointly select 2-3 FEB regions outside of the capital where there are significant overlapping needs in MCOs.
As this pilot moves forward, it is imperative that OMB and OPM empower on-the-ground federal leaders to drive surge hiring and equip them with flexible hiring authorities where needed.
Recommendation 2. Empower Frontline Leadership from the FEBs
FEB field staff are well positioned to play a coordinating role to help drive surges, starting by convening agency leadership in their regions to validate hiring needs and make amendments as necessary. Together, they should set a reasonable, measurable goal for surge hiring in the coming year that reflects both total need and headline MCOs (e.g., “in the next 12 months, federal agencies in greater Columbus will hire 750 new employees, including 75 HR Specialists, 45 Data Scientists, and 110 Engineers”).
To begin to develop a regional talent strategy, the FEB should form a small task force drawn from standout hiring managers and HR professionals, and then begin to develop a stakeholder map of key educational institutions and civic partners with access to talent pools in the region, sharing existing relationships and building new ones. The FEB should bring these external partners together to socialize shared needs and listen to their impressions of federal career opportunities in the region.
With these insights, the project team should announce publicly the number and types of roles needed and prepare sharp public-facing collateral that foregrounds headline MCOs and raises the profile of local federal agencies. In support, OPM should launch regional USAJOBS skins (e.g., “Columbus.USAJOBS.gov”) to make it easy to explore available positions. The team should make sustained, targeted outreach at local educational institutions aligned with hiring needs, so all federal agencies are on graduates’ and administrators’ radar.
These activities should build toward one or more signature large, in-person, cross-agency recruitment and hiring fairs, perhaps headlined by a high profile Administration leader. Candidates should be able to come to an event, learn what it means to hold a job in their discipline in federal service, and apply live for roles at multiple agencies, all while exploring what else the federal government has to offer and building tangible relationships with federal recruiters. Ahead of the event, the project team should work with agencies to align their hiring cycles so the maximum number of jobs are open at the time of the event, potentially launching a pooled hiring action to coincide. The project team should capture all interested jobseekers from the event to seed the new Talent Campaigns function in USAStaffing that enables agencies to bucket tranches of qualified jobseekers for future sourcing.
Recommendation 3. Replicate and Celebrate
Following each regional surge, the center of government and frontline teams should collaborate to distill key learnings and conclude the sprint engagement by developing a playbook for regional recruitment surges. Especially successful surges will also present an opportunity to spotlight excellence in recruitment and hiring, which is rarely celebrated.
The center of government team should also identify geographies with effective relationships between agencies and talent providers for key roles and leverage the growing use of remote work and location negotiable positions to site certain roles in “friendly” labor markets.
Conclusion
Regional, cross-agency hiring surges are an opportunity for federal agencies to fill high-need roles across the country in a manner that is proactive and collaborative, rather than responsive and competitive. They would aim to facilitate a new level of information sharing between the frontline and the center of government, and inform agency strategic planning efforts, allowing headquarters to better understand the realities of recruitment and hiring on the ground. They would enable OPM and OMB to reach, engage, and empower frontline HR specialists and hiring managers who are sufficiently numerous and fragmented that they are difficult to reach in the present course of business.
Finally, engaging regionally will emphasize that most of the federal workforce resides outside of Washington, D.C., and build understanding and respect for the work of federal public servants in communities across the nation.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
Enhancing Local Capacity for Disaster Resilience
Across the United States, thousands of communities, particularly rural ones, don’t have the capacity to identify, apply for, and manage federal grants. And more than half of Americans don’t feel that the federal government adequately takes their interests into account. These factors make it difficult to build climate resilience in our most vulnerable populations. AmeriCorps can tackle this challenge by providing the human power needed to help communities overcome significant structural obstacles in accessing federal resources. Specifically, federal agencies that are part of the Thriving Communities Network can partner with the philanthropic sector to place AmeriCorps members in Community Disaster Resilience Zones (CDRZs) as part of a new Resilient Communities Corps. Through this initiative, AmeriCorps would provide technical assistance to vulnerable communities in accessing deeply needed resources.
There is precedent for this type of effort. AmeriCorps programming, like AmeriCorps VISTA, has a long history of aiding communities and organizations by directly helping secure grant monies and by empowering communities and organizations to self-support in the future. The AmeriCorps Energy Communities is a public-private partnership that targets service investment to support low-capacity and highly vulnerable communities in capitalizing on emerging energy opportunities. And the Environmental Justice Climate Corps, a partnership between the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and AmeriCorps, will place AmeriCorps VISTA members in historically marginalized communities to work on environmental justice projects.
A new initiative targeting service investment to build resilience in low-capacity communities, particularly rural communities, would help build capacity at the local level, train a new generation of service-oriented individuals in grant writing and resilience work, and ensure that federal funding gets to the communities that need it most.
Challenge and Opportunity
A significant barrier to getting federal funding to those who need it the most is the capacity of those communities to search and apply for grants. Many such communities lack both sufficient staff bandwidth to apply and search for grants and the internal expertise to put forward a successful application. Indeed, the Midwest and Interior West have seen under 20% of their communities receive competitive federal grants since the year 2000. Low-capacity rural communities account for only 3% of grants from the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)’s flagship program for building community resilience. Even communities that receive grants often lack the capacity for strong grant management, which can mean losing monies that go unspent within the grant period.
This is problematic because low-capacity communities are particularly vulnerable to natural disasters from flooding to wildfires. Out of the nearly 8,000 most at-risk communities with limited capacity to advocate for resources, 46% are at risk for flooding, 36% are at risk for wildfires, and 19% are at risk for both.
Ensuring communities can access federal grants to help them become more climate resilient is crucial to achieving an equitable and efficient distribution of federal monies, and to building a stronger nation from the ground up. These objectives are especially salient given that there is still a lot of federal money available through the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) that low-capacity communities can tap into for climate resilience work. As of April 2024, only $60 billion out of the $145 billion in the IRA for energy and climate programs had been spent. For the IIJA, only half of the nearly $650 billion in direct formula funding had been spent.
The Biden-Harris Administration has tried to address the mismatch between federal resilience funding and community capacity in a variety of ways. The Administration has deployed resources for low-capacity communities, agencies tasked with allocating funds from the IRA and IIJA have held information sessions, and the IRA and IIJA contain over a hundred technical assistance programs. Yet there still is not enough support in the form of human capacity at the local level to access grants and other resources and assistance provided by federal agencies. AmeriCorps members can support communities in making informed decisions, applying for federal support, and managing federal financial assistance. Indeed, state programs like the Maine Climate Corps, include aiding communities with both resilience planning and emergency management assistance as part of their focus. Evening the playing field by expanding deployment of human capital will yield a more equitable distribution of federal monies to the communities that need it the most.
AmeriCorps’ Energy Communities initiative serves as a model for a public-private partnership to support low-capacity communities in meeting their climate resilience goals. Over a three-year period, the program will invest over $7.8 million from federal agencies and philanthropic dollars to help communities designated by the Interagency Working Group on Coal & Power Plant Communities & Economic Revitalization on issues revolving around energy opportunity, environmental cleanup, and economic development to help communities capitalize on emerging energy opportunities.
There is an opportunity to replicate this model towards resilience. Specifically, the next Administration can leverage the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA’s) Community Disaster Resilience Zone (CDRZ) designations to target AmeriCorps support to the communities that need it most. Doing so will not only build community resilience, but will help restore trust in the federal government and its programs (see FAQ).
Plan of Action
The next administration can support vulnerable communities in building climate resilience by launching a new Resilient Communities Corps through AmeriCorps. The initiative can be launched through a three-part Plan of Action: (1) find a philanthropic partner to fund AmeriCorps placements in CDRZs, (2) engage federal agencies that are part of the Thriving Communities Network to provide resilience training and support to Corps members, and (3) use the CDRZ designations to help guide where AmeriCorps members should be placed.
Recommendation 1. Secure philanthropic funding
American service programs have a history of utilizing philanthropic monies to fund programming. The AmeriCorps Energy Communities is funded with philanthropic monies from Bloomberg Philanthropies. California Volunteers Fund (CVF), the Waverly Street Foundation, and individual philanthropists helped fund the state Climate Corps. CVF has also provided assistance and insights for state Climate Corps officials as they develop their programs.
A new Resilient Communities Corps under the AmeriCorps umbrella could be funded through one or several major philanthropic donors, and/or through grassroots donations. Widespread public support for AmeriCorps’ ACC that transcends generational and party lines presents the opportunity for new grassroots donations to supplement federal monies allocated to the program along with tapping the existing network of foundations, individuals, companies, and organizations that have provided past donations. The Partnership for the Civilian Climate Corps (PCCC), which has had a history of collaborating with the ACC’s federal partners, would be well suited to help spearhead this grassroots effort.
America’s Service Commissions (ASC), which represents state service commissions, can also help coordinate with state service commissions to find local philanthropic monies to fund AmeriCorps work in CDRZs. There is precedent for this type of fundraising. Maine’s state service commission was able to secure private monies for one Maine Service Fellow. The fellow has since worked with low-capacity communities in Maine on climate resilience. ASC can also work with state service commissions to identify current state, private, and federally funded service programming that could be tapped to work in CDRZs or are currently working in CDRZs. This will help tie in existing local service infrastructure.
Recommendation 2. Engage federal agencies participating in the Thriving Communities Network and the American Climate Corps (ACC) interagency working group.
Philanthropic funding will be helpful but not sufficient in launching the Resilient Communities Corps. The next administration should also engage federal agencies to provide AmeriCorps members participating in the initiative with training on climate resilience, orientations and points of contact for major federal resilience programs, and, where available, additional financial support for the program. The ACC’s interagency working group has centered AmeriCorps as a multiagency initiative that has directed resources and provides collaboration in implementing AmeriCorps programming. The Resilient Communities Corps will be able to tap into this cross-agency collaboration in ways that align with the resilience work already being done by partnership members.
There are currently four ACC programs that are funded through cooperation with other federal agencies. These are the Working Lands Climate Corps with the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)’s Natural Resources and Conservation Service, AmeriCorps NCCC Forest Corps with the USDA Forest Service, Energy Communities AmeriCorps with the Department of Interior and the Department of Commerce, and the Environmental Justice Corps, which was announced in September 2024 and will launch in 2025, with the EPA. The Resilient Communities Corps could be established as a formal partnership with one or more federal agencies as funding partners.
In addition, the Resilient Communities Corps can and should leverage existing work that federal agencies are doing to build community capacity and enhance community climate resilience. For instance, USDA’s Rural Partners Network helps rural communities access federal funding while the EPA’s Environmental Justice Thriving Communities Technical Assistance Centers Program provides training and assistance for communities to build the capacity to navigate, develop proposals, and manage federal grants. The Thriving Communities Network provides a forum for federal agencies to provide technical assistance to communities trying to access federal monies. Corps members, through the network, can help federal agencies provide communities they are working with building capacity to access this technical assistance.
Recommendation 3. Use CDRZ designations and engage with state service commissions to guide Resilient Communities Corps placements
FEMA, through its National Risk Index, has identified communities across the country that are most vulnerable to the climate crisis and need targeted federal support for climate resilience projects. CDRZs provide an opportunity for AmeriCorps to identify low-capacity communities that need their assistance in accessing this federal support. With assistance from partner agencies and philanthropic dollars, the AmeriCorps can fund Corps members to work in these designated zones to help drive resources into them. As part of this effort, the ACC interagency working group should be broadened to include the Department of Homeland Security (which already sponsors FEMA Corps).
In 2024, the Biden-Harris Administration announced Federal-State partnerships between state service commissions and the ACC. This partnership with state service commissions will help AmeriCorps and partner agencies identify what is currently being done in CDRZs, what is needed from communities, and any existing service programming that could be built up with federal and philanthropic monies. State service commissions understand the communities they work with and what existing programming is currently in place. This knowledge and coordination will prove invaluable for the Resilient Communities Corps and AmeriCorps more broadly as they determine where to allocate members and what existing service programming could receive Resilient Communities Corps designation. This will be helpful in deciding where to focus initial/pilot Resilient Communities Corps placements.
Conclusion
A Resilient Communities Corps presents an incredible opportunity for the next administration to support low-capacity communities in accessing competitive grants in CDRZ-designated areas. It will improve the federal government’s impact and efficiency of dispersing grant monies by making grants more accessible and ensure that our most vulnerable communities are better prepared and more resilient in the face of the climate crisis, introduce a new generation of young people to grant writing and public service, and help restore trust in federal government programs from communities that often feel overlooked.
This action-ready policy memo is part of Day One 2025 — our effort to bring forward bold policy ideas, grounded in science and evidence, that can tackle the country’s biggest challenges and bring us closer to the prosperous, equitable and safe future that we all hope for whoever takes office in 2025 and beyond.
PLEASE NOTE (February 2025): Since publication several government websites have been taken offline. We apologize for any broken links to once accessible public data.
Funding for one AmeriCorps member in each of FEMA’s 483 designated Community Disaster Resilience Zones would cost around $14,500,000 per year. This is with an estimate of $30,000 per member. However, this figure will be subject to change due to overhead and living adjustment costs.
There are many communities that could benefit from additional support when it comes to building resilience. Headwater Economics, a research institute in Montana, has flagged that the CDRZ does not account for all low-capacity communities hampered in their efforts to become more climate resilient. But the CDRZ designation does provide a federal framework that can serve as a jumping-off point for AmeriCorps to begin to fill capacity gaps. These designations, identified through the National Risk Index, provide a clear picture for where federal, public and private monies are needed the most. These communities are some of the most vulnerable to climate change, lack the resources for resilience work, and need the human capacity to access them. Because of these reasons, the CDRZ communities provide the ideal and most appropriate area for the Resilient Communities Corps to first serve in.
Funding for national service programming, particularly for the ACC, has bipartisan support. 53% of likely voters say that national service programming can help communities face climate-related issues.
On the other hand, 53% of Americans also feel that the federal government doesn’t take into account “the interests of people like them.” ACC programming, like what Maine’s Climate Corps is doing in rural areas, can help reach communities and build support among Americans for government programs that can be at times met with hostility.
For example, in Maine, the small and politically conservative town of Dover-Foxcroft applied for and was approved to host a Maine Service Fellow (part of the Maine Climate Corps network) to help the local climate action committee to obtain funding for and implement energy efficiency programs. The fellow, a recent graduate from a local college, helped Dover-Foxcroft’s new warming/cooling emergency shelter create policies, organized events on conversations about climate change, wrote a report about how the county will be affected by climate change, and recruited locals at the Black Fly Festival to participate in energy efficiency programs.
Like the Maine Service Fellows, Resilient Communities Corps members will be integral members of the communities in which they serve. They will gather essential information about their communities and provide feedback from the ground on what is working and what areas need improvement or are not being adequately addressed. This information can be passed up to the interagency working groups that can then be relayed to colleagues administering the grants, improving information flow, and creating feedback channels to better craft and implement policy. It also presents the opportunity for representatives of those agencies to directly reach out to those communities to let them know they have been heard and proactively alert residents to any changes they plan on making.
Building Talent Capacity for Permitting: Insights from Civil Servants
Have you ever asked a civil servant in the federal government what it was like to hire new staff? It’s quite common to hear how challenging it is to navigate the hiring process and how long it takes to get someone through the door. At FAS, we know it’s hard. We’ve seen how it works, and we’ve heard stories from civil servants in government.
Following the wave of legislation aimed at addressing infrastructure, environment, and economic vulnerabilities (i.e., the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), and the CHIPS and Science Act (CHIPS)), we knew that the federal government’s hiring needs were going to soar. As we previously stated, permitting is a common bottleneck that would hinder the implementation of BIL, IRA, and CHIPS. The increase in work following this legislation came in conjunction with a push for faster permits, which in turn significantly increased agency workload. Many agencies did not have the capacity to clear the existing backlogs of permitting projects they already had in their pipeline, which would not even begin to address the new demand that would result from these laws. As such, talent capacity, or having staff with the knowledge and skills needed to meet the work demands, presented a major bottleneck.
We also knew that surge hiring is not a strength of the government, and there are a number of reasons for that; some we highlighted in our recent blog post. It’s a difficult task to coordinate, manage, and support the hiring process for a variety of roles across many agencies. And agencies that are responsible for permitting activities, like environmental reviews and authorizations, do not have standardized roles and team structures to make it easier to hire. Furthermore, permitting responsibility and roles are disaggregated within and across agencies – some roles are permanent, others are temporary. Sometimes responsibility for permitting is core to the job. In other cases, the responsibility is part of other program or regional/state needs. This makes it hard to take concerted and sustained action across government to improve hiring.
While this sounds like a challenge, FAS saw an opportunity to apply our talent expertise to permitting hiring with the aim of reducing the time to hire and improving the hiring experience for both hiring managers and HR specialists. Our ultimate goal was to enable the implementation of this new legislation. We also knew that focusing on hiring for permitting would offer a lens to better understand and solve for systemic talent challenges across government.
As part of this work, we had the opportunity to connect and collaborate with the Permitting Council, which serves as a central body to improve the transparency, predictability, and accountability of the federal environmental review and authorization process, to gain a broad understanding of the hiring difficulties experienced across permitting agencies. This helped us identify some of the biggest challenges preventing progress, which enabled us to co-host two webinars for hiring managers, HR specialists, HR leaders, and program leaders within permitting agencies, focused on showcasing tactical solutions that could be applied today to improve hiring processes.
Our team wanted to complement this understanding of the core challenges with voices from agencies – hiring managers, HR specialists, HR teams, and leaders – who have all been involved in the process. We hoped to validate the challenges we heard and identify new issues, as well as capture best practices and talent capacity strategies that had been successfully employed. The intention of this blog is to capture the lessons from our discussions that could support civil servants in building talent capacity for permitting-related activities and beyond, as many solutions identified are broadly applicable across the federal government.
Approach
Our team at FAS reached out to over 55 civil servants who work across six agencies and 17 different offices identified through our hiring webinars to see if they’d be willing to share about their experiences trying to hire for permitting-related roles in the implementation of IRA, BIL, and CHIPS. Through this outreach, we facilitated 14 interviews and connected with 18 civil servants from six different organizations within the Environmental Protection Agency, Department of Defense, Department of Interior, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and the Department of Commerce. The roles of the participants varied; it included Hiring Managers, HR Specialists, HR Leaders, Chief Environmental Review and Permitting Officers, and Chief Human Capital Officers.
In our conversations, we focused on identifying their hiring needs to support permitting-related activities within their respective organization, the challenges they experience in trying to hire for those new positions, what practices were successful in their hiring efforts, and any recommendations they had for other agencies. We synthesized the data we gathered through these discussions and identified common challenges in hiring, successful hiring practices, talent capacity strategies, and additional tips for civil servants to consider.
Challenges to Hiring
We identified many challenges hindering agencies from quickly bringing on new staff to fill their open roles. From the start, many teams responsible for permitting were already very understaffed. One interviewee explained that they had serious backlogs requiring complex analysis, but were only able to triage and take on what was feasible. Another shared that they initially were only processing 60% of their workload annually. A third interviewee explained that some of their staff had previously been working on 4-5 Environment Impact Statements (EIS) at one time, which is very high and not common for the field. Their team had a longstanding complaint about high workload that led to a high attrition rate, which only increased the need for more hires. In addition to the permitting teams being under resourced, many HR counterpart teams were also understaffed. This created an environment where teams needed to hire a significant number of new staff, but did not necessarily have the HR support necessary to execute.
The budget was the next issue many agencies faced. The budget constraints resulting from the time-bound funding of IRA and BIL raised a number of important questions for the agencies. BIL funds expire at the end of FY2026 and IRA funds expire anywhere between 2-10 years from the legislation passing in 2022. For example, the funds allocated to the Permitting Council in the IRA expire at the end of FY2031, and some of these funds have been given to agencies to bolster workforce capacity for supporting timely permitting reviews. Ultimately, agencies needed to decide if they wanted to hire temporary or full time employees. This decision cannot be made without additional information and analysis of retirement rates, attrition rates, and other funding sources.
In addition to managing the budgetary constraints, agencies needed to determine how they would allocate the funds provided to their bureaus and programs. This required negotiations, justifications, and many discussions. The ability of Program Leaders to negotiate and justify their allocation is dependent upon their ability to accurately conduct workforce planning, which was a challenge identified through interviews. Specifically, some managers were challenged to accurately plan in an environment that is demand-driven and continuously evolving. Additionally, managing staff who have a variety of responsibilities and may only work on permitting projects for a portion of their time only increases the complexity of the planning process.
A number of challenges we heard were common pain points in the federal government’s hiring process, as noted in Many Chutes and Few Ladders in the Federal Hiring Process. These include:
- Assessments: Inadequate assessments have led to issues with the certificate lists of eligible candidates provided from the HR Specialist to the hiring manager. Some hiring managers have received lists with too many candidates to choose from, while others have been disappointed to not see qualified candidates on the list. This is largely a result of assessments that do not effectively screen qualified applicants. Self-assessments are an example of this, where applicants score their own abilities in response to a series of multiple choice questions. From our conversations, self-assessments are still a commonly used practice, and skills-based assessments have not been widely adopted.
- Job Descriptions: Both creating new and updating job descriptions has caused delays in the hiring process. Some agencies have started moving towards standardized job descriptions with the goal of making the process more efficient, but this has not been an easy task and has required a lot of time for collaboration across a variety of stakeholders.
- Background Checks: Delays in background checks have slowed the process. These delays often result from mistakes in or incomplete Electronic Questionnaires for Investigations Processing (e-QIP) forms, delays in scheduling fingerprint appointments, a lack of infrastructure for sharing and tracking information between key stakeholders (e.g., selected applicant, suitability manager, hiring manager), and delayed responses to notifications in the process.
- Candidate Declinations: Candidates declining a job offer have set a number of agencies back, especially those lacking deep applicant pools. The reasons provided have varied. Some applicants believed that the temporary positions were negotiable or did not realize they had applied to a term position, and they were no longer interested. In some cases, agency hiring managers did not know they had hiring flexibilities or incentives to offer that may have bridged the gap for the candidate. Others were unable to accept the offer for the specific location, citing the increased cost of living and housing prices as a barrier.
Lastly, recruiting was noted as a challenge by a number of participants. Recruiting for a qualified applicant pool has been difficult, especially for those looking to hire very specialized roles. One participant explained their need for someone with experience working in a specific region of the country and the limitations that came with not being able to offer a relocation bonus. Another participant described the difficulty in finding qualified candidates at the right grade level because the pay scale was very limiting for the expertise required. These challenges are exacerbated in agencies that lack recruiting infrastructure and dedicated resources to support recruitment.
These challenges manifested as bottlenecks in the hiring process and present opportunities for improvement. Apart from the new, uncertain funding, these challenges are not novel. Rather, these are issues agencies have been facing for many years. The new legislation has drawn broader attention back to these problems and presents an opportunity for action.
Successful Hiring Practices
Despite these bottlenecks, participants shared a number of practices they employed to improve the hiring process and successfully bring new staff onboard. We wanted to share seven (7) practices that could be adopted by civil servants today.
Establish Hiring Priority and Gain Leadership Support
One agency leveraged the Biden-Harris Permitting Action Plan to establish and elevate their hiring needs. Following the guidance shared by OMB, CEQ, and the Permitting Council, this agency set out to develop an action plan that would function as a strategic document over the next few years. They employed a collaborative approach to develop their plan. The Chief Environmental Review and Permitting Officer (CERPO) and Deputy CERPO, the roles responsible for overseeing environmental review and permitting projects within their agencies and under their jurisdiction, brought together a team of NEPA Specialists and other staff engaged in environmental reviews and permitting across their organizations with equities. This group collectively brainstormed what they could do to strengthen and streamline permitting and environmental reviews at their agency. From this list, they prioritized five key focus areas for the first phase of their plan. This included hiring as the highest priority because it had been identified as a critical issue. Given their positioning within the organization and the Administration’s mandate, they were able to gain the support of the Secretary, and as a result, escalate their hiring needs to fill over 30 open positions over the course of FY24.
Collaborate and Share Across the Organization
Sharing and collaborating across the agency helped many expedite the hiring process. Here are examples that highlight the importance of this for success.
(1) One agency described how they share position descriptions across the enterprise. They have a system that allows any hiring manager to search for a similar position that they could use themselves or refine for their specific role. This reduces the time spent by hiring managers recreating positions.
(2) Another agency explained how they created an open tracking tool of positions they were interested in hiring across the organization. This tool allowed hiring managers across the agency to share the positions they wanted to hire. The initial list included 300 potential positions; it allowed them to prioritize and identify opportunities for collaboration. By leveraging shared certificates, they were able to reduce duplication. This tool evolved into an open repository of positions the organization was looking to recruit and a timeline for when they would be recruiting for those roles. Once announcements were closed, they would share the certificate lists widely to hiring managers.
(3) In another example, the participant explained how they facilitated ongoing collaboration between the CERPO, CHCO, HQ, and both HR and Program Leads from each relevant bureau to drive forward the hiring process. They initially worked with the Program Leads from the key bureaus impacted to identify their hiring needs and discuss the challenges they were facing. Then they reached out to the CHCO to engage them and share their priority hiring needs and worked to bring in each bureau’s respective HR teams to provide technical assistance. With everyone engaged, they set up a regular check-in to discuss progress, and the group collaborated to develop and classify position descriptions for the open positions. Later once candidates had been selected, they collaborated with operations to prioritize their hires in suitability. This ultimately saved time and streamlined the process.
Improve Hiring Processes
Participants described improving hiring processes within their organization through a variety of approaches. One method that we heard numerous times is standardizing job descriptions across the enterprise to reduce duplicative job revision and classification efforts and support the use of shared certifications. One agency approached this by facilitating focus groups with key stakeholders to define the non-negotiable and “nice to have” duties for the role. These sessions included classifiers, domain specialists, leadership, and data analysts. They found that when the group started discussing the knowledge and skills that really mattered, they were able to understand why combining efforts would help them achieve their goals more quickly. They realized that some of the minute details (e.g., expertise in Atlantic Salmon) did not need to be in the position description and rather could be deduced through the interview process. While this took a great deal of buy in and leadership support, they were successful in standardizing some position descriptions.
Other methods for improving hiring processes included standardizing the process for establishing pay to reduce competition across the agency, setting a 30-day time limit for making selections, setting applicant limits for closing job announcements, and using data to drive improvements. In one interview with an agency’s HR team, we learned about their role in collecting and analyzing data in each step of the hiring process (e.g., overall hiring time, time at each step, etc.). They use this information to monitor progress, track performance, understand which incentives are being employed, and identify opportunities for improvement in the overall process. This data helps inform their decisions and allows them to identify where they need to provide more support.
Leverage Position and Recruiting Incentives
Multiple participants described using incentives to make a position more attractive to a candidate and encourage the acceptance of a job offer. Multiple agencies offered remote and hybrid positions where possible, which they cited as generating more interest in the role. One HR team shared how they employ a series of OPM approved recruiting incentives to make positions more compelling. These included starting bonuses, student loan repayment, credit for industry work, advanced leave, higher step options, relocation bonuses, and additional leave time. They find these incentives to be particularly helpful when the location requires a far move (e.g., Alaska, Hawaii) or is difficult to hire into for whatever reason.
Leverage Hiring Flexibilities
Multiple agencies cited using different hiring flexibilities to hire for their open positions and remove some of the barriers embedded in the competitive service hiring process. The flexibilities included, Direct Hire Authority, Schedule A, Pathways Programs, retired annuitants, internship conversions, internal detailees, Presidential Innovation Fellows via GSA, Digital Service Fellows Program, as well as contract staff to support IT development. Many agencies also hired for term or temporary positions that ranged from three to 10 years, depending on the additional funding sources that could be found. Employing these authorities helped to streamline the hiring process.
Seek HR Recruiting Support
One agency described how their HR office supported and collaborated with hiring managers throughout the hiring process, especially in bolstering their recruitment efforts. One HR team helped lead recruitment outreach, sharing their open positions on a variety of media in coordination with their communications team (i.e., their website, facebook, instagram). They also developed standard language for hiring managers to share with their networks that highlighted information about the role and mistakes to avoid when applying. This helped relieve the pressure on the hiring manager to lead the recruiting effort.
Invest in Dedicated HR Staff to Manage and Support Permitting Hiring
Multiple agencies shared how they hired a dedicated resource to oversee the hiring process for their organization. One agency hired a retired annuitant (i.e., someone who retired from working in the federal government and is rehired) to help manage the organization’s hiring process after they realized that they were making minimal progress against their hiring needs. This individual returned to the government workforce and brought a deep understanding of government hiring. They collaborated with the HR Specialists and hiring managers to develop position descriptions, organize procurement packages, schedule interviews, and support the applicant selection process. They said, “we would not have been able to do any of the 40 hires without this person.”
Another agency described how they detailed someone to manage BIL and IRA hiring requests across their organization. This person was situated outside of HR, and they were responsible for tracking the end-to-end hiring and recruitment efforts. They maintained a repository of the positions each office needed to recruit and generated weekly reports on BIL and IRA hiring efforts that highlighted how many positions are open, how many are closed, and where certificate lists are available. This allowed the broader team to identify how they could drive progress.
While there were a number of challenges, many participants described successfully hiring 15-30+ new employees over the last year alone. One agency in particular described hiring over 2,000 people in 2024 for the IRA, which was an all time high for their organization. These seven practices have enabled agencies to be successful in filling new positions to support permitting-related activities, and they can be applied to other hiring needs as well. Any future talent surge in the federal government could benefit from adopting these hiring practices.
Solutions to Build Talent Capacity
While the majority of the interviews focused on hiring due to concerns of understaffed teams and the new funding availability, there are many other ways to build talent capacity in government. Some of the participants we interviewed shared other strategies they employed to address high workload demands, which present opportunities for other agencies to consider, especially as we move into the new administration. Here are six (6) strategies for building workforce capacity.
Establish Strike Teams
During our conversations, two different agencies described creating a strike team, or making an investment in additional, flexible staff, to provide supplemental capacity where there is insufficient staff for the current demand. One organization accomplished this by hiring project managers with NEPA expertise into their CERPO Office. These Project Managers could then be detailed out to specific bureaus to fill capacity gaps and provide management for high priority, multi-agency projects. This helped fill immediate capacity gaps, as teams were continuing to hire.
Another agency piloted a relief brigade, or a pool of Headquarters (HQ) staff who could be detailed to support regional staffing needs on large projects, consultations, and backlogs with temporary funding. This team was formed from a national perspective and aimed to reduce the pressure on each region and center. Based on this organization’s needs, the team was composed of natural resource management and biological science generalists. Participants shared that some efficiencies have been gained, but there was a substantial learning curve that required training and learning on the job. One hiring manager stated, the “relief brigade is the permanent embodiment of what we need more of.” These types of teams can help address dynamic capacity needs and provide more flexibility to the organization more broadly.
Conduct Bottom Up Workforce Analysis
One Program Manager shared their experience joining a new team and conducting workforce analysis to quantify their staffing needs and inform strategic decisions for their organizational structure. In their initial discussions with staff, they learned that many employees were feeling overworked and capacity was a major concern. To understand the need, they conducted a bottom up workforce analysis to estimate the office’s workload and identify gaps. This involved gathering project data from the past two years, identifying the average time frame by activity type and NEPA category, the staff hours needed to accomplish the work, and the delta between existing and needed staff hours. This data provided evidence of capacity gaps, which they were able to bring to their senior leadership to advocate and secure approval for a team expansion. This analysis enabled them to make data informed decisions about hiring that would reduce the overall workload of staff and ultimately increase staff morale and improve retention rates, which had been a concern. This approach can serve as a model for other agencies who have had difficulty in workforce planning.
Reorganize Team to Drive Efficiencies
The Program Manager who conducted bottom-up workforce analysis applied this new understanding of the work and the demands to reorganize their team to drive efficiencies and share the workload. They established three branches in their team and added four supervisory roles. The branches included one NEPA Branch, one Archeological Branch, and a Program and Policy Branch, and a supervisor was established for each. An additional leadership Deputy role was created to focus on overseeing their programs and coordinating on integration points with relevant agencies.
With this shift, they created new processes and roles to support continuous improvements and fill outstanding duties. Specifically, the Program and Policy Branch is designed to be more proactive, support throughput, and build programmatic and tribal agreements. They added an environmental trainer who is responsible for educating both internal staff and external stakeholders. Two Environmental Protection Specialists now oversee project intake, collaborate with applicants to ensure the applications are complete, manage applicant communications, and then distribute the projects to the assigned owner. A GIS Program Manager was added to the team to support data and analytics. Their role is to identify process delays and their causes, analyze points of failure, and create a geological database to understand where there are project overlaps to expedite and streamline processes. In addition to these internal changes, the Program Manager has also brought on additional contractors to provide greater capacity.
These changes have significantly increased their team’s capacity and has over doubled the number of projects they are able to complete in a year, from 400 projects two years ago to over 900+ projects this year.
Reallocate Work Across Offices and Regions
Numerous participants described work reallocation as a solution to addressing some of their capacity gaps. For example, when one agency was struggling to hire people in a particular location due to the high cost of living, they redistributed the work to another region in the country, where the cost of living was lower. This made it easier to hire into the position. Another HR Leader described supporting their overcapacity teams by redistributing hiring efforts from one office to another in the same region. The original office had minimal bandwidth, while the other had capacity, so they were able to help post the job announcement for the region. They explained the importance of encouraging local offices to help one another deliver, when appropriate.
Others described the reallocation of staff and projects to different regions. This not only allows the organization to match staff with demand, but it also allows for staff to gain experience and knowledge working on a new topic or in a new region. For example, most offshore wind projects are located in the greater Atlantic region, but these projects are gaining traction in the Pacific, so they assigned staff to work in the Atlantic region with the goal of building experience and gaining lessons learned to apply to future Pacific projects. One of these participants emphasized the value and efficiencies that could be derived from developing staff to have more interagency and interservice experience. These examples highlight how leaders can be creative in addressing workload gaps by strategically reallocating work to pair capacity and demand.
Invest in Recruiting Networks
One agency stood out as being an exemplar for their recruiting efforts, which have the potential to be replicated across agencies. They have spent significant time and effort investing in building out their recruitment networks and engaging in career fairs to hire talent. Their organization has been building a repository of potential candidates that is maintained in a system to capture candidate information, educational background, contact information, locations of interest, areas of interest, and remote and relocation preferences. This has been used to generate a list of potential candidates for hiring managers.
They have made connections through affinity groups, communities of practice, and social media. They’ve also built many partnerships with schools and organizations and have a calendar of events (e.g., career fairs) that they attend over the course of the year. At some events, they’ll have their HR team facilitate breakout sessions to discuss the benefits of working at their organization. To make sure they’re getting diverse candidates, they are continuously reaching out to new sources and potential candidate pools.
In addition to engaging in others’ events, they have hosted their own career fair, where they hired about 200 people. Prior to the event, they reviewed and vetted resumes to know who might be a qualified candidate for a position. With Direct Hire Authority for some of their positions, this allowed hiring managers to interview candidates at the fair and immediately make temporary job offers to attendees. HR staff also worked with the hiring managers at the career fair. This infrastructure sets hiring managers up for success and enables them to easily tap into a variety of networks to find qualified candidates.
Invest in Hiring Manager Training
One agency’s training and support for hiring managers can serve as a model for other HR teams to learn from. This agency offers a robust toolkit for supporting hiring managers through the hiring process. While the Supervisor is ultimately responsible for the hiring, the HR team ensures that they have the tools needed to execute and are equipped to be successful. These tools include:
- Handouts on HR highlights to ensure key information is simple and clear;
- Videos on Recruitment, Relocation, and Retention Incentives and Direct Hire Authority, which are posted on their website for all employees to access;
- Annual talent acquisition workshops in-person and virtually to hear from speakers and discuss recruitment and marketing strategies; and
- A Train-the-Trainer program on how to have recruitment conversations.
In addition to these tools and training, HR Specialists work with hiring managers to coach them on how to determine the duties for their open position, especially if they need to re-announce a position multiple times. They are also developing a new marketing strategy centered on everyone being a recruiter. This strategy will result in a new resource to support all staff in recruiting and retaining staff based on their needs.
Another participant identified this as a key opportunity. “Agencies need to educate hiring managers on those processes and what’s out there and available to them… [hiring managers need to] utilize those tools and work with HR to get the best candidates.” This agency’s approach empowers hiring managers to navigate the process, leverage incentives, and successfully recruit.
Establish Apprenticeship Programs
One participant highlighted the need for apprenticeship programs in their permitting work. Short-term or summer internship programs present difficulties with early career staff because there is not enough time for the interns to learn. They explained that it takes about six months for a new employee to become independent. Given this need, they have invested in a 1-year internship program through GeoCorps America. This duration provides interns with the time needed to learn on-the-job through practice, understand the laws and regulations, and gain exposure to the work (e.g., problem solving and stakeholder communication). This program has been successful in creating a pipeline of early career talent; 12 of their interns have moved into permanent federal service positions at different agencies (i.e., DOI, USFS, USGS, and BLM). This type of apprenticeship program could serve as a model for developing early career talent that can be trained on the job and build expertise to take on more complex projects as they grow.
These strategies offer a few examples for how agencies could build workforce capacity. These strategies do not necessarily require bringing on new talent, but rather finding opportunities to improve their internal processes to drive efficiencies and build a more dynamic, flexible workforce to respond to new demand.
Other Considerations
At the end of our interviews, we asked participants if they had any tips or recommendations that they’d want to share with others looking to hire in the government. Here are a few things we heard that we have not already captured in our best practices or talent capacity strategies.
- Always Be Recruiting: Everyone is a recruiter, and you should always be building relationships and connections, being present at events even if you do not have any active job announcements.
- Maintain Communication with Candidates: Stay in touch with potential candidates before there is a job open, while recruiting, and throughout the entire hiring process. This can keep them engaged and help you ultimately receive a job acceptance.
- Invest in Suitability Case Management: Invest in a case management system that sends automatic notifications to each user (i.e., hiring manager, HR specialist, applicant, suitability team) when an action is required. This will streamline the process and ensure that no cases slip through the cracks.
- Cast a Wide Net: Invest in a wide distribution for your job announcements, interview as many qualified people as you can, and identify multiple candidates that you would like to hire, in case someone declines. Also, leave the announcement open for longer, and if you have large offices with continuous turnover, consider keeping a job open on USAJobs, where you can always accept resumes.
- Keep Certificate Lists Open: Keep certificate lists open for a long time, so if a candidate declines, you can return to the list of potential candidates. If it is a shared certificate, then this can also assist your colleagues in quickly finding qualified candidates to interview and hire.
- Regularly Update Position Descriptions: Update your position descriptions to accurately capture the duties of the role and to align with any updated technology. Many agencies have policies for how regularly position descriptions need to be updated, but many question how well these guidelines are followed.
- Listen to Your Staff’s Plans: Engage with your staff on a regular basis and pay attention to who says they may retire or leave in the next year. This will allow you to more proactively plan and predict your future staffing needs.
Hiring into the federal government is not easy – you will very likely experience challenges even if you follow the practices and strategies highlighted here. However, there are things you can do to set yourself up for success in the future and strategies you can use to address workload demands even if you are not currently hiring. This permitting hiring surge has offered an opportunity to learn how you can effectively hire people into the federal workforce, which can serve as an example for future talent surges. Within the permitting space itself, these strategies have proven successful in supporting more timely and efficient reviews. Bolstering workforce capacity has enabled more effective mission execution.