How Permitting Reform Can Unlock Clean Energy Development
“Permitting reform” may not pass many message tests as the most motivating rallying cry of the clean energy revolution. Despite that, stakeholders’ ability to responsibly site, build, and deploy critical clean energy infrastructure is absolutely necessary to meet the federal government’s climate goals, as well as important infrastructure and broadband targets.
As a critical step in creating a modern, robust permitting system that unlocks clean energy development, the White House Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) laid out its vision for reform via revised regulations that dictate how the government implements the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
FAS and our partners at the Environmental Policy Innovation Center (EPIC) and NEPAAccess weighed in on the proposed regulation with a call to consider how the policy change will manifest in technology that facilitates community engagement and interagency cooperation.
Put simply, we believe that any NEPA reforms should be conceived, developed, and deployed with the end users (federal agency staff, applicants, and other stakeholders) in mind. Regulators must prioritize how those reforms will manifest in requirements for the technology that will ultimately dictate how federal employees and constituents engage with the process.
Given both the pace of climate change and the long-standing challenges linked to federal permitting, we see technology and data as essential to achieving climate goals. Effective and well-designed IT systems can only be built with input from strong technical teams, and our recommendations reflect how CEQ can leverage and amplify leading practices with talent and new technology. To this end, we offered six interrelated recommendations for building effective technology:
- Follow Human Centered Design (HCD) processes.
- Centralize access to NEPA documents and ensure that a user-friendly platform is available to facilitate public engagement.
- Pilot interagency programs to coordinate permitting data for existing and future needs.
- Prioritize digital applications with easy-to-use forms.
- Bolster the use of decision support tools.
- Utilize e-NEPA to improve deadline tracking.
These recommendations are anchored in tenets of successful technology delivery from across sectors and federal agencies and embrace user-centered, agile approaches to delivering on customer needs.
If you doubt that permitting is a major way the federal government interfaces with the general public, our organizations’ joint public comment was one of the approximately 82,000+ that CEQ received in response to the proposed rule change. Leveraging ChatGPT, EPIC analyzed these comments and found that very few of them focused on technology as a conduit for change. According to ChatGPT:
“These comments relate to technology insofar as they prioritize the need for a rapid transition to clean energy, which could involve the development of new technologies and infrastructure projects. The inclusion of future climate impacts and consideration of natural sustainable energy in project proposals also relate to the potential role of technology in mitigating climate change impacts. They also emphasize the importance of considering future climate impacts when evaluating new projects, as well as the need for transparency and community involvement in the project development process which can be facilitated through technological tools and platforms. [emphasis added] Lastly, the comments highlight the importance of environmental justice and respecting tribal sovereignty throughout the project development process.”
The public comment period represents only the beginning of a long path towards implementing the reformed policy and technology that will empower communities to deploy clean energy, broadband, and other critical infrastructure while protecting environmental quality and human health. CEQ’s proposed “Bipartisan Permitting Reform Implementation Rule” should center users and tech implementers’ seats at the table with those writing policy. With these reforms, the federal government can build adaptive, resilient permitting systems that will help us meet our climate goals.
We need to address the housing supply crisis
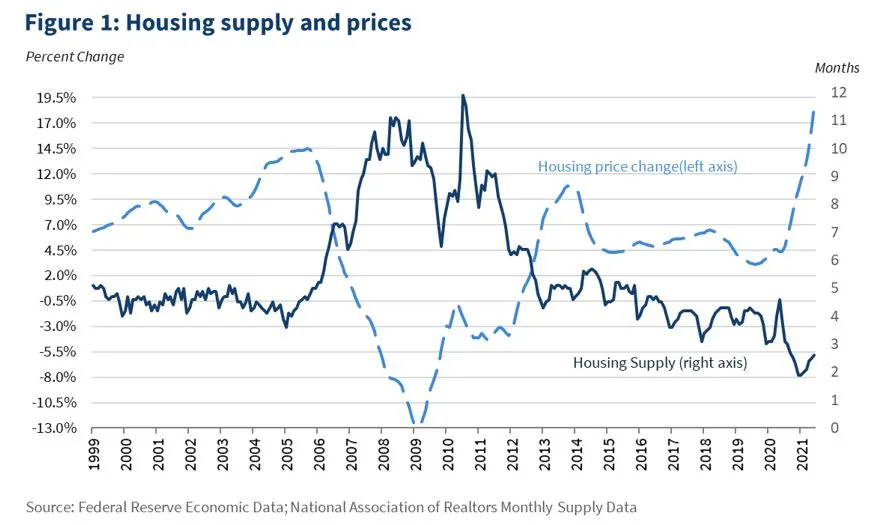
Housing costs have ballooned, far outpacing the broader cost of living in the U.S. Renters devote more and more of their already limited budget to housing costs and home ownership feels out of reach for many Americans. One key reason for this is the dwindling housing supply across the US.
Addressing the housing crisis is a bipartisan issue. Officials at all levels of government want to ensure that the communities and families they represent have a chance to feel secure in their own home and future. FAS launched our housing policy challenge to uplift ideas that can tackle the crisis and boost housing supply across the country.
The causes of the housing supply crisis are many. Local regulations against density are the main barrier, but there are a host of other important factors. To list a few:
- the difficulties of constructing and organizing public transit systems,
- incentive misalignment for project developers,
- a scarcity of available land in urban areas,
- underfunding of public housing resources,
- lack of access to financing options,
- supply being snatched up by large institutional investors,
- a lack of support for novel arrangements like ADUs and manufactured homes,
- the persistent effects of redlining, and many more.
These challenges to home supply are some of the areas where creative policy thinking could have a meaningful impact. We think the federal government is poised to do more on this issue, and that bipartisan agreement is possible across a range of housing policies. We’re turning to YOU—experts, non-experts, home owners, renters, and neighbors to crowdsource ideas for boosting housing supply.
Creative thinking to boost housing supply
We highlighted the main areas we’re interested in for this challenge but ultimately we’re relying on you to get creative. If you think a given overlooked policy lever could have an impact on housing supply we want to hear about it.
Here are some areas we are excited and motivated by, and there’s always more to discuss.
Construction Innovation
Construction innovation has gotten more attention in recent years. While such innovation only matters if you can build more housing in the first place, construction efficiencies will only grow in importance. Brian Potter of the Institute for Progress writes about the overlooked roles of modular housing, the rise and fall of the mail order home, and building components. Novel ideas on how best to alter restrictive building codes will also be important. The Center for Building in North America has been doing much original work on this subject.
The limited rise of Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) is promising, but it seems like more remains to be done to promote familiarity with the opportunity they provide. Are there ways to incentivize folks across urban areas to take advantage of ADUs?
Financing Innovation
Federal financing is another area where creative arrangements, properly designed and communicated, could massively help everyday people. The White House already sought to make Construction to Permanent loans more widely available. Efforts to reform the Low Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) and improve the housing enterprises’ ‘Duty to Serve’ underserved mortgage markets are underway. What other financing needs can be met at the federal level?
Public Land Innovation
The scarcity of available land, especially in urban areas, seems like an insurmountable barrier. However, a closer accounting of public lands and facilities can reveal opportunities and assets that cities may not have realized they could take advantage of to do things like build housing or transit. The Putting Assets to Work initiative is helping cities better account for the value of their physical assets. How can we incentivize locales to assess and use their assets most efficiently?
Effective Measurement
What gets measured gets done. Ways to improve or introduce new federal data resources to measure the housing crisis are critical. There’s a wide range of datasets available from FHFA, Census Bureau, the Federal Reserve, HUD, and more agencies. Organizations like the National Low-Income Housing Center also provide key information . But are there key things like home loss rate that we’re not fully tracking?
Finally, what incentives to boost home supply are we not thinking about in any form right now? We are not looking for the federal government to get directly involved in local zoning issues; instead we want to hear about other productive paths you can help us identify to increase the national housing supply.
To submit an idea, head over to our challenge page.
Cultural Burning: How Age-Old Practices Are Reshaping Wildfire Policy
The Wildland Fire Mitigation and Management Commission called for input from diverse stakeholders and FAS, along with partners Conservation X Labs (CXL), COMPASS, and the California Council on Science and Technology (CCST), answered the call.
Recruiting participants from academia, the private sector, national labs, and other nonprofits, the Wildland Fire Policy Accelerator produced 24 ideas for improving the way the country lives with wildland fire.
‘Cultural Burning’ is a phrase that is cropping up more and more in wildland fire policy discussions, but it’s still not widely understood or even consistently defined.
Liam Torpy of Conservation X Labs sat down with FAS to discuss why ‘cultural burning’ is garnering more attention in the world of wildfire mitigation and management.
FAS: Liam – thanks for joining us. To start, just give us a quick introduction to Conservation X Labs and its mission.
LT: The founders of Conservation X Labs [Paul Bunje and Alex Dehgan] wanted to create a conservation technology organization that, you know, isn’t just doing the same traditional conservation methods of protected areas and command and control. CXL wants to find innovative solutions to these problems that can harness market forces or that develop new technologies that will allow for breakthroughs–because the problems have been increasing exponentially in the conservation field, but the solutions haven’t kept pace. We’re not, in a lot of these critical ecosystems like in the American West with wildfire, or the Amazon, were simply not doing enough. And the problem is getting worse as global forces, like climate change, worsen the problem.
FAS: CXL has been convening what you call “Little Think” events – roundtable discussions aimed at surfacing new ideas in the area of wildfire management – when you decided to partner with FAS on this Wildland Fire Policy Accelerator. Cultural burning became one of the big areas of focus for the recommendations coming out of this process. Some people may be familiar with the idea of “prescribed burning” – using fire to reduce the risk of uncontrolled megafires down the road – but ‘cultural burning’ is something quite different. Can you explain what’s different and why it’s important?
LT: You can read a lot of reports, or see some statutes on the books, legally, that will oftentimes not reference cultural burning at all. Some do – but it’s kind of a footnote that’s put under ‘prescribed burning’ – many publications treat it the same way. But prescribed burning, which can have real ecological benefits, is often only measured by the government using acreage: how much land can we burn?
With cultural burning, there’s not a single definition, because each Tribe has their own version of it. But it’s often to cultivate natural resources or encourage new growth of a particularly important plant. So it’s much more targeted than prescribed burning – it’s suited to the land and the resources a Tribe has. It’s deeply rooted in place-based knowledge.
It’s also a very important method of intergenerational knowledge transfer as well. [Cultural fire practitioners] say sometimes that ‘when you burn together and you learn together’. It’s a way to teach the rest of your group of what resources there are, how to steward them, and how everybody is coming together to manage the land and take care of it.
FAS: So why is there a tension between traditional federal and state fire management methods and cultural burning?
A lot of people I think don’t really recognize this: you think that because a lot of Tribes have reservations, or Tribal trust land or some of their own free land, they can just go and burn as they wish. But the people on the ground that we’ve talked to, including some participants in this accelerator, say Tribal trust land is some of the hardest land to burn on. It’s pretty much considered federal land, administered by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). That means pretty much every time you want to burn on the land, you have to have a burn plan and submit that to the BIA, which is generally very understaffed. Only one person may be looking over those documents. Then a BIA ‘burn boss’ is considered the only person qualified to actually lead the burn – and that is already kind of infringing on the sovereignty of the tribe itself: having their own burn led by this outsider within the federal government. And oftentimes you have to go through a NEPA (National Environmental Policy Act) permitting process which is a very long and expensive process that requires public comments. There are local air districts that regulate smoke. Then you have to have an approved burn window where they say, okay, the conditions are good. And that often happens very rarely. And so a lot of tribes don’t even attempt to go through this whole process. It’s simply too much administrative burden on them.
FAS: And it’s not just the administrative burden, right? There seems to be some real hesitancy to allowing more cultural burning from the agencies who manage this land, and from communities nearby. Why is that?
LT: The public is often skeptical of both prescribed and cultural burning. They’re scared of fire because of all the megafires. So it’s can be hard to get the public support sometimes. And because of that a lot of these federal agencies that by their nature are very risk averse. They’re unwilling to move forward with some of these plans that can be perceived as risky when it’s easier just to do nothing. Their approach is just when a fire comes through, try to fight it. Say you did the best you could even though it burns down half the forest and becomes a high severity fire.
FAS: Tell us about the Accelerator participants you worked with.
LT: We talked with Nina Fontana, Chris Adlam, Ray Guttierez, and then [FAS’] Jessica Blackband worked with Kyle Trefny and Ryan Reed. Ryan and Ray are both members of Tribes, and the others non-Indigenous, but working in that sphere and trying to support cultural fire. These are already busy people, trying to kind of reestablish some of these traditions and fighting against these institutional barriers. Their first priority may not be to fly out to Washington to talk with federal policymakers or sit down at their computer and develop and research these recommendations. But they have a really deep on-the-ground perspective that a lot of people in Washington that don’t have, and that a lot of people the Commission don’t have.
FAS: Can you give us an example of what kinds of recommendations emerged from the process?
LT: One thing that’s important to understand is that these recommendations are not the be all and end all of this issue. These are steps – often the most basic steps we can take to start to give cultural fire the respect and the place it deserves with fire management. Fire has been functionally banned from the land for over a century – over a century of extreme fire suppression tactics in the American West. A lot of these tribes that previously had been burning for centuries, or sometimes even millennia, weren’t allowed to continue that cycle. It was illegal – it was criminalized. And so that knowledge is just lost. And so some tribes are seeking to regain that knowledge.
There’s a Tribal Ranger Program recommended by Chris Adlam – which is modeled after Canada and Australia – creating permanent long term opportunities for Tribal members to exercise their traditions, to put fire on the land to build up that intergenerational knowledge. These would not be just short-term, one-summer, internship opportunities, but real employment opportunities that allow them to put fire on the land.
Another important recommendation, from Raymond Guttierez, is establishing a federal definition of ‘cultural fire’ and ‘cultural fire practitioner’. Right now, there’s not even really a legally recognized definition for the very practice itself – only for prescribed burning. And it wouldn’t just be one definition, it’d be regionally specific. And Tribes would help develop that in each area.
FAS: What part of the process was most rewarding for you, personally?
LT: I think one of the things that was rewarding is that these participants, in the beginning, were a little skeptical that what they had to say would actually be important, or would be more useful than the information that decision makers in Washington already had at their disposal. But they really did have a lot to say and a lot to contribute to this national conversation. And so I think it was really cool to see just how, by the end, they got validation that they have really useful information and experience that needs to be heard by people in power.
FAS: The Biden Administration has made a point of incorporating Indigenous knowledge into federal decision-making. But guidance from the Executive Branch is one thing – real impact on the ground is another. Do you think Indigenous practices, like cultural burning, are actually gaining support in the communities affected by wildfire?
LT: I think there’s also a broader movement within our society focused on diversity and equity and inclusion. Looking at the historical injustices that Tribes have faced, and trying to give them compensation when they do participate in these processes, and give their input and share their traditional knowledge – we need to make sure we are adequately valuing that. And so I think that’s also another element that’s giving this a boost. Hopefully, we see more and more people in power incorporating these ideas. And really, it’s not just about them incorporating the ideas – it’s about allowing Tribes to lead this movement, and to lead these burns. Some of it is just getting out of their way. Some of it is giving them more of a platform. But what we don’t want is just for the system in place to kind of co-opt the Tribal practices and leave the cultural fire practitioners in the dust.
But I also think having the White House make that statement about Indigenous knowledge is really significant. By getting encouragement from the top that [agencies] should look into cultural burning, or look into place-based knowledge and traditional ecological management, that kind of gives them more of a push to go and form these partnerships. And I think there’s been, there’s more and more attention on these issues. As we look at the wildland fire crisis right now, it’s going out of control. The amount of money that we’re spending on it – asking questions about whatever we’ve been doing for the last century or so is warranted. Before that century of suppression, tribes were getting more fire on the ground. People are looking at this more and more, trying to learn, and giving it the respect that it really deserves, and the attention that it deserves.
Environmental Assessment Reveals New Details About the Air Force’s ICBM Replacement Plan
Any time a US federal agency proposes a major action that “has the potential to cause significant effects on the natural or human environment,” they must complete an Environmental Impact Statement, or EIS. An EIS typically addresses potential disruptions to water supplies, transportation, socioeconomics, geology, air quality, and other factors in great detail––meaning that one can usually learn a lot about the scale and scope of a federal program by examining its Environmental Impact Statement.
What does all this have to do with nuclear weapons, you ask?
Well, given that the Air Force’s current plan to modernize its intercontinental ballistic missile force involves upgrading hundreds of underground and aboveground facilities, it appears that these actions have been deemed sufficiently “disruptive” to trigger the production of an EIS.
To that end, the Air Force recently issued a Notice of Intent to begin the EIS process for its Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD) program––the official name of the ICBM replacement program. Usually, this notice is coupled with the announcement of open public hearings, where locals can register questions or complaints with the scope of the program. These hearings can be influential; in the early 1980s, tremendous public opposition during the EIS hearings in Nevada and Utah ultimately contributed to the cancellation of the mobile MX missile concept. Unfortunately, in-person EIS hearings for the GBSD have been cancelled due to the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic; however, they’ve been replaced with something that might be even better.
The Air Force has substituted its in-person meetings for an uncharacteristically helpful and well-designed website––gbsdeis.com––where people can go to submit comments for EIS consideration (before November 13th!). But aside from the website being just a place for civic engagement and cute animal photos, it is also a wonderful repository for juicy––and sometimes new––details about the GBSD program itself.
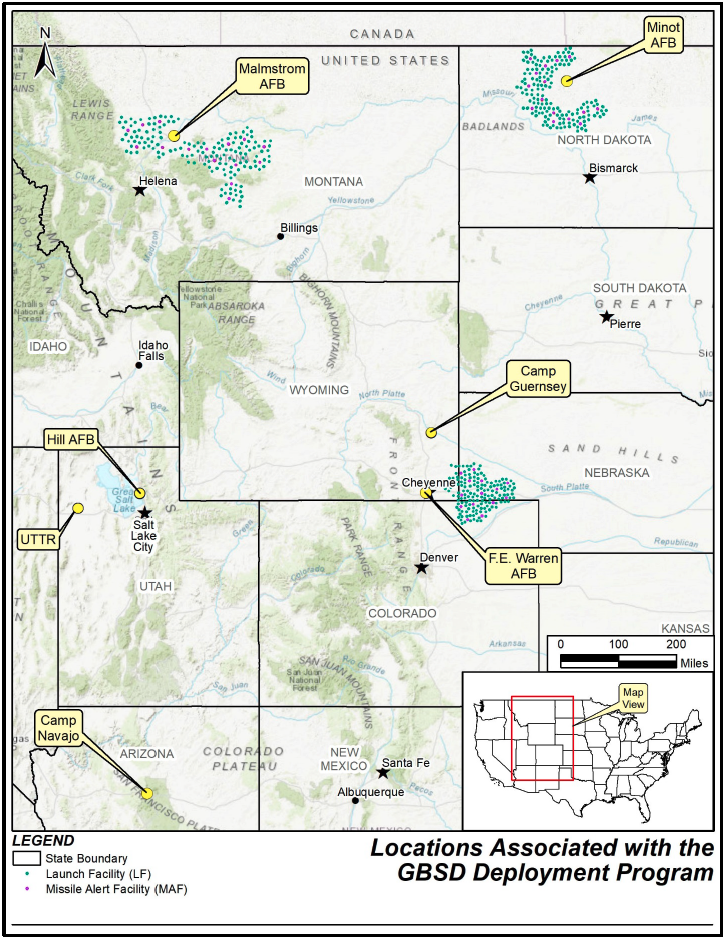
The website includes detailed overviews of the GBSD-related work that will take place at the three deployment bases––F.E. Warren (located in Wyoming, but responsible for silos in Wyoming, Colorado, and Nebraska), Malmstrom (Montana), and Minot (North Dakota)––plus Hill Air Force Base in Utah (where maintenance and sustainment operations will take place), the Utah Test and Training Range (where missile storage, decommissioning, and disposal activities will take place), Camp Navajo in Arizona (where rocket boosters and motors will be stored), and Camp Guernsey in Wyoming (where additional training operations will take place).
Taking a closer look at these overviews offers some expanded details about where, when, and for how long GBSD-related construction will be taking place at each location.
For example, previous reporting seemed to indicate that all 450 Minuteman Launch Facilities (which contain the silos themselves) and “up to 45” Missile Alert Facilities (each of which consists of a buried and hardened Launch Control Center and associated above- or below-ground support buildings) would need to be upgraded to accommodate the GBSD. However, the GBSD EIS documents now seem to indicate that while all 450 Launch Facilities will be upgraded as expected, only eight of the 15 Missile Alert Facilities (MAF) per missile field would be “made like new,” while the remainder would be “dismantled and the real property would be disposed of.”
Currently, each Missile Alert Facility is responsible for a group of 10 Launch Facilities; however, the decision to only upgrade eight MAFs per wing––while dismantling the rest––could indicate that each MAF could be responsible for up to 18 or 19 separate Launch Facilities once GBSD becomes operational. If this is true, then this near-doubling of each MAF’s responsibilities could have implications for the future vulnerability of the ICBM force’s command and control systems.
The GBSD EIS website also offers a prospective construction timeline for these proposed upgrades. The website notes that it will take seven months to modernize each Launch Facility, and 12 months to modernize each Missile Alert Facility. Once construction begins, which could be as early as 2023, the Air Force has a very tight schedule in order to fully deploy the GBSD by 2036: they have to finish converting one Launch Facility per week for nine years. It is expected that construction and deployment will begin at F.E. Warren between 2023 and 2031, followed by Malmstrom between 2025 and 2033, and finally Minot between 2027 and 2036.
Although it is still unclear exactly what the new Missile Alert Facilities and Launch Facilities will look like, the EIS documents helpfully offer some glimpses of the GBSD-related construction that will take place at each of the three Air Force bases over the coming years.
In addition to the temporary workforce housing camps and construction staging areas that will be established for each missile wing, each base is expected to receive several new training, storage, and maintenance facilities. With a single exception––the construction of a new reentry system and reentry vehicle maintenance facility at Minot––all of the new facilities will be built outside of the existing Weapons Storage Areas, likely because these areas are expected to be replaced as well. As we reported in September, construction has already begun at F.E. Warren on a new underground Weapons Generation Facility to replace the existing Weapons Storage Area, and it is expected that similar upgrades are planned for the other ICBM bases.
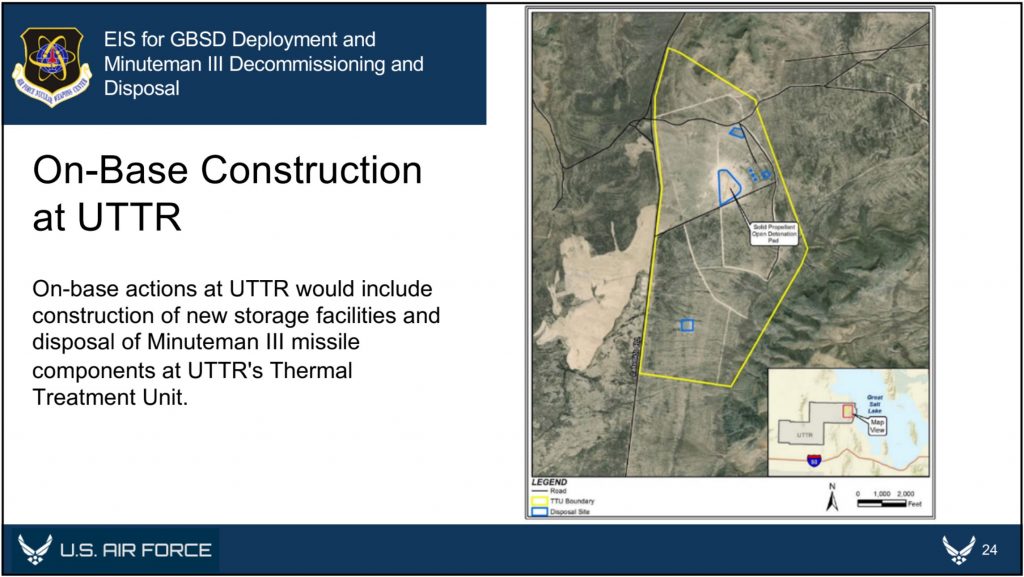
Finally, the EIS documents also provide an overview of how and where Minuteman III disposal activities will take place. Upon removal from their silos, the Minutemen IIIs will be transported to their respective hosting bases––F.E. Warren, Malmstrom, or Minot––for temporary storage. They will then be transported to Hill Air Force Base, the Utah Test and Training Range (UTTR), or Camp Najavo, in Arizona. It is expected that the majority of the rocket motors will be stored at either Hill AFB or UTTR until their eventual destruction at UTTR, while non-motor components will be demilitarized and disposed of at Hill AFB. To that end, five new storage igloos and 11 new storage igloos will be constructed at Hill AFB and UTTR, respectively. If any rocket motors are stored at Camp Navajo, they will utilize existing storage facilities.
After the completion of public scoping on November 13th (during which anyone can submit comments to the Air Force via Google Form), the next public milestone for the GBSD’s EIS process will occur in spring 2022, when the Air Force will solicit public comments for their Draft EIS. When that draft is released, we should learn even more about the GBSD program, and particularly about how it impacts––and is impacted by––the surrounding environment. These particular aspects of the program are growing in significance, as it is becoming increasingly clear that the US nuclear deterrent––and particularly the ICBM fleet deployed across the Midwest––is uniquely vulnerable to climate catastrophe. Given that the GBSD program is expected to cost nearly $264 billion through 2075, Congress should reconsider whether it is an appropriate use of public funds to recapitalize on elements of the US nuclear arsenal that could ultimately be rendered ineffective by climate change.
Additional background information:
- United States nuclear forces, 2020
-
Construction of New Underground Nuclear Warhead Facility At Warren AFB
This publication was made possible by generous contributions from the Carnegie Corporation of New York, the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the New Land Foundation, the Ploughshares Fund, and the Prospect Hill Foundation. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
Image sources: Air Force Global Strike Command. 2020. “Environmental Impact Statement for the Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent Deployment and Minuteman III Decommissioning and Disposal: Public Scoping Materials.”
Trump Admin Would Curtail Carbon Capture Research
The Trump Administration budget request for FY 2018 would “severely reduce” Energy Department funding for development of carbon capture and sequestration technologies intended to combat the climate change effects of burning fossil fuels.
The United States has “more than 250 years’ worth of clean, beautiful coal,” President Trump said last month, implying that remedial measures to diminish the environmental impact of coal power generation are unnecessary.
Research on the carbon capture technology that could make coal use cleaner by removing carbon dioxide from power plant exhaust would be cut by 73% if the Trump Administration has its way.
“The Trump Administration’s approach would be a reversal of Obama Administration and George W. Bush Administration DOE policies, which supported large carbon-capture demonstration projects and large injection and sequestration demonstration projects,” the Congressional Research Service said this week in a new report.
“We have finally ended the war on coal,” President Trump declared.
However, congressional approval of the Administration’s proposal to slash carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) development is not a foregone conclusion.
“The House Appropriations Committee’s FY2018 bill funding DOE disagrees with the Administration budget request and would fund CCS activities at roughly FY2017 levels,” the CRS report said.
“This report provides a summary and analysis of the current state of CCS in the United States.” It also includes a primer on how CCS could work, and a profile of previous funding in this area. See Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) in the United States, July 24, 2017.
Other new and updated reports from the Congressional Research Service include the following.
Methane and Other Air Pollution Issues in Natural Gas Systems, updated July 27, 2017
The U.S. Export Control System and the Export Control Reform Initiative, updated July 24, 2017
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS): OECD Tax Proposals, July 24, 2017
Oman: Reform, Security, and U.S. Policy, updated July 25, 2017
Lebanon, updated July 25, 2017
Aviation Bills Take Flight, but Legislative Path Remains Unclear, CRS Insight, July 25, 2017
Military Officers, CRS In Focus, July 3, 2017
Military Enlisted Personnel, CRS In Focus, July 3, 2017
Transgender Servicemembers: Policy Shifts and Considerations for Congress, CRS Insight, July 26, 2017
Systematic, authorized publication of CRS reports on a government website came a step closer to reality yesterday when the Senate Appropriations Committee voted to approve “a provision that will make non-confidential CRS reports available to the public via the Government Publishing Office’s website.”
Rising Sea Levels and U.S. Coasts, & More from CRS
“With few exceptions, sea levels are rising relative to the coastlines of the contiguous United States, as well as parts of the Alaskan and Hawaiian coastlines,” a new report from the Congressional Research Service observes.
“Although the extent of future sea-level rise remains uncertain, sea-level rise is anticipated to have a range of effects on U.S. coasts. It is anticipated to contribute to flood and erosion hazards, permanent or temporary land inundation, saltwater intrusion into coastal freshwaters, and changes in coastal terrestrial and estuarine ecosystems.”
The new CRS report reviews the policy choices that Congress could make to meet the challenges posed by rising sea levels. See Sea-Level Rise and U.S. Coasts: Science and Policy Considerations, September 12, 2016.
Other new and updated reports from the Congressional Research Service include the following.
Dakota Access Pipeline: Siting Controversy, CRS Insight, September 9, 2016
Paris Agreement: United States, China Move to Become Parties to Climate Change Treaty, CRS Insight, September 12, 2016
The Microsoft Ireland Decision: U.S. Appeals Court Rules that ECPA Does Not Require Internet Service Providers To Produce Electronic Communications Stored Overseas, CRS Legal Sidebar, September 12, 2016
The Financial CHOICE Act: Policy Issues, September 12, 2016
Domestic Content Restrictions: The Buy American Act and Complementary Provisions of Federal Law, updated September 12, 2016
House of Representatives v. Burwell and Congressional Standing to Sue, September 12, 2016
Military Retirement: Background and Recent Developments, updated September 12, 2016
Environmental Considerations in Military Operations
The environmental impacts of military operations are increasingly becoming factors in the planning and execution of military activities.
“The military has a new appreciation for the interdependence between military missions, the global community, and the environment,” according to a newly revised and reissued Army doctrinal manual. See Environmental Considerations, ATP 3-34.5, August 10, 2015.
Of course, military operations by their nature are not environment-friendly. “The primary mission of the military is to fight and win wars. Warfare is destructive to humans and to the natural environment.”
Even so, environmental impacts of military action can be limited and managed up to a point, the Army manual says. “Integrating environmental considerations into the planning process helps to identify, prevent, and mitigate potential threats to the environment (including those that affect historical and cultural resources) and environmental threats to personnel.”
This is not a matter of sentimentality or political correctness, the manual emphasizes, but of military self-interest and tactical necessity. “Integrating environmental considerations into operations will benefit FHP [force health protection, i.e. the health of U.S. and allied soldiers]. Environmental degradation jeopardizes the well-being of the local population and can undermine HN [host nation] support for U.S. policies.”
“Environmental damage created by U.S. forces conducting operations, however unintentional (such as the damage to Babylon), may be used as a weapon in the public information campaign against U.S. operations and can undermine U.S. strategic objectives,” the manual says.
Establishment of a U.S. military base in Iraq’s historic city of Babylon in 2003 caused “major damage” to surviving antiquities at the site, the Washington Post and other news organizations reported.