A Carbon Tax to Combat Climate Change and Support Low-Income Households
Summary
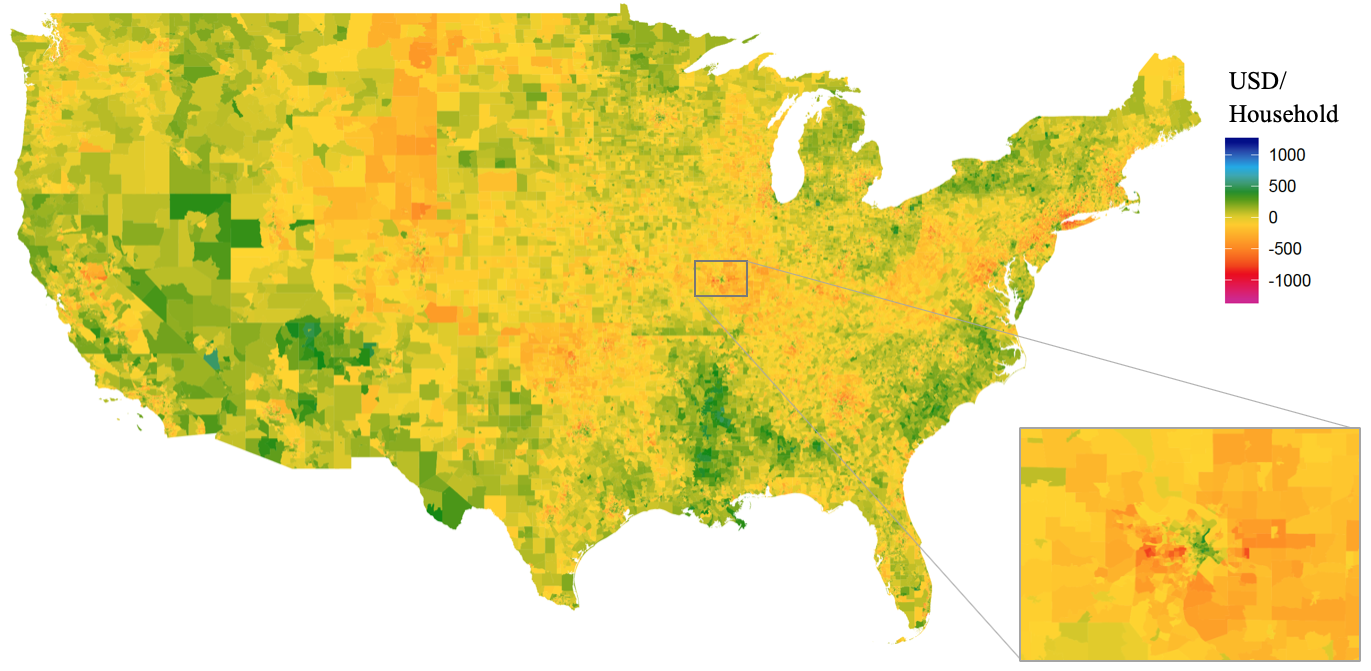
Putting a price on carbon is fundamental to achieving U.S. climate goals for 2050. Many options for carbon price-setting exist, and in this policy brief we propose a tax-and-dividend approach that mitigates the challenging impacts that carbon policies have on poor and suburban/rural communities, particularly those in Middle America. Such a plan will be a net gain for low-income households, in contrast to other proposed climate change policies which will adversely affect the poor. Furthermore, it has been shown that even a modest carbon tax can have large benefits in terms of cost-effectiveness.
For that reason, we propose the following:
- Introduce a carbon tax-and-dividend plan as part of any federal climate policy.
- Use revenue to offset impacts on low-income households, taking into account enormousregional disparities.
- If political dynamics favor regulatory standards, consider coupling such standards with amodest carbon tax whose revenue can be used to offset their regressive effects.
FAS is launching the Center for Regulatory Ingenuity (CRI) to build a new, transpartisan vision of government that works – that has the capacity to achieve ambitious goals while adeptly responding to people’s basic needs.
This runs counter to public opinion: 4 in 5 of all Americans, across party lines, want to see the government take stronger climate action.
Cities need to rapidly become compact, efficient, electrified, and nature‑rich urban ecosystems where we take better care of each other and avoid locking in more sprawl and fossil‑fuel dependence.
Hurricanes cause around 24 deaths per storm – but the longer-term consequences kill thousands more. With extreme weather events becoming ever-more common, there is a national and moral imperative to rethink not just who responds to disasters, but for how long and to what end.