Administration Increases Submarine Nuclear Warhead Production Plan
 |
|
The slim Mk4A reentry body for the W76-1 warhead. The administration plans to produce 2,000 between 2007 and 2021. |
By Hans M. Kristensen
The Bush administration has decided to more than double the number of nuclear warheads undergoing an expensive upgrade for potential future deployment on the Navy’s 14 ballistic missile submarines, according to answers provided by the National Nuclear Security Administration in response to questions from the Federation of American Scientists.
The decision preempts a debate in Congress about how the United States should size its future nuclear weapons arsenal.
The upgrade concerns the W76, the most numerous warhead in the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile. The Clinton administration decided to upgrade 25 percent, but the Bush administration’s Nuclear Posture Review (NPR) in 2001 recommended that significantly more warheads had to be upgraded. An assessment completed by the Department of Defense in 2005 increased the plan to 63 percent of the W76 stockpile, corresponding to an estimated 2,000 warheads.
More than just a refurbished weapon, official sources indicate, the new weapon will have significantly increased military capabilities against hard targets.
Expansion of the W76 Life Extension Program
The W76 Life Extension Program (LEP) was initially approved in March 2000, when the Nuclear Weapons Council approved life-extension of approximately 800 W76s (Block 1). The decision whether to proceed with Block 2 and how many W76s to life-extend in total was deferred. Block 1 completion was initially set for 2012, but in subsequent DOE budget requests the W76 LEP completion date gradually began to slide: 2013 in the FY 2005 request; 2017 in the FY 2006 request; 2020 in the FY 2007 budget request; and most recently 2021 in the FY 2008 request. It was this slide that in May prompted FAS to submit questions to the National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA).
The NNSA letter explains that DOD requirements before 2001 called for 25 percent of the W76 stockpile to be life-extended, or approximately 800 of the roughly 3,200 W76 warheads estimated to be in the stockpile at the time. But the Bush administration’s 2001 Nuclear Posture Review “resulted in plans to refurbish a significantly greater quantity.” The NPR was implemented by the March 2003 Nuclear Posture Review Implementation Plan, a 26-page document that instructed government agencies which parts of the NPR they must implement and when. Finally, the “most recent classified [W76 LEP]Selected Acquisition Report estimate is for a planned refurbishment of 63 percent of the stockpile,” according to NNSA.
|
|
 |
|
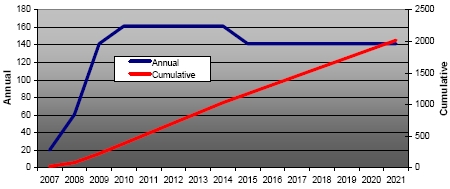
The Bush administration’s plan to life-extend 63 percent of the W76 stockpile requires production of approximately 2,000 W76-1 warheads between 2007 and 2021. Authorization to produce the Reliable Replacement Warhead (RRW) from 2014 could affect the second half of the plan. |
The 63 percent requirement (roughly 2,000 warheads) contained in the 2007 W76 LEP Selected Acquisition Report was set, the NNSA letter reveals, by the Strategic Capabilities Assessment, a review completed in 2005 in preparation for the Quadrennial Defense Review by the DOD of the assumptions used for the 2001 NPR. The DOD Assessment concluded that “the NPR’s planning assumptions remain valid, although conditions are trending toward − if anything − a more stressing strategic landscape, for example, with respect to North Korea, Iran and nuclear proliferation.”
The W76-1/Mk4A
Approximately 3,250 W76 warheads were produced between 1978 and 1988. The weapons armed the Poseidon C3 and Trident I C4 and currently the Trident II D5 missiles (together with about 400 W88 warheads). A modified W76 also arms Trident II missiles on British submarines. With the service life limit of the oldest units approaching, the Clinton administration in the late 1990s ordered a W76 Life Extension Program (LEP) to extend the service life for another 30 years. Major milestones for the program are:
|
|
|
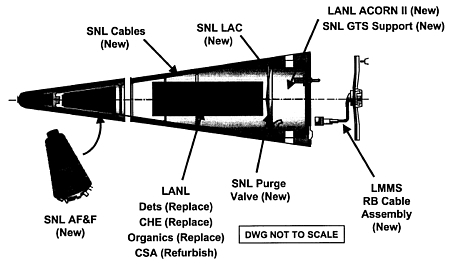
The W76 LEP creates a modified warhead called the W76-1. The cone-shaped Mk4 reentry body designed to protect the warhead against the heat created by the fiery reentry through the earth’s atmosphere will also be modified; the new reentry body is called the Mk4A. The W76 LEP is a major overhaul of the warhead that involves changes to both the reentry body and the warhead package: Replacing “organics” in the primary; replacing detonators; replacing chemical high explosives; refurbishing the secondary; adding a new Arming, Fuzing & Firing (AF&F) system, a new gas reservoir, a new gas transfer support system, a new lightning arrestor connector (LAC) (see Sandia National Laboratories drawing below).
|
|
 |
|
The W76 LEP includes significant changes to the both the W76 warhead and the Mk4A reentry body. Guide: AF&F, Arming, Fuzing & Firing; CHE, Chemical High Explosives; CSA, Canned Secondary Assembly; Dets, detonators; GTS, Gas Transfer System; LAC, Lightning Arrestor Connector; LANL, Los Alamos National Laboratory; LMMS, Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space; SNL, Sandia National Laboratories. |
Boosting Hard Target Kill Capability
Government documents and statements by government officials hint that the W76 LEP is quietly creating a weapon with significantly improved military capability over the old version. Whereas the old fuze only permitted targeting of soft targets, the new MC4700 Arming, Fuzing and Firing (AF&F) system gives the W76 hard target kill capability for the first time. The former head of the navy’s Strategic Systems Program, Rear Admiral George P. Nanos, who later became the Director of Los Alamos National Laboratory which designed the W76, explained in an article in The Submarine Review in April 1997 that the “capability for the [existing] Mk4…is not very impressive by today’s standards, largely because the Mk4 was never given a fuze that made it capable of placing the burst at the right height to hold other than urban industrial targets at risk.” But “with the accuracy of D5 and Mk4, just by changing the fuse in the Mk4 re-entry body, you get a significant improvement,” Nanos stated. In fact, “the Mk4, with a modified fuze and Trident II accuracy, can meet the original D5 hard target requirement.”
|
|
 |
|
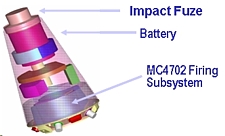
The new MC4700 Arming, Fuzing and Firing system developed for the W76-1/Mk4A will enable the warhead to take advantage of the accuracy of the Trident II D5 missile to “meet the original D5 hard target requirement.” |
The added capability is normally not highlighted in official presentations of the W76 LEP. Yet the purpose of developing a new AF&F system on the W76-1/Mk4A, according to the Department of Energy’s 1997 Stockpile Stewardship and Management Plan (excerpt), is to “enable [the] W76 to take advantage of [the] higher accuracy of the D5 missile.”
There are two reasons for increasing the accuracy. First, the previous hard target kill missile – the Peacekeeper ICBM – was withdrawn from operational service in 2005, and the modernized Minuteman III apparently has not been able to achieve the same degree of accuracy. Second, as the number of weapons in the nation’s arsenal is reduced, the ones remaining must be more flexible and capable of holding a wider range of targets than before.
With “advanced fuzing options” the AF&F system will allowing targeteers to set the Height of Burst (HOB) more accurately and significantly improve the ability to hold hard targets at risk. Because 63 percent of the W76 stockpile is being added the new fuze, if Admiral Nanos is correct, the U.S. inventory of reentry vehicles with hard target kill capability will increase from 400 today to 2,400 in 2021.
Sizing the Arsenal
The disclosure of the 63 percent number adds new information about how the administration envisions the structure of the future nuclear arsenal. Under the SORT agreement signed with Russia in 2002, no more than 2,200 strategic warheads may be operationally deployed by 2012. Yet the total stockpile will be significantly larger, about two and a half times, and include an estimated 5,467 warheads.
|
|
 |
|
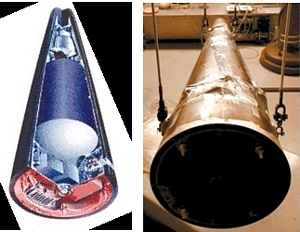
The government has only recently begun to show pictures of the W76 reentry vehicle. Los Alamos National Laboratory has published a drawing of a W76 interior layout (left), and Sandia National Laboratories has published photographs of the Mk4A reentry body (right). |
Under SORT, the Navy plans to deploy up to an estimated 1,150 warheads on 12 ballistic missile submarines (an average of four warheads per missile). Another two submarines will normally be in overhaul. Approximately 750 of the warheads will be W76-1 with the balance made up by the more powerful W88 warheads. Because SORT doesn’t set limits on reserve warheads or regulate how Russia and the United States can distribute their nuclear weapons below the ceiling, most of the planned W76-1 warheads will not be deployed but kept in storage as a “hedge” against a nuclear-armed adversary suddenly increasing its nuclear arsenal. The 63 percent production plan suggests that the administration wants to retain the capability to increase the warhead loading to as much as eight warheads per missile, the same number it deployed during the Cold War. Another reason for retaining spare W76 warheads is to have replacement warheads in case of technical failure of deployed warheads.
The administration has proposed to replace some of the W76s with the Reliable Replacement Warhead (RRW-1) to increase the “diversity” of the type of warheads at sea. If Congress approves RRW-1 production, the second half of the 76-1 production plan would probably be changed to RRW-1 warheads beginning (under current plans) in 2014, in which case the future sea-based posture would be made up of a mix of W76-1, W88 and RRW-1 warheads.
In Congress both the Senate and House have called for a review of U.S. nuclear policy to ensure the right size and role of the nuclear posture. The 63 percent W76-1 production set by the 2005 Strategic Capabilities Assessment would appear to preempt that effort.
Background:
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.