 |
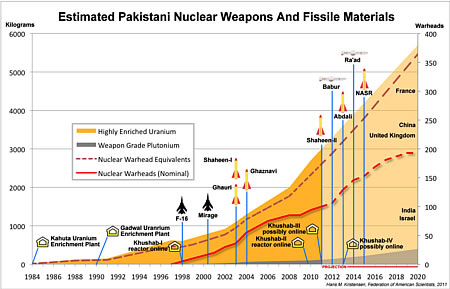
| Pakistan’s nuclear arsenal has doubled since 2004 and could double again in the next 10 years if the current trend continues, according to the latest Nuclear Notebook. Click on chart to download full size version. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen and Robert S. Norris
The latest Nuclear Notebook on Pakistan’s nuclear forces is available on the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists web site. Since our previous Notebook on Pakistan in 2009 there have been several important developments.
Based on our own estimates, official statements, and fissile material production estimates produced by the International Panel of Fissile Materials, we conclude that Pakistan’s current nuclear weapons stockpile of 90-110 warheads might increase to 150-200 within the next decade. This would bring the Pakistani stockpile within range of the British stockpile, the smallest of the original five nuclear weapon states, but still far from that of France (despite some recent news reports to the contrary).
This development is precipitated by the anticipated introduction of several new nuclear delivery systems over the next years, including cruise missiles and short-range ballistic missiles. The capabilities of these new systems will significantly change the composition and nature of Pakistan’s nuclear posture.
India is following this development closely and is also modernizing its nuclear arsenal and fissile material production capability. The growing size, diversity, and capabilities of the Pakistani and Indian nuclear postures challenge their pledge to only acquire a minimum deterrent. Bilateral arms control talks and international pressure are urgently needed to halt what is already the world’s fastest growing nuclear arms race.
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.