 |
| China’s new DF-21C missile launcher shows itself in Western China. Image: GoogleEarth |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
The latest Pentagon report on Chinese military forces recently triggered sensational headlines in the Indian news media that China had deployed new nuclear missiles close to the Indian border.
The news reports got it wrong, but new commercial satellite images reveal that launch units for the new DF-21C missile have deployed to central-western China.
New DF-21C Launch Units
Analysis of commercial satellite imagery reveals that launch units for the road-mobile DF-21C medium-range ballistic missile now deploy several hundred kilometers west of Delingha in the western part of central China.
| Location of DF-21C Launch Units |
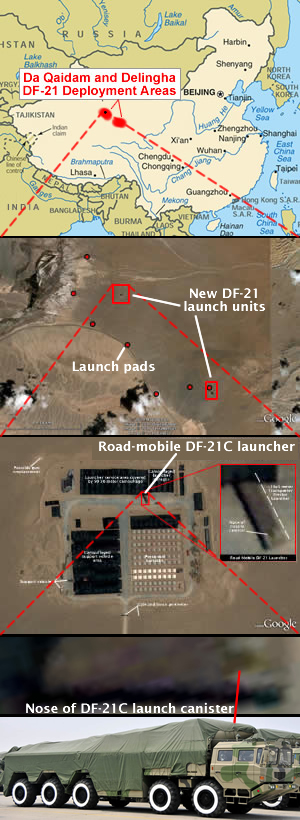 |
| For larger versions of the two middle satellite images, click here and here. Images: GoogleEarth and chinamil.com.cn |
In one image, taken by the GeoEye-1 satellite on June 14, 2010, two launch units are visible in approximately 230 km west of Delingha. The units are dug into the dry desert slopes near Mount Chilian along national road G215. Missile launchers, barracks, maintenance and service units are concealed under large dark camouflage, which stands out clearly in the brown desert soil.
The eastern launch unit (38° 6’37.75″N, 94°59’2.19″E) includes a central area with red barracks clearly visible below the camouflage, which probably also covers logistic units such as communications vehicles, fuel trucks, and personnel carriers. An 88×17 meter garage of brown camouflaged probably covers the launcher service area, with five 15-meter garages nearby probably housing the TELs. Approximately 130 meters north of the central area, brown camouflage and dirt barriers possibly house the unit’s remote fuel area. Two launch pads are visible, one only 180 meters from the main section, the other on the access road leading to national road G215.
The western launch unit (38° 9’32.82″N, 94°55’37.02″E) is located approximately 7 km further west about 2.4 km to the north of national road G215. The unit consists of four sections: personnel barracks (almost 100 with more possibly under camouflage); a logistic vehicles area; a launcher service area with a 90×33 meter camouflage and four garages; and what is possibly a remote fuel storage area. A launch pad is located along the access road close to G215.
The satellite image shows what appears to be a DF-21C entering or leaving the camouflaged launcher service area. The characteristic nose cone of the missile canister embedded into the rear of the driver cockpit is clearly visible, with the rest of launcher probably covered by a tarp.
This is, to my knowledge, the first time that the DF-21C has been identified in a deployment area. In 2007, I used commercial satellite images to describe the first visual signs of the transition from DF-4 to DF-21 at Delingha. A second article in 2008 described the extensive system of launch pads that extends west from Delingha along national road G215 past Da Qaidam.
There are five launch pads within five miles of the two launch units, with dozens other pads along and north of G215 in both directions.
More Invulnerable but with Limits
China’s ongoing modernization from old liquid-fuel missiles to new solid-fuel missiles is getting a lot of attention. The new systems are more mobile and thus less vulnerable to attack. Yet the satellite images also give hints about limitations.
First, the launch units are large with a considerable footprint that covers an area of approximately 300×300 meters. They are manpower-intensive requiring large numbers of support equipment. This makes them harder to move quickly and relatively easy to detect by satellite images.
| DF-21C Launch Unit on the Move |
 |
| The DF-21C medium-range ballistic missile may be more mobile and harder to target than older missiles, but it still relies on a large support unit that can be detected. Image: CCTV-7 |
.
Individual launchers of course would be dispersed into the landscape in case of war. But although the road-mobile launcher has some off-road capability, it requires solid ground when launching to prevent damage from debris kicked up by the rocket engine. As a result, launchers would have to stay on roads or use the pre-made launch pads that stand out clearly in high-resolution satellite images. Moreover, a launcher would not simply drive off and launch by itself, but need to be followed by support vehicles for targeting, repair, and communication.
Indian News Media (Mis)reporting
The deployment of DF-21 missiles caused constipation in Indian last month after the 2010 Pentagon report of Chinese military forces stated that China is replacing DF-4 missiles with DF-21 missiles to improve regional deterrence. The statement was contained in a section dealing with Chinese-Indian affairs and was picked up by the Press Trust of India, which mistakenly reported that the Pentagon report stated that, “China has moved advanced longer range CSS-5 [DF-21] missiles close to the border with India.” The Times of India even wrote the missiles were being deployed “on border” with India.
| India News Media Makes a Bad Situation Worse |
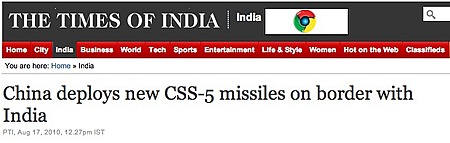 |
| The India news media significantly misreported what the Pentagon report said about the Chinese DF-21 deployment. Not the finest hour of Indian journalism. |
.
Not surprisingly, the misreporting triggered dramatic news articles in India, including rumors that the Indian Strategic Forces Command was considering or had already moved nuclear-capable missile units north toward the Chinese border in retaliation.
The Pentagon report, however, said nothing about moving DF-21 missiles close to or “on” the Indian border. Here is the actual statement: “To improve regional deterrence, the PLA has replaced older liquid-fueled, nuclear-capable CSS-3 intermediate-range ballistic missiles with more advanced and survivable solid-fueled CSS-5 MRBM….” The statement echoes a statement in the 2009 report: “The [People’s Liberation Army] has replaced older liquid-fueled nuclear-capable CSS-3 [DF-4 medium-range ballistic missiles] MRBMs with more advanced solid-fueled CSS-5 MRBMs in Western China.”
The sentence appears to describe the apparent near-completion of China’s replacement of DF-4 missiles with DF-21 missiles, probably at two army base areas in Hunan and Qinghai provinces, a transition that has been underway for two decades. The two deployment areas are each more than 1,500 kilometers from the Indian border.
Range Confusion
The unclassified ranges of Chinese DF-21 versions published by the U.S. intelligence community are 1,770+ km (1,100+ miles) for the two nuclear versions (DF-21, CSS-5 Mod 1; and DF-21A, CSS-5 Mod 2). The DF-21A appears to have an extended range of 2,150 km. The dual-capable “conventional” DF-21C has a maximum range of 1,770 km, and the yet-to-be-deployed DF-21D anti-ship missile has a shorter range of 1,450+ km. Private publications frequently credit the DF-21D with a much longer range (CSBA: 2,150 km; sinodefence.com and Wikipedia: 3,000 km).
DOD maps are misleading because they depict missile ranges measured from the Chinese border, as if the launchers were deployed there rather than at their actual deployment areas far back from the border. The 2008 report, for example, includes a map essentially showing China’s border extended outward in different colors for each missile range. The result is a DF-21 range of about 3,000 km if measured from the actual deployment areas.
| DF-21 Range According to 2008 Pentagon Report |
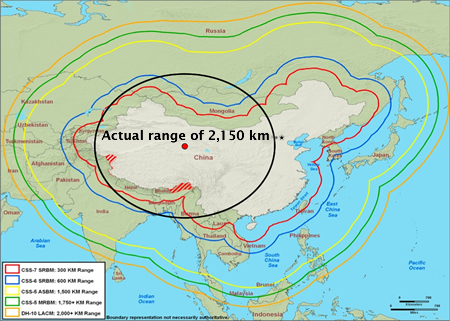 |
| The 2008 Pentagon report on China’s military forces misrepresents missile ranges. |
.
The 2010 report is even worse because it shows the ranges without the border contours as circles but measured from the most extreme border position. The result is a map that is even more misleading, suggesting a DF-21 range of as much as 3,500 km from actual deployment areas. The actual maximum range is 2,150 km for DF-21A (CSS-5 Mod 2), and 1,770 km for the DF-21C.
| DF-21 Range According to 2010 Pentagon Report |
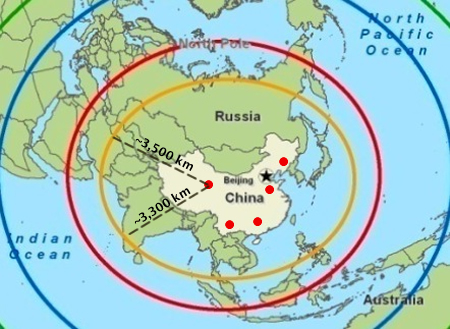 |
| The 2010 Pentagon report on Chinese military issues greatly exaggerates the reach of the DF-21 by drawing a ring around China that doesn’t reflect actual deployment areas. |
.
Although a DF-21 launcher could theoretically drive all the way up to the border to launch, the reality is that DF-21 bases and roaming areas are located far back from the border to protect the fragile launchers from air attack. DOD maps should reflect that reality.
Additional Resources: earlier China blogs; Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.