Russian Missile Test Creates Confusion and Opposition in Washington
The recent test-launch of a modified Russian ballistic missile has nuclear arms reduction opponents up in arms with claims that Russia is fielding a new missile in violation of arms control agreements and that the United States therefore should not pursue further reductions of nuclear forces.
The fact that the Russian name of the modified missile – Rubezh – sounds a little like rubbish is a coincidence, but it fits some of the complaints pretty well.
Although many of the facts are missing – what the missile is and what the U.S. Intelligence Community has concluded – public information and statements indicate that the missile is a modified RS-24 Yars (SS-27 Mod 2) with intercontinental range.
Whatever the missile is, it is certainly no reason for why the United States should not seek to reduce U.S. and Russian nuclear forces further. On the contrary, the continued modernization of nuclear weapons underscores why it is important that the United States continues its push for reducing the numbers and role of nuclear weapons.
The Accusations
Under the headline “Russian Aggression: Putin violating nuclear missile treaty,” the article on Washington Times Free Beacon web site accuses Russia of being engaged in “a major violation” of the terms of the Intermediate-range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty signed with the United States in 1987.
The treaty bans all nuclear ground-launched ballistic and cruise missiles with range between 500 and 5,500 km (about 300-3,400 miles).
Claims of Russian cheating are frequent in the Washington arms control debate – just as claims about U.S. cheating is frequent in the Moscow arms control debate – and the ones in the article are largely consistent with the claims made by Mark Schneider, a former DOD official and now with the National Institute for Public Policy.
The “new” in the article is that it quotes “one official” saying: “The intelligence community believes it’s an intermediate-range missile that [the Russians] have classified as an ICBM because it would violate the INF treaty.” In total, “Two U.S. intelligence officials said the Yars M is not an ICBM,” according to the article.
Two members of Congress, House Armed Services Committee chairman Howard “Buck” McKeon (R-CA) and House Permanent Select Intelligence Committee chairman Mike Rodgers (R-MI), have written President Obama about alleged Russian violations. They complain that they haven’t received a response but the administration says it deals with treaty compliance issue directly with Russia and informs Congress accordingly.
Accusations Disputed
The accusations that the Yars-M is not an ICBM and in violation of the INF Treaty are disputed by Russian officials and, interestingly, previous flight tests of the missile itself.
To its credit, the Washington Times took the trouble of asking Colonel General Victor Yesin about the missile. Yesin is former Chief of Staff of the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces and apparently a consultant to the Chief of the General Staff. But Yesin clearly disputed the claim by the U.S. intelligence officials, saying that the Yars-M is a “Topol-M class ICBM” and that “its range is over 5,500 km.”
That assessment fits the description made by a source in the General Staff in November 2012, following the first Yars-M launch from Kapustin Yar in October 2012 and news media rumors that Russia was developing a “fundamentally new missile.” “There are no fundamentally new missiles ‘on the approach’ for [the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces]. We are talking about modernizing the existing Yars class by improving the warhead,” he told Interfax and explained:
“Take the Layner [modification of the SS-N-23] sea-based intercontinental ballistic missile, reported by some media to be a completely new missile. It is in fact a Sineva. Only the warhead is new. Novelty lies in greater missile defense penetration capabilities, achieved owing to, among other things, a greater number of re-entry vehicles (boyevoy blok) in the warhead. The same applies to the prototype missile that was successfully launched from Kapustin Yar (Astrakhan Region) recently. There is nothing new in the missile itself. Only the ‘head’ is new. Its creators went down the same route as the designers of the Layner.”
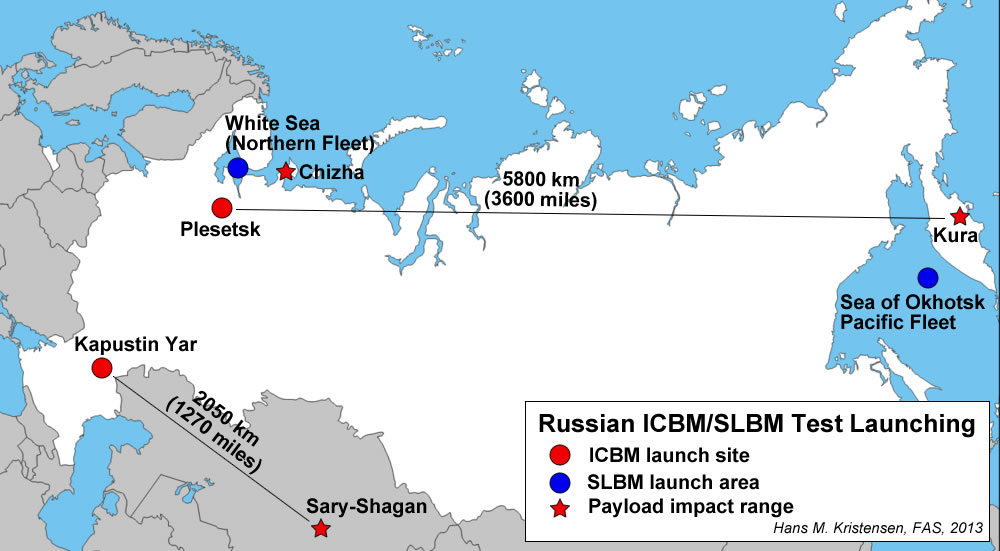
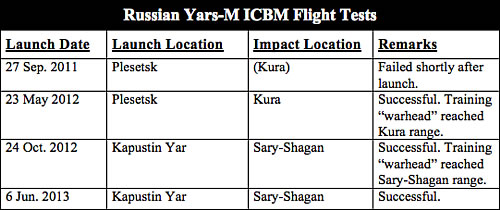
Moreover, the claim that the short flight range of the missile test launched from Kaputsin Yar in June 2013 would indicate that the Yars-M is not an ICBM ignores that an earlier flight test of the missile last year flew 5,800 kilometers from Plesetsk north of Moscow to the Kura test range on the Kamchatka Peninsula (see table).
After the May 2012 flight test, Colonel-General Vladimir Zarudnitsky of the General Staff said: “As part of the approved plan of your building the armed forces of the Russian Federation last night made a promising test launch rocket system” Frontier “with an intercontinental ballistic missile high-precision shooting.” (Emphasis added).
Col. Vadim Koval, a Russian defense ministry spokesperson, said “the main goals and tasks of the launch consisted of receiving experimental data on confirming the correctness of the scientific-technical and technological decisions in developing the intercontinental ballistic missile as well as checking the performance and determining the technical characteristics of its systems and components.” (Emphasis added).
Rather than an entirely new missile, Koval explained further, “This missile is being created by using and developing, to the maximum extent, already existing new capacities and technological solutions, which were obtained in the development of fifth generation missile complexes, which substantially reduces the terms and expenditures on its creation.”
After the successful initial launch from Plesetsk, the second test was moved to Kapustin Yar apparently to test the capability of the Yars-M payload to evade ballistic missile defense systems. An industry sources told Interfax that, “The use of new fuel is one of the features of the missile. It reduces boost phase engine operation time. Consequently, the missile’s capabilities to penetrate missile defense will go up.”
It is rare, but not unheard of, that ICBMs are launched from Kapustin Yar into the Sary-Sagan test range. It appears to happen when ICBM payloads are being tested against missile defense systems. In addition to the recent tests of the modified SS-27, an SS-25 was test launched from the site on June 7, 2012. The test flight verified the “extended service life” of the SS-25 and “the latest test of an ICBM combat payload.” During the test “information was received which in future will be used in the interests of developing effective means for overcoming missile defense,” according to the Russian Ministry of Defense.
After the June 2013 test, Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin, called the modified SS-27 a “missile defense killer.”
It is not unusual that ballistic missiles with intercontinental range are test-flown in a compressed trajectory with much shorter range. That doesn’t make them less than strategic weapons, however. In March 2006, for example, the U.S. Navy launched a Trident II D5 sea-launched ballistic missile with a range of well over 7,400 kilometer (4,000 miles) in a compressed trajectory of 2,200 kilometers (1,380 miles) – about the same range as the Yars-M test on June 6, 2013. No one has suggested that the Trident II D5 therefore is an INF weapon.

The USS Tennessee (SSBN-734) launches a Trident II D5 SLBM on March 2, 2005, on a compressed trajectory of only 2,200 km – about the same range as the Yars-M test in June 2013.
Conclusions and Recommendations
If there are Russian violations of the INF Treaty, then the United States certainly should raise it directly with Moscow.
But the claim that the Yars-M missile flight-tested on June 6 to a range of 2,050 kilometers is an intermediate-range ballistic missile in violation of the INF treaty seems strange since the same missile apparently was flight tested to an ICBM range of 5,800 kilometers just a year ago.
Of course, we don’t know who the U.S. intelligence officials cited in the Washington Times article are, if what they say is accurate, and to what extent it reflects a coordinated assessment by the U.S. Intelligence Community. We may learn more about the Yars-M in the future.
But several Russian government, military, and industry officials have consistently stated that the Yars-M is not a new missile but a modification of the RS-24 Yars (SS-27 Mod 2) and that it has intercontinental range.
The intension of the allegations in the article seems clear: to create doubts about further reductions of U.S. nuclear forces. One of the “officials” quoted in the article directly questions: “How can President Obama believe [the Russians] are going to live up to any nuclear treaty reductions when he knows they are violating the INF treaty by calling one of their missiles something else?”
The thought that Americans would use INF treaty allegations to argue against reducing the number of strategic nuclear weapons that can hit the United States seems kind of bizarre. After all, under current Russian war plans, many of the 400-500 warheads President Obama has proposed can be offloaded under a new agreement, are most likely currently tasked to hold at risk several hundred targets in the United States – including some in California and Michigan.
Since Russia – unlike the United States – is already below the New START Treaty limit on deployed nuclear weapons and likely to drop further before the treaty enters into force in 2018, it seems like a no-brainer that it is in the U.S. interest to nurture that trend by reducing its own forces further.
This is even more important because the very reason some Russian officials could potentially be tempted to argue that an INF-missile was needed is that China is modernizing of its medium-range missile forces. Ironically, many of those in the United States who make the accusations about Russian INF violations are the same people who also warn about China’s nuclear modernization.
What the article completely seems to miss is that the only way that China and smaller nuclear weapons states may be persuaded to place limits on their nuclear arsenals is if the United States and Russia take bold steps to reduce their still enormous nuclear arsenals. Why then nitpick about dubious INF accusations to block that from happening?
This publication was made possible by grants from the New-Land Foundation and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.