Chinese Nuclear Modernization: Smaller and Later
 |
| DIA threat assessment shows slower Chinese nuclear modernization. |
.
By Hans M. Kristensen
At about the same time nuclear arms reduction opponents last week incorrectly accused the Obama administration of considering “reckless” cuts in nuclear forces that would leave the United States “with fewer warheads than China,” Congress received its annual threat assessment from the U.S. intelligence community.
China’s nuclear arsenal is at a size that makes comparison with U.S. nuclear force level meaningless – even at the lowest level feared by the critics – but the threat assessment showed that China’s nuclear force modernization has been slower than predicted during the Bush administration.
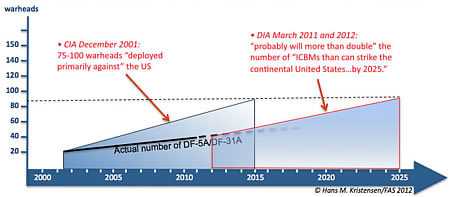
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs)
Back in December 2001, the Central Intelligence Agency predicted that China’s ICBM force “deployed primarily against the United States” would increase to “75 to 100 warheads” by 2015. At the time, China had 20 single-warhead DF-5A ICBMs with a range to strike the continental United States.
Last week’s threat assessment by the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) repeats the assessment from last year that China currently has “fewer than 50 ICBMs that can strike the United States, but that it probably will more than double that number by 2025.” The expected increase refers to the addition of the DF-31A, a single-warhead mobile ICBM that was first deployed in 2007 after more than two decades of development.
But while the 2001 prediction implied deployment of 55-80 DF-31As by 2015, the number by now is less than 30 (tracking the precise number has become a little harder after the United States last year started to assist Chinese secrecy by no longer providing a breakdown of the missile force in the Pentagon’s annual Chinese military power report).
Moreover, the projection for when the portion of the ICBM force that can strike the continental United States will reach close to 100 has slipped by a decade, from 2015 to 2025.
.
Sea-Launched Ballistic Missile Submarines (SSBNs)
Last week’s threat assessment also showed that China’s modernization of its sea-launched ballistic missile force has been slower than projected a few years ago. China is developing the Julang-2 (JL-2) sea-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) for deployment on its new Jin-class SSBNs. Two submarines have been delivered and a couple more may be under construction.
Development of the JL-2, a sea-based version of the land-based DF-31, has been troubled by setbacks. After projecting in 2006 that the JL-2 would reach initial operational capability in 2007-2010, the Pentagon last year said it was uncertain when the missile would become fully operational on the Jin SSBN. And despite unconfirmed Internet-rumors last year about a JL-2 test launch, the DIA told Congress last week that the JL-2 “may reach initial operational capability by 2014.”
So three decades after China launched its first SSBN – the Xia (Type 092), and nearly a decade after launching the first Jin-class (Type 094) SSBN, it still doesn’t have an operational sea-based nuclear force.
| Chinese Jin-Class SSBNs |
 |
| After more than two decades in development, China’s new Jin-class SSBNs – see here Xiaopingdao in March 2011 – are still awaiting their loadout of JL-2 missiles. Image: Google |
.
That’s not to say they’re not trying but development of advanced weapons like the JL-2 is difficult (just look a Russia’s problems with its Bulava SLBM), and predictions have been too optimistic.
Once the Jin/JL-2 weapon system becomes operational, the Chinese military will have to figure out how to operate the force; Chinese SSBNs have never conducted a deterrent patrol, they’re noisy, and would need to hide to provide a real secure second-strike capability.
Implications
The point is not that China is not modernizing its nuclear forces (like the other nuclear weapon states, it unfortunately is) or that the intelligence community makes mistakes. The point is to remind that projections like these always tend to promise too much too soon.
Last week’s threat assessment is probably no different but it is interesting because it shows, when compared with previous assessments, that China’s nuclear modernization has been slower than anticipated a decade ago. And there is no indication that China has embarked upon a nuclear build-up intended to “sprint to parity” with the United States or Russia.
That at least ought to be taken into account by those who use China’s nuclear modernization to argue against deeper U.S. (and, by implication, Russian) nuclear reductions.
This publication was made possible by a grant from Carnegie Corporation of New York and Ploughshares Fund. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the author.
The last remaining agreement limiting U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons has now expired. For the first time since 1972, there is no treaty-bound cap on strategic nuclear weapons.
The Pentagon’s new report provides additional context and useful perspectives on events in China that took place over the past year.
Successful NC3 modernization must do more than update hardware and software: it must integrate emerging technologies in ways that enhance resilience, ensure meaningful human control, and preserve strategic stability.
The FY2026 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) paints a picture of a Congress that is working to both protect and accelerate nuclear modernization programs while simultaneously lacking trust in the Pentagon and the Department of Energy to execute them.